
The Netherlands Armed Forces are the military services of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The core of the armed forces consists of the four service branches: the Royal Netherlands Navy, the Royal Netherlands Army, the Royal Netherlands Air Force and the Royal Netherlands Marechaussee. The service branches are supplemented by various joint support organisations. In addition, local conscript forces exist on the Dutch Caribbean islands of Aruba (AruMil) and Curaçao (CurMil). These operate under the auspices of the Royal Netherlands Navy and the Netherlands Marine Corps. The armed forces are organisationally part of the Ministry of Defence.
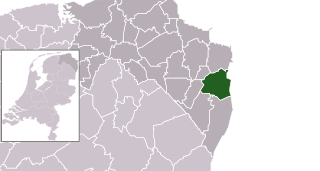
Bellingwedde was a municipality with a population of data missing in the province Groningen in the northeast of the Netherlands. Bellingwedde was established in 1968, when the municipalities of Bellingwolde and Wedde had merged. It contained the villages Bellingwolde, Blijham, Oudeschans, Veelerveen, Vriescheloo, and Wedde. After almost 50 year, Bellingwedde was disestablished in 2018, when the municipalities of Bellingwedde and Vlagtwedde had merged into Westerwolde.

Bloemendaal is a municipality and town in the Western Netherlands, in the province of North Holland. Bloemendaal is, together with Wassenaar, the wealthiest place in the Netherlands. It is located just west of Haarlem, on the North Sea.
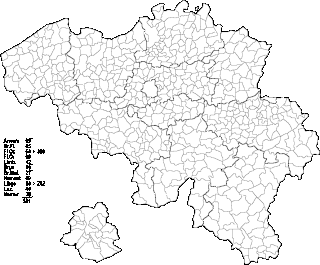
Belgium comprises 581 municipalities, 300 of them grouped into five provinces in Flanders and 262 others in five provinces in Wallonia, while the remaining 19 are in the Brussels Capital Region, which is not divided in provinces. In most cases, the municipalities are the smallest administrative subdivisions of Belgium, but in municipalities with more than 100,000 inhabitants, on the initiative of the local council, sub-municipal administrative entities with elected councils may be created. As such, only Antwerp, having over 500,000 inhabitants, became subdivided into nine districts. The Belgian arrondissements, an administrative level between province and municipality, or the lowest judicial level, are in English sometimes called districts as well.
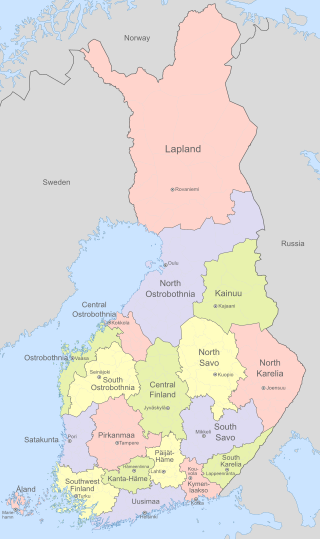
Finland is divided into 19 regions which are governed by regional councils that serve as forums of cooperation for the municipalities of each region. The councils are composed of delegates from the municipal councils. The main tasks of regional councils are regional planning, the development of enterprises, and education. Between 2004 and 2012, the regional council of Kainuu was elected via popular elections as part of an experimental regional administration.

Since 1 January 2023, there have been 342 regular municipalities and three special municipalities in the Netherlands. The latter is the status of three of the six island territories that make up the Dutch Caribbean. Municipalities are the second-level administrative division, or public bodies, in the Netherlands and are subdivisions of their respective provinces. Their duties are delegated to them by the central government and they are ruled by a municipal council that is elected every four years. Municipal mergers have reduced the total number of municipalities by two-thirds since the first official boundaries were created in the mid 19th century. Municipalities themselves are informally subdivided into districts and neighbourhoods for administrative and statistical purposes.

The Flemish Region, usually simply referred to as Flanders, is one of the three regions of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and the Brussels-Capital Region. Covering the northern portion of the country, the Flemish Region is primarily Dutch-speaking. With an area of 13,522 km2 (5,221 sq mi), it accounts for only 45% of Belgium's territory, but 57% of its population. It is one of the most densely populated regions of Europe with around 490/km2 (1,300/sq mi).
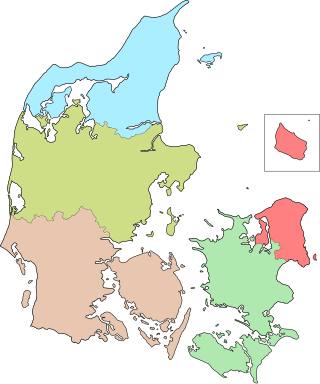
The five Regions of Denmark were created as administrative entities at a level above the municipalities and below the central government in the public sector as part of the 2007 Danish Municipal Reform, when the 13 counties (amter) were abolished. At the same time, the number of municipalities (kommuner) was cut from 270 to 98. The reform was approved and made into a law by the lawmakers in the Folketing 26 June 2005 with elections to the 98 municipalities and 5 regions being held Tuesday 15 November 2005.

The National Institute for Public Health and the Environment is a Dutch research institute that is an independent agency of the Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport.

The Netherlands Coastguard is civil organisation that carries out tasks on the Netherlands North Sea for six Ministries under administration of the Royal Netherlands Navy. Its operational command falls under the Ministry of Defence, and the Royal Netherlands Navy is responsible for its coordination.

National Police Corps, colloquially in English as Dutch National Police or National Police Force, is divided in ten regional units, two national units, the police academy, police services center, and national dispatch center cooperation. The law-enforcement purposes of these agencies are the investigation of suspected criminal activity, referral of the results of investigations to the courts, and the temporary detention of suspected criminals pending judicial action. Law enforcement agencies, to varying degrees at different levels of government and in different agencies, are also commonly charged with the responsibilities of deterring criminal activity and preventing the successful commission of crimes in progress. The police commissioner in the Netherlands is Janny Knol since March 1, 2024.

The Caribbean Netherlands is a geographic region of the Netherlands located outside of Europe, in the Caribbean, consisting of three so-called special municipalities. These are the islands of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba, as they are also known in legislation, or the BES islands for short. The islands are officially classified as public bodies in the Netherlands and as overseas territories of the European Union; as such, European Union law does not automatically apply to them.

The Metropoolregio Eindhoven, until 1 January 2014 the Samenwerkingsverband Regio Eindhoven, is a regional governmental agency for the city region of Eindhoven, Netherlands. The MRE comprises 21 municipalities in the Eindhoven agglomeration, with a total area of 1,457.81 square kilometres. The region has nearly three quarters of a million inhabitants and some 35,000 companies.

Beek is a town and municipality in the southeastern Netherlands, in the province of Limburg. As of 2012, Beek has a population of about 16,400, of which about 8,800 live in the town of Beek.

Public Health England (PHE) was an executive agency of the Department of Health and Social Care in England which began operating on 1 April 2013 to protect and improve health and wellbeing and reduce health inequalities. Its formation came as a result of the reorganisation of the National Health Service (NHS) in England outlined in the Health and Social Care Act 2012. It took on the role of the Health Protection Agency, the National Treatment Agency for Substance Misuse and a number of other health bodies. It was an executive agency of the Department of Health and Social Care, and a distinct delivery organisation with operational autonomy.

The Health and Youth Care Inspectorate is a governmental institution that supervises public health in the Netherlands. It is part of the Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport, located in Utrecht. The IGJ supervises the quality, safety and accessibility of health care, and guards the rights of patients. The current Inspector-General is dr. Ronnie van Diemen-Steenvoorde.

The COVID-19 pandemic in the Netherlands has resulted in 8,636,143 confirmed cases of COVID-19 and 22,986 deaths.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Bonaire was part of the ongoing global viral pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which was confirmed to have reached the Dutch Caribbean island of Bonaire on 16 April 2020. On 28 April, all cases recovered. On 14 July, two new cases were discovered. On 13 August, all cases recovered.
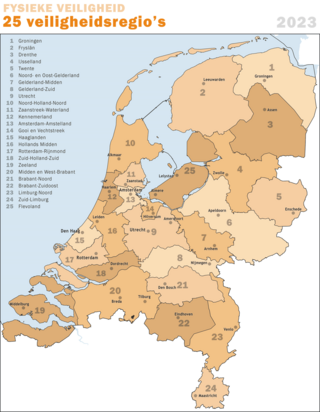
In the European Netherlands, a safety region is a public body whose task is to facilitate regional cooperation in dealing with crises, disasters and disruptions of public order.
Operation Gloria was a Swedish military operation conducted in support of handling the COVID-19 pandemic in Sweden.




















