Related Research Articles

The Bantu languages are a language family of about 600 languages that are spoken by the Bantu peoples of Central, Southern, Eastern and Southeast Africa. They form the largest branch of the Southern Bantoid languages.

Niger–Congo is a hypothetical language family spoken over the majority of sub-Saharan Africa. It unites the Mande languages, the Atlantic–Congo languages, and possibly several smaller groups of languages that are difficult to classify. If valid, Niger–Congo would be the world's largest in terms of member languages, the third-largest in terms of speakers, and Africa's largest in terms of geographical area. Austronesian has almost as many member languages, although this is complicated by the ambiguity about what constitutes a distinct language; the number of named Niger–Congo languages listed by Ethnologue is 1,540.
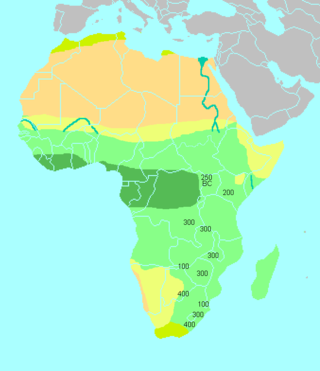
The Bantu expansion was a major series of migrations of the original Proto-Bantu-speaking group, which spread from an original nucleus around West-Central Africa. In the process, the Proto-Bantu-speaking settlers displaced, eliminated or absorbed pre-existing hunter-gatherer and pastoralist groups that they encountered.

The Bamiléké are a group of 90 closely related peoples who inhabit the Western High Plateau of Cameroon. According to Dr John Feyou de Hapy, Bamiléké means people of faith.

Southern Bantoid is a branch of the Bantoid language family. It consists of the Bantu languages along with several small branches and isolates of eastern Nigeria and west-central Cameroon. Since the Bantu languages are spoken across most of Sub-Saharan Africa, Southern Bantoid comprises 643 languages as counted by Ethnologue, though many of these are mutually intelligible.

The Tikar is an umbrella term for a group of closely related peoples who mostly inhabit the Northwest Region of Cameroon with a small minority in the Adamawa Region. They are known to be great artists, artisans and storytellers. Once a nomadic people, some oral traditions trace the origin of the Tikar people to the Nile River Valley in present-day Sudan. Such ethnic groups were referred to in the 1969 official statistics as "Semi-Bantus" and "Sudanese Negroes." They speak a Northern Bantoid language called Tikar. One of the few African ethnic groups to practice a monotheistic traditional religion, the Tikar refer to God the Creator by the name Nyuy. They also have an extensive spiritual system of ancestral reverence.

Cameroon is home to at least 250 languages, with some accounts reporting around 600. These include 55 Afro-Asiatic languages, two Nilo-Saharan languages, four Ubangian languages, and 169 Niger–Congo languages. This latter group comprises one Senegambian language (Fulfulde), 28 Adamawa languages, and 142 Benue–Congo languages . French and English are official languages, a heritage of Cameroon's colonial past as a colony of both France and the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1961. Eight out of the ten regions of Cameroon are primarily francophone and two are anglophone. The official percentage of French and English speakers by the Presidency of Cameroon is estimated to be 70% and 30% respectively.

The Beboid languages are any of several groups of languages spoken principally in southwest Cameroon, although two languages are spoken over the border in Nigeria. They are probably not most closely related to each other. The Eastern Beboid languages may be most closely related to the Tivoid and Momo groups, though some of the geographical Western Beboid grouping may be closer to Ekoid and Bantu.

The Ekoid languages are a dialect cluster of Southern Bantoid languages spoken principally in southeastern Nigeria and in adjacent regions of Cameroon. They have long been associated with the Bantu languages, without their status being precisely defined. Crabb (1969) remains the major monograph on these languages, although regrettably, Part II, which was to contain grammatical analyses, was never published. Crabb also reviews the literature on Ekoid up to the date of publication.
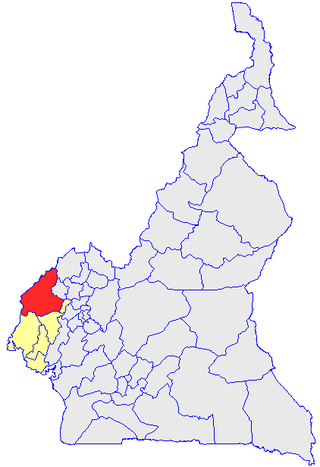
Manyu is a division of the Southwest Region in Cameroon. The division covers an area of 9,565 km2 and as of 2005 had a total population of 181,039. The capital of the division is Mamfe.

Jita is a Bantu language of Tanzania, spoken on the southeastern shore of Lake Victoria/Nyanza and on the island of Ukerewe.
Mungbam is a Southern Bantoid language of the Lower Fungom region of Cameroon. It is traditionally classified as a Western Beboid language, but the language family is disputed. Good et al. uses a more accurate name, the 'Yemne-Kimbi group,' but proposes the term 'Beboid.'
Fang is a Southern Bantoid language of Cameroon.
Koshin is a Southern Bantoid language of Cameroon. It is traditionally classified as a Western Beboid language, but that has not been demonstrated to be a valid family.
Mbuʼ, or Ajumbu, is a Southern Bantoid language of Cameroon. It is traditionally classified as a Western Beboid language, but that has not been demonstrated to be a valid family. Inasmuch as Western Beboid may be valid, Mbuʼ would appear to be the most divergent of its languages.
Kung is a Grassfields Bantu language of Cameroon.
Missong is a Southern Bantoid language of the Lower Fungom region of Cameroon, spoken in the village of Missong. It is closely related to Mungbam. There are around 400 speakers.
Proto-Bantu is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Bantu languages, a subgroup of the Southern Bantoid languages. It is thought to have originally been spoken in West/Central Africa in the area of what is now Cameroon. About 6,000 years ago, it split off from Proto-Southern Bantoid when the Bantu expansion began to the south and east. Two theories have been put forward about the way the languages expanded: one is that the Bantu-speaking people moved first to the Congo region and then a branch split off and moved to East Africa; the other is that the two groups split from the beginning, one moving to the Congo region, and the other to East Africa.
Buu is a Southern Bantoid language of Cameroon. It is closely related to Mundabli.
Lung is a poorly attested extinct language that appears to have been closely related to Ajumbu, a Southern Bantoid language of Cameroon.
References
- ↑ Mundabli at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ↑ Good, Jeff and Lovegren, Jesse and Mve, Jean Patrick and Tchiemouo, Nganguep Carine and Voll, Rebecca and Di Carlo, Pierpaolo. 2011. The languages of the Lower Fungom region of Cameroon: Grammatical overview. Africana Linguistica 17. 101–164.
- ↑ Good, Jeff and Lovegren, Jesse and Mve, Jean Patrick and Tchiemouo, Nganguep Carine and Voll, Rebecca and Di Carlo, Pierpaolo. 2011. The languages of the Lower Fungom region of Cameroon: Grammatical overview. Africana Linguistica 17. 101–164.
- Blench, Roger, 2011. 'The membership and internal structure of Bantoid and the border with Bantu'. Bantu IV, Humboldt University, Berlin.
- Good, Jeff, & Jesse Lovegren. 2009. 'Reassessing Western Beboid'. Bantu III.
- Good, Jeff, & Scott Farrar. 2008. 'Western Beboid and African language classification'. LSA.
- Voll, R.M. (2017). A grammar of Mundabli: a Bantoid (Yemne-Kimbi) language of Cameroon (Doctoral thesis). LOT (Leiden University). hdl: 1887/56258 . ISBN 9789460932540.