
Vilas County is a county in the state of Wisconsin, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 23,047. Its county seat is Eagle River. The county partly overlaps the reservation of the Lac du Flambeau Band of Lake Superior Chippewa.

Oneida County is a county in the state of Wisconsin, United States. At the 2020 census, the population was 37,845. Its county seat is Rhinelander.

Anishinaabe traditional beliefs cover the traditional belief system of the Anishinaabeg peoples, consisting of the Algonquin/Nipissing, Ojibwa/Chippewa/Saulteaux/Mississaugas, Odawa, Potawatomi and Oji-Cree, located primarily in the Great Lakes region of North America.

Minocqua is a town in northwestern Oneida County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 4,414 as of 2018. The census-designated place of Minocqua and the unincorporated community of Rantz are both located in the town. Minocqua is commonly referred to as "The Island City."

Georgian Bay is a large bay of Lake Huron, in the Laurentia bioregion. It is located entirely within the borders of Ontario, Canada. The main body of the bay lies east of the Bruce Peninsula and Manitoulin Island. To its northwest is the North Channel.

The Song of Hiawatha is an 1855 epic poem in trochaic tetrameter by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow which features Native American characters. The epic relates the fictional adventures of an Ojibwe warrior named Hiawatha and the tragedy of his love for Minnehaha, a Dakota woman. Events in the story are set in the Pictured Rocks area of Michigan on the south shore of Lake Superior. Longfellow's poem is based on oral traditions surrounding the figure of Manabozho, but it also contains his own innovations.
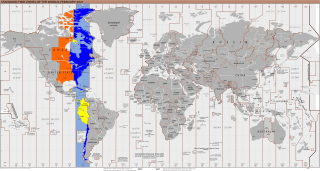
UTC−05:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of −05:00. In North America, it is observed in the Eastern Time Zone during standard time, and in the Central Time Zone during the other eight months. The western Caribbean uses it year round.
Wenonah may refer to:

Nanabozho, also known as Nanabush, is a spirit in Anishinaabe aadizookaan, particularly among the Ojibwe. Nanabozho figures prominently in their storytelling, including the story of the world's creation. Nanabozho is the Ojibwe trickster figure and culture hero.

Minnehaha is a Native American woman documented in Henry Wadsworth Longfellow's 1855 epic poem The Song of Hiawatha. She is the lover of the titular protagonist Hiawatha and comes to a tragic end. The name, often said to mean "laughing water", literally translates to "waterfall" or "rapid water" in Dakota.
Lake Hiawatha is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) located within Parsippany–Troy Hills Township in Morris County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. The U.S. Postal Service serves the community as ZIP Code 07034. As of the 2020 census, the population was 10,194.
The culture of Minnesota is a subculture of the United States with influences from Scandinavian Americans, Finnish Americans, Irish Americans, German Americans, Native Americans, Czechoslovak Americans, among numerous other immigrant groups. They work in the context of the cold agricultural and mining state.

Nokomis Library, formerly Nokomis Community Library, is a branch library serving the Nokomis East area of Minneapolis, Minnesota. One of 41 libraries in the Hennepin County Library system, Nokomis was designed by Buetow and Associates, Inc and opened in 1968 as a replacement for the nearby Longfellow Community Library. After being deemed crowded and outdated in 1999, the library underwent a renovation beginning in 2009 that saw it gain a number of environmentally friendly features and an expansion of 4,300 square feet (399 m2). The building reopened in 2011 and includes a restored Wind and Water Chime, a stabile that was part of the original library and that was refurbished and reinstalled by July 2013. The library contains over 35 computers, a public meeting room, and a Spanish-language collection of materials.
The Wenonah community was the name of one of a series of Red Mountain ore mining camps for employees of the Tennessee Coal and Iron Company (TCI).

Pelican Lake is a 3,585-acre (14.51 km2) lake located in Oneida County in Wisconsin. It has a maximum depth of 39 ft (12 m). Visitors have access to the lake from five public boat landings. A dam is located on the lake's primary outlet, which feeds into the Pelican River. Pelican Lake serves as one of 21 reservoirs used to regulate and maintain optimal water flow on the Wisconsin and Tomahawk rivers, the process of which is facilitated in part by the Wisconsin Valley Improvement Company.

The Turtle-Flambeau Flowage is a 12,942 acres (52.37 km2) lake in Iron County, Wisconsin. It has a maximum depth of 15 meters and is the seventh largest lake in the state of Wisconsin by surface area. The flowage is home to unique wetland patterns and plant species as well as several species of sport and game fish, including musky, panfish, largemouth bass, smallmouth bass, northern pike, walleye and sturgeon. The lake's water clarity is low, but can vary in different locations. Fishing, camping, boating, and hunting are popular activities on the flowage, and Ojibwe people traditionally harvest fish and game on the lake. Environmental concerns on the flowage include mercury contamination, algal blooms, and several types of invasive species.