Related Research Articles

The Nuristanis are an ethnic group native to the Nuristan Province of northeastern Afghanistan and Chitral District of northwestern Pakistan. Their languages comprise the Nuristani branch of Indo-Iranian languages.

Nuristan, also spelled as Nurestan or Nooristan, is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in the eastern part of the country. It is divided into seven districts and is Afghanistan's least populous province, with a population of around 167,000. Parun serves as the provincial capital. Nuristan is bordered on the south by Laghman and Kunar provinces, on the north by Badakhshan province, on the west by Panjshir province, and on the east by Pakistan.

The Nuristani languages, also known as Kafiri languages, are one of the three groups within the Indo-Iranian language family, alongside the much larger Indo-Aryan and Iranian groups. They have approximately 130,000 speakers primarily in eastern Afghanistan and a few adjacent valleys in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa's Chitral District, Pakistan. The region inhabited by the Nuristanis is located in the southern Hindu Kush mountains, and is drained by the Alingar River in the west, the Pech River in the center, and the Landai Sin and Kunar rivers in the east. More broadly, the Nuristan region is located at the northern intersection of the Indian subcontinent and the Iranian plateau. The languages were previously often grouped with Indo-Aryan or Iranian until they were finally classified as forming a third branch in Indo-Iranian.
Âṣkuňu is a language of Afghanistan spoken by the Ashkun people – also known as the Âṣkun, Ashkun, Askina, Saňu, Sainu, Yeshkun, Wamas, or Grâmsaňâ – from the region of the central Pech Valley around Wâmâ and in some eastern tributary valleys of the upper Alingar River in Afghanistan's Nuristan Province. Other major places where the language of Ashkun is spoken are Nuristan Province, Pech Valley in Wama District, eastern side of the Lower Alingar Valley in Nurgaram and Duab districts, Malil wa Mushfa, Titin, Kolatan and Bajagal valleys.

The Kafir harp is a traditional four- or five-stringed arched harp used by the Nuristanis native to the Nuristan Province of northeastern Afghanistan and Lower Chitral District of northwestern Pakistan. It is played during social gatherings, and to accompany epic storytelling or songs of heroic tales.
The Kom or Kam are a Nuristani tribe in Afghanistan and Pakistan.
The Katir are a Nuristani tribe in Afghanistan and Pakistan.

Kalasha is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Kalash people, in the Chitral District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. There are an estimated 4,100 speakers of Kalasha. It is an endangered language and there is an ongoing language shift to Khowar.

Palula and also known as Ashreti (Aćharêtâʹ) or Dangarikwar, is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by approximately 10,000 people in the valleys of Ashret and Biori, as well as in the village of Puri in the Shishi valley and at least by a portion of the population in the village Kalkatak, in the Chitral District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan.

Kamviri is a dialect of the Kamkata-vari language spoken by 5,000 to 10,000 of the Kom people of Afghanistan and Pakistan. There are slight dialectal differences of the Kamviri speakers of Pakistan. The most used alternative names are Kati, Kamozi, Shekhani or Bashgali.
Tregami (Trigami), or Katar Gambiri, is a language spoken in the villages of Gambir, Kaṭâr, and Devoz in the Tregâm Valley off the lower Pech River in the Watapur District of Kunar Province in Afghanistan. The area is in the Hindu Kush along the border with Pakistan. Tregami belongs to the Nuristani group of the Indo-Iranian language family. It is spoken by approximately 3,500 people (2011). Most individuals speak Pashto in addition to Tregami.
Waigali, also known as Nuristani Kalasha, is a language spoken by about 10,000 Nuristani people of the Waigal Valley in the Nuristan Province of Afghanistan. The native name is Kalaṣa-alâ 'Kalasha-language'. "Waigali" refers to the dialect of the Väi people of the upper part of the Waigal Valley, centered on the town of Waigal, which is distinct from the dialect of the Čima-Nišei people who inhabit the lower valley. The word 'Kalasha' is the native ethnonym for all the speakers of the southern Nuristani languages.
Kata-vari (Kâta-vari) is a dialect of the Kamkata-vari language spoken by the Kata in parts of Afghanistan and Pakistan. The most used alternative names are Kati, Kativiri or Bashgali.
Wasi-wari is the language of the Wasi people, spoken in a few villages in the Pārūn Valley in Afghanistan. It also goes by the name Prasun or Paruni.

Kamkata-vari, also known as Katë or Kati, is the largest Nuristani language. It contains the main dialects Kata-vari, Kamviri and Mumviri. Kata-vari and Kamviri are sometimes erroneously reckoned as two separate languages, but according to linguist Richard Strand they form one language.

The Kalash, or Kalasha, are a small Indo-Aryan indigenous (minority) people residing in the Chitral District of the Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. The term is also used to refer to several distinct Nuristani speaking people, including the Väi, the Čima-nišei, the Vântä, plus the Ashkun- and Tregami-speakers.
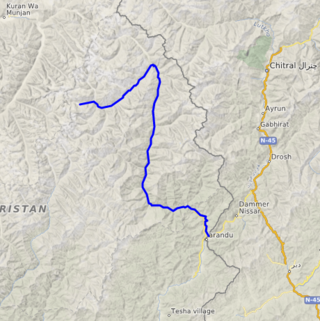
The Landai Sin River, also called the Bashgal River, is located in eastern Afghanistan. It rises in the Hindu Kush range near the Mandol Pass in the Nuristan Province of Afghanistan, and is fed from glaciers and snow to its north. The Landai Sin is a tributary of Kunar River.

Eastern Kata-vari also locally known as Shekhani is a variety of the Kata-vari language spoken in Chitral district of Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. The Kamviri language is also known as Shekhani. The Khowar name for the dialect is Sheikhwar which means "Language of the Sheikhs or converts." Some linguists consider Shekhani or Eastern Kata-vari a different language due to the isolation from other Nuristani languages other than Kamviri. Kamviri Shekhani is different than Eastern Kata-vari which is also called Shekhani.
Disani, known in Kamviri as Disaňi and Kata-vari as Disai, from which Prasuni Disni was borrowed from, was a goddess of the Nuristani people before their conversion to Islam. To the people of Nuristan, she was depicted as living in the terrestrial world, appearing in the shape of a woman with a golden garland. Milk and milk-products were offered to her at the altar on the hillside.
The Palula, or Dangerik, also known as the Ashreti or Biori are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group who inhabit Ashret and parts of the former Chitral district, primarily in the south.
References
- ↑ Richard F. Strand