In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dog teeth, fangs, or eye teeth, are relatively long, pointed teeth. However, they can appear more flattened, causing them to resemble incisors and leading them to be called incisiform. They developed and are used primarily for firmly holding food in order to tear it apart, and occasionally as weapons. They are often the largest teeth in a mammal's mouth. Individuals of most species that develop them normally have four, two in the upper jaw and two in the lower, separated within each jaw by incisors; humans and dogs are examples. In most species, canines are the anterior-most teeth in the maxillary bone.
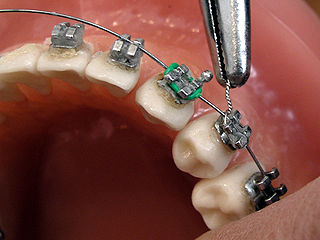
Orthodontics and dentofacial orthopedics, formerly referred to as orthodontia, is a specialty of dentistry that deals with the diagnosis, prevention and correction of malpositioned teeth and jaws. The field was established by such pioneering orthodontists as Edward Angle and Norman William Kingsley.

A malocclusion is a misalignment or incorrect relation between the teeth of the two dental arches when they approach each other as the jaws close. The term was coined by Edward Angle, the "father of modern orthodontics", as a derivative of occlusion. This refers to the manner in which opposing teeth meet.

Thrinaxodon is an extinct genus of cynodonts, most commonly regarded by its species T. liorhinus which lived in what are now South Africa and Antarctica. Thrinaxodon has been dated between the Permian–Triassic boundary and the mid-Triassic. Its survival of the extinction may have been due to its burrowing habits.

Maxillary Central Incisor Video Demonstrationhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rd2wsVqxpD4&t=60s The maxillary central incisor is a human tooth in the front upper jaw, or maxilla, and is usually the most visible of all teeth in the mouth. It is located mesial to the maxillary lateral incisor. As with all incisors, their function is for shearing or cutting food during mastication (chewing). There is typically a single cusp on each tooth, called an incisal ridge or incisal edge. Formation of these teeth begins at 14 weeks in utero for the deciduous (baby) set and 3–4 months of age for the permanent set.

A temporary crown is a temporary (short-term) crown used in dentistry. Like other interim restorations, it serves until a final (definitive) restoration can be inserted. Usually the temporary crown is constructed from acrylic resins based or, chemical-cure / light cure composite, although alternative systems using aluminium crown forms are occasionally used. Temporary crowns function to protect the tooth, prevent teeth shifting, provide cosmetics, shape the gum tissue properly, and prevent sensitivity.

In anatomy, the Curve of Spee is defined as the curvature of the mandibular occlusal plane beginning at the premolar and following the buccal cusps of the posterior teeth, continuing to the terminal molar. According to another definition the curve of Spee is an anatomic curvature of the occlusal alignment of the teeth, beginning at the tip of the lower incisor, following the buccal cusps of the natural premolars and molars and continuing to the anterior border of the ramus. It is named for the German embryologist Ferdinand Graf von Spee (1855–1937), who was first to describe the anatomic relations of human teeth in the sagittal plane.
Dens evaginatus is a rare odontogenic developmental anomaly that is found in teeth where the outer surface appears to form an extra bump or cusp.

Talon Cusp is a rare dental anomaly. Generally a person with this develops "cusp-like" projections located on the inside surface of the affected tooth. Talon cusp is an extra cusp on an anterior tooth. Although talon cusp may not appear serious, it can cause clinical, diagnostic, functional problems and alters the aesthetic appeal.

Dental attrition is a type of tooth wear caused by tooth-to-tooth contact, resulting in loss of tooth tissue, usually starting at the incisal or occlusal surfaces. Tooth wear is a physiological process and is commonly seen as a normal part of aging. Advanced and excessive wear and tooth surface loss can be defined as pathological in nature, requiring intervention by a dental practitioner. The pathological wear of the tooth surface can be caused by bruxism, which is clenching and grinding of the teeth. If the attrition is severe, the enamel can be completely worn away leaving underlying dentin exposed, resulting in an increased risk of dental caries and dentin hypersensitivity. It is best to identify pathological attrition at an early stage to prevent unnecessary loss of tooth structure as enamel does not regenerate.

Dental anatomy is a field of anatomy dedicated to the study of human tooth structures. The development, appearance, and classification of teeth fall within its purview. Tooth formation begins before birth, and the teeth's eventual morphology is dictated during this time. Dental anatomy is also a taxonomical science: it is concerned with the naming of teeth and the structures of which they are made, this information serving a practical purpose in dental treatment.

A cusp is a pointed, projecting, or elevated feature. In animals, it is usually used to refer to raised points on the crowns of teeth.
This is a list of commonly used terms of location and direction in dentistry. This set of terms provides orientation within the oral cavity, much as anatomical terms of location provide orientation throughout the body.

Crossbite is a form of malocclusion where a tooth has a more buccal or lingual position than its corresponding antagonist tooth in the upper or lower dental arch. In other words, crossbite is a lateral misalignment of the dental arches.
The Dahl effect or Dahl concept is used in dentistry where a localized appliance or localized restoration is used to increase the available interocclusal space available for restorations.
A Dahl appliance is a dental appliance that includes a flat anterior bite plane that causes a planned posterior disclusion. The Dahl appliance causes Dahl effect dental adaptation; posterior overeruption and mild intrusion of the anterior teeth, creating anterior interocclusal space which may be desired for either orthodontics, restorative dentistry such as restoring non-carious tooth surface loss, or for fixed prosthodontics.

Overbite medically refers to the extent of vertical (superior-inferior) overlap of the maxillary central incisors over the mandibular central incisors, measured relative to the incisal ridges.
Intrusion is a movement in the field of orthodontics where a tooth is moved partially into the bone. Intrusion is done in orthodontics to correct an anterior deep bite or in some cases intrusion of the over-erupted posterior teeth with no opposing tooth. Intrusion can be done in many ways and consists of many different types. Intrusion, in orthodontic history, was initially defined as problematic in early 1900s and was known to cause periodontal effects such as root resorption and recession. However, in mid 1950s successful intrusion with light continuous forces was demonstrated. Charles J. Burstone defined intrusion to be "the apical movement of the geometric center of the root (centroid) in respect to the occlusal plane or plane based on the long axis of tooth".
Open bite is a type of orthodontic malocclusion which has been estimated to occur in 0.6% of the people in the United States. This type of malocclusion has no vertical overlap or contact between the anterior incisors. The prevalence varies between different populations, for instance, occurring with 16% in black people and 4% in white people. The term "open bite" was coined by Carevelli in 1842.