A mummy is a dead human or an animal whose soft tissues and organs have been preserved by either intentional or accidental exposure to chemicals, extreme cold, very low humidity, or lack of air, so that the recovered body does not decay further if kept in cool and dry conditions. Some authorities restrict the use of the term to bodies deliberately embalmed with chemicals, but the use of the word to cover accidentally desiccated bodies goes back to at least the early 17th century.

Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objects in it, and covering it over. A funeral is a ceremony that accompanies the final disposition. Evidence suggests that some archaic and early modern humans buried their dead. Burial is often seen as indicating respect for the dead. It has been used to prevent the odor of decay, to give family members closure and prevent them from witnessing the decomposition of their loved ones, and in many cultures it has been seen as a necessary step for the deceased to enter the afterlife or to give back to the cycle of life.

Guanajuato is a municipality in central Mexico and the capital of the state of the same name. It is part of the macroregion of the Bajío. It is located in a narrow valley, which makes its streets narrow and winding. Most are alleys that cars cannot pass through, and some are long sets of stairs up the mountainsides. Many of the city's thoroughfares are partially or fully underground. The historic center has numerous small plazas and colonial-era mansions, churches, and civil constructions built using pink or green sandstone. The city historic center and the adjacent mines were proclaimed a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1988.

The Capuchin Catacombs of Palermo are burial catacombs in Palermo, Sicily, southern Italy. Today they provide a somewhat macabre tourist attraction as well as an extraordinary historical record.

The ancient Egyptians had an elaborate set of funerary practices that they believed were necessary to ensure their immortality after death. These rituals included mummifying the body, casting magic spells, and burials with specific grave goods thought to be needed in the afterlife.
Disposal of human corpses, also called final disposition, is the practice and process of dealing with the remains of a deceased human being. Disposal methods may need to account for the fact that soft tissue will decompose relatively rapidly, while the skeleton will remain intact for thousands of years under certain conditions.

Tuna el-Gebel was the necropolis of Khmun. It is the largest known Greco-Roman necropolis in Egypt, dating from the New Kingdom to the Roman Period, and seeing heavy use in the Ptolemaic Period. Tuna el-Gebel is located in Al Minya Governorate in Middle Egypt.

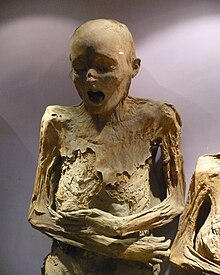
The Chinchorro mummies are mummified remains of individuals from the South American Chinchorro culture, found in what is now northern Chile. They are the oldest examples of artificially mummified human remains, having been buried up to two thousand years before the Egyptian mummies. The earliest mummy that has been found in Egypt dates from around 3000 BCE, while the oldest purposefully artificially preserved Chinchorro mummy dates from around 5050 BCE.
Julia Buccola Petta was a housewife who became known following her death as The Italian Bride. She was the daughter of Filomena Buccola and the wife of Matthew Petta. She died at the age of 29 in 1921 while giving birth to a stillborn son, Filippo.

"Victims of the Riddle" is a song by the English new wave band Toyah, fronted by Toyah Willcox, released as the band's debut single in 1979 by Safari Records. The song later featured on the band's album Sheep Farming in Barnet.

The Gebelein predynastic mummies are six naturally mummified bodies, dating to approximately 3400 BC from the Late Predynastic period of Ancient Egypt. They were the first complete predynastic bodies to be discovered. The well-preserved bodies were excavated at the end of the nineteenth century by Wallis Budge, the British Museum Keeper for Egyptology, from shallow sand graves near Gebelein in the Egyptian desert.

Hannah Beswick, of Birchin Bower, Hollinwood, Oldham, Greater Manchester, was a wealthy woman who had a pathological fear of premature burial. Following her death in 1758, her body was embalmed and kept above ground, to be periodically checked for signs of life.
The Fire Mummies of the Philippines, also known as the Kabayan Mummies, Benguet Mummies, or Ibaloi Mummies, are a group of mummies found along the mountain slopes of Kabayan, Benguet, a town in northern Philippines. They were made from as early as 2000 BCE. Today, they remain in natural caves and a museum in Kabayan.
Charles Henry "Speedy" Atkins (1875–1928) was an American tobacco worker in Paducah, Kentucky. A pauper at his death, he drowned in the Ohio River. The city turned over his body for a pauper's burial to his friend A.Z. Hamock, the only African-American undertaker in town. Hamock preserved Atkins' body in an experiment with preservatives, and occasionally displayed it after his death. Hamock's wife had custody of the remains for 45 years, during which Atkins' mummy acquired increasing notoriety. His body was finally buried in 1994, 66 years after he drowned. The event was covered by national media and TV.

Animal mummification was common in ancient Egypt. Animals were an important part of Egyptian culture, not only in their role as food and pets, but also for religious reasons. Many different types of animals were mummified, typically for four main purposes: to allow people's beloved pets to go on to the afterlife, to provide food in the afterlife, to act as offerings to a particular god, and because some were seen as physical manifestations of specific deities that the Egyptians worshipped. Bastet, the cat goddess, is an example of one such deity. In 1888, an Egyptian farmer digging in the sand near Istabl Antar discovered a mass grave of felines, ancient cats that were mummified and buried in pits at great numbers.

Aztec mummy refers to an intentionally prepared or naturally desiccated human body of Aztec origin.

The Presbyterian Burying Ground, also known as the Old Presbyterian Burying Ground, was a historic cemetery which existed between 1802 and 1909 in the Georgetown neighborhood of Washington, D.C., in the United States. It was one of the most prominent cemeteries in the city until the 1860s. Burials there tapered significantly after Oak Hill Cemetery was founded nearby in 1848. The Presbyterian Burying Ground closed to new burials in 1887, and about 500 to 700 bodies were disinterred after 1891 when an attempt was made to demolish the cemetery and use the land for housing. The remaining graves fell into extensive disrepair. After a decade of effort, the District of Columbia purchased the cemetery in 1909 and built Volta Park there, leaving nearly 2,000 bodies buried at the site. Occasional human remains and tombstones have been discovered at the park since its construction. A number of figures important in the early history of Georgetown and Washington, D.C., military figures, politicians, merchants, and others were buried at Presbyterian Burying Ground.
Mummification was practiced in the Philippines only on those able to prove the loss of baby teeth. The baby teeth represented youth, losing them illustrated wisdom gained in their mouth. It also portrayed the journey of maturity. Dying without losing baby teeth was a sign of someone who never reached their full potential. Once you lose and grow your first grill, the second time you lose the teeth, it's time to go. That's because they were given a chance of proper dental hygiene. The caves containing the mummies were untouched until the 19th century.
Fagg El Gamous is an ancient Egyptian cemetery located in the Faiyum Governorate dating from the 1st to the 7th century AD, the period of Roman rule in Egypt.

The Princess of Xiaohe or Little River Princess was found in 2003 at Xiaohe Cemetery in Lop Nur, Xinjiang. She is one of the Tarim mummies, and is known as M11 for the tomb she was found in. Buried approximately 3,800 years ago, she has European and Siberian genes and has white skin and red hair. She is unusually well preserved, with clothes, hair, and eyelashes still intact.