Related Research Articles

Lithography is a planographic method of printing originally based on the immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by the German author and actor Alois Senefelder and was initially used mostly for musical scores and maps. Lithography can be used to print text or images onto paper or other suitable material. A lithograph is something printed by lithography, but this term is only used for fine art prints and some other, mostly older, types of printed matter, not for those made by modern commercial lithography.

MEMS is the technology of microscopic devices incorporating both electronic and moving parts. MEMS are made up of components between 1 and 100 micrometres in size, and MEMS devices generally range in size from 20 micrometres to a millimetre, although components arranged in arrays can be more than 1000 mm2. They usually consist of a central unit that processes data and several components that interact with the surroundings.
Photolithography is a process used in the manufacturing of integrated circuits. It involves using light to transfer a pattern onto a substrate, typically a silicon wafer.
An actuator is a component of a machine that produces force, torque, or displacement, when an electrical, pneumatic or hydraulic input is supplied to it in a system. The effect is usually produced in a controlled way. An actuator translates such an input signal into the required form of mechanical energy. It is a type of transducer. In simple terms, it is a "mover".

In technology, soft lithography is a family of techniques for fabricating or replicating structures using "elastomeric stamps, molds, and conformable photomasks". It is called "soft" because it uses elastomeric materials, most notably PDMS.

Extreme ultraviolet lithography is a technology used in the semiconductor industry for manufacturing integrated circuits (ICs). It is a type of photolithography that uses 13.5 nm extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light from a laser-pulsed tin (Sn) plasma to create intricate patterns on semiconductor substrates.
In semiconductor fabrication, a resist is a thin layer used to transfer a circuit pattern to the semiconductor substrate which it is deposited upon. A resist can be patterned via lithography to form a (sub)micrometer-scale, temporary mask that protects selected areas of the underlying substrate during subsequent processing steps. The material used to prepare said thin layer is typically a viscous solution. Resists are generally proprietary mixtures of a polymer or its precursor and other small molecules that have been specially formulated for a given lithography technology. Resists used during photolithography are called photoresists.
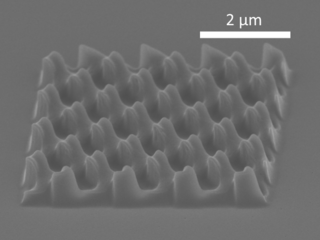
Nanoimprint lithography (NIL) is a method of fabricating nanometer-scale patterns. It is a simple nanolithography process with low cost, high throughput and high resolution. It creates patterns by mechanical deformation of imprint resist and subsequent processes. The imprint resist is typically a monomer or polymer formulation that is cured by heat or UV light during the imprinting. Adhesion between the resist and the template is controlled to allow proper release.
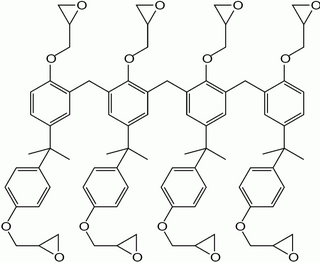
SU-8 is a commonly used epoxy-based negative photoresist. Negative refers to a photoresist whereby the parts exposed to UV become cross-linked, while the remainder of the film remains soluble and can be washed away during development.

Nonwoven fabric or non-woven fabric is a fabric-like material made from staple fibre (short) and long fibres, bonded together by chemical, mechanical, heat or solvent treatment. The term is used in the textile manufacturing industry to denote fabrics, such as felt, which are neither woven nor knitted. Some non-woven materials lack sufficient strength unless densified or reinforced by a backing. In recent years, non-wovens have become an alternative to polyurethane foam.

LIGA is a fabrication technology used to create high-aspect-ratio microstructures. The term is a German acronym for Lithographie, Galvanoformung, Abformung – lithography, electroplating, and molding.
In-mould labelling is the use of paper or plastic labels during the manufacturing of containers by blow molding, injection molding, or thermoforming processes. The label serves as the integral part of the final product, which is then delivered as pre-decorated item. Combining the decoration process with the moulding process cuts the total cost, but can increase the manufacturing time. The technology was first developed by Owens-Illinois in cooperation with Procter & Gamble to supply pre-labelled bottles that could be filled on the product filling line. This was first applied to Head & Shoulders shampoo bottles.
Layer-by-layer (LbL) deposition is a thin film fabrication technique. The films are formed by depositing alternating layers of complementary materials with wash steps in between. This can be accomplished by using various techniques such as immersion, spin, spray, electromagnetism, or fluidics.
MSL may refer to:

A diamond grinding cup wheel is a metal-bonded diamond tool with diamond segments welded or cold-pressed on a steel wheel body, which usually looks like a cup. Diamond grinding cup wheels are usually mounted on concrete grinders to grind abrasive building materials like concrete, granite and marble.
The polymer solution casting process utilizes a mandrel, or inner diameter mold, that is immersed in a tank of polymer solution or liquid plastic that has been specifically engineered for the process. Due to a combination of thermal and frictional properties, the polymer solution then forms a thin film around the mold. The mold is then extracted from the tank in a precisely controlled manner, followed by a curing or drying process. Once the first layer of thin film is appropriately solidified, secondary features can be added to the product such as braided or coiled wire, laser-cut hypotubes or engineered metal reinforcements to prevent kinking, or imaging targets specific to the intended medical application. Multiple casting steps can then be repeated to encapsulate the reinforcements, build up wall thickness, add additional lumens and optimize column strength. The part is then removed from the mold after it is cured or solidified.
In microfluidics, hydrodynamic trapping is a technique for trapping very small particles in an aqueous solution for a long period of time in order to isolate particles and observe their behavior.

Co-fired ceramic devices are monolithic, ceramic microelectronic devices where the entire ceramic support structure and any conductive, resistive, and dielectric materials are fired in a kiln at the same time. Typical devices include capacitors, inductors, resistors, transformers, and hybrid circuits. The technology is also used for robust assembly and packaging of electronic components multi-layer packaging in the electronics industry, such as military electronics, MEMS, microprocessor and RF applications.
Projection micro-stereolithography (PμSL) adapts 3D printing technology for micro-fabrication. Digital micro display technology provides dynamic stereolithography masks that work as a virtual photomask. This technique allows for rapid photopolymerization of an entire layer with a flash of UV illumination at micro-scale resolution. The mask can control individual pixel light intensity, allowing control of material properties of the fabricated structure with desired spatial distribution.
Three-dimensional (3D) microfabrication refers to manufacturing techniques that involve the layering of materials to produce a three-dimensional structure at a microscopic scale. These structures are usually on the scale of micrometers and are popular in microelectronics and microelectromechanical systems.
References
- ↑ Unger, Marc A.; Chou, Hou-Pu; Thorsen, Todd; Scherer, Axel; Quake, Stephen R. (2000-04-07). "Monolithic Microfabricated Valves and Pumps by Multilayer Soft Lithography". Science. 288 (5463): 113–116. Bibcode:2000Sci...288..113U. doi:10.1126/science.288.5463.113. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 10753110.