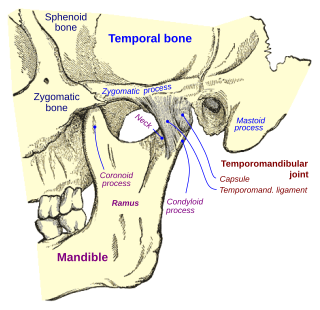
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction is an umbrella term covering pain and dysfunction of the muscles of mastication and the temporomandibular joints. The most important feature is pain, followed by restricted mandibular movement, and noises from the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) during jaw movement. Although TMD is not life-threatening, it can be detrimental to quality of life; this is because the symptoms can become chronic and difficult to manage.

Bruxism is excessive teeth grinding or jaw clenching. It is an oral parafunctional activity; i.e., it is unrelated to normal function such as eating or talking. Bruxism is a common behavior; reports of prevalence range from 8% to 31% in the general population. Several symptoms are commonly associated with bruxism, including aching jaw muscles, headaches, hypersensitive teeth, tooth wear, and damage to dental restorations. Symptoms may be minimal, without patient awareness of the condition. If nothing is done, after a while many teeth start wearing down until the whole tooth is gone.

In anatomy, the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) are the two joints connecting the jawbone to the skull. It is a bilateral synovial articulation between the temporal bone of the skull above and the mandible below; it is from these bones that its name is derived. This joint is unique in that it is a bilateral joint that functions as one unit. Since the TMJ is connected to the mandible, the right and left joints must function together and therefore are not independent of each other.

Trismus, commonly called lockjaw as associated with tetanus, is a condition of limited jaw mobility. It may be caused by spasm of the muscles of mastication or a variety of other causes. Temporary trismus occurs much more frequently than permanent trismus. It is known to interfere with eating, speaking, and maintaining proper oral hygiene. This interference, specifically with an inability to swallow properly, results in an increased risk of aspiration. In some instances, trismus presents with altered facial appearance. The condition may be distressing and painful. Examination and treatments requiring access to the oral cavity can be limited, or in some cases impossible, due to the nature of the condition itself.

In neuroanatomy, the mandibular nerve (V3) is the largest of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth cranial nerve (CN V). Unlike the other divisions of the trigeminal nerve (ophthalmic nerve, maxillary nerve) which contain only afferent fibers, the mandibular nerve contains both afferent and efferent fibers. These nerve fibers innervate structures of the lower jaw and face, such as the tongue, lower lip, and chin. The mandibular nerve also innervates the muscles of mastication.

In anatomy, the temporalis muscle, also known as the temporal muscle, is one of the muscles of mastication (chewing). It is a broad, fan-shaped convergent muscle on each side of the head that fills the temporal fossa, superior to the zygomatic arch so it covers much of the temporal bone.Temporal refers to the head's temples.

There are four classical muscles of mastication. During mastication, three muscles of mastication are responsible for adduction of the jaw, and one helps to abduct it. All four move the jaw laterally. Other muscles, usually associated with the hyoid, such as the mylohyoid muscle, are responsible for opening the jaw in addition to the lateral pterygoid.

In human anatomy, the masseter is one of the muscles of mastication. Found only in mammals, it is particularly powerful in herbivores to facilitate chewing of plant matter. The most obvious muscle of mastication is the masseter muscle, since it is the most superficial and one of the strongest.

The medial pterygoid muscle, is a thick, quadrilateral muscle of the face. It is supplied by the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (V). It is important in mastication (chewing).

The lateral pterygoid muscle (or external pterygoid muscle) is a muscle of mastication. It has two heads. It lies superior to the medial pterygoid muscle. It is supplied by pterygoid branches of the maxillary artery, and the lateral pterygoid nerve (from the mandibular nerve, CN V3). It depresses and protrudes the mandible. When each muscle works independently, they can move the mandible side to side.

Masticatory muscle myositis (MMM) is an inflammatory disease in dogs affecting the muscles of mastication (chewing). It is also known as atrophic myositis or eosinophilic myositis. MMM is the most common inflammatory myopathy in dogs. The disease mainly affects large breed dogs. German Shepherd Dogs and Cavalier King Charles Spaniels may be predisposed. There is a similar disease of the eye muscles found in Golden Retrievers. Symptoms of acute MMM include swelling of the jaw muscles, drooling, and pain on opening the mouth. Ophthalmic signs may include third eyelid protrusion, red eyes, and exophthalmos. In chronic MMM there is atrophy of the jaw muscles, and scarring of the masticatory muscles due to fibrosis may result in inability to open the mouth (trismus). The affected muscles include the temporalis, masseter, and pterygoid muscles. The disease is usually bilateral.

The pterygoid processes of the sphenoid, one on either side, descend perpendicularly from the regions where the body and the greater wings of the sphenoid bone unite.
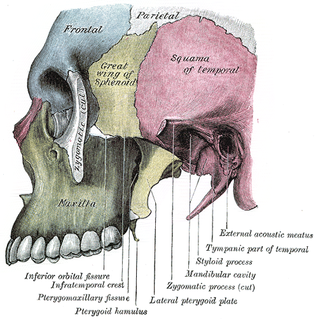
The infratemporal fossa is an irregularly shaped cavity that is a part of the skull. It is situated below and medial to the zygomatic arch. It is not fully enclosed by bone in all directions. It contains superficial muscles, including the lower part of the temporalis muscle, the lateral pterygoid muscle, and the medial pterygoid muscle. It also contains important blood vessels such as the middle meningeal artery, the pterygoid plexus, and the retromandibular vein, and nerves such as the mandibular nerve (CN V3) and its branches.

The deep cervical fascia lies under cover of the platysma, and invests the muscles of the neck; it also forms sheaths for the carotid vessels, and for the structures situated in front of the vertebral column. Its attachment to the hyoid bone prevents the formation of a dewlap.
Mouth infections, also known as oral infections, are a group of infections that occur around the oral cavity. They include dental infection, dental abscess, and Ludwig's angina. Mouth infections typically originate from dental caries at the root of molars and premolars that spread to adjacent structures. In otherwise healthy patients, removing the offending tooth to allow drainage will usually resolve the infection. In cases that spread to adjacent structures or in immunocompromised patients, surgical drainage and systemic antibiotics may be required in addition to tooth extraction. Since bacteria that normally reside in the oral cavity cause mouth infections, proper dental hygiene can prevent most cases of infection. As such, mouth infections are more common in populations with poor access to dental care or populations with health-related behaviors that damage one's teeth and oral mucosa. This is a common problem, representing nearly 36% of all encounters within the emergency department related to dental conditions.

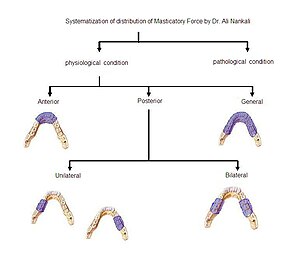
Nankali’s masticatory force systematization categorizes the locations of the forces on different part of mandible/maxilla, which are important in designing a prosthetic and implant treatment in dentistry.

Dislocations occur when two bones that originally met at the joint detach. Dislocations should not be confused with Subluxation. Subluxation is when the joint is still partially attached to the bone.
Fascial spaces are potential spaces that exist between the fasciae and underlying organs and other tissues. In health, these spaces do not exist; they are only created by pathology, e.g. the spread of pus or cellulitis in an infection. The fascial spaces can also be opened during the dissection of a cadaver. The fascial spaces are different from the fasciae themselves, which are bands of connective tissue that surround structures, e.g. muscles. The opening of fascial spaces may be facilitated by pathogenic bacterial release of enzymes which cause tissue lysis. The spaces filled with loose areolar connective tissue may also be termed clefts. Other contents such as salivary glands, blood vessels, nerves and lymph nodes are dependent upon the location of the space. Those containing neurovascular tissue may also be termed compartments.

The Infratemporal space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space in the side of the head, and is paired on either side. It is located posterior to the maxilla, between the lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone medially and by the base of skull superiorly. The term is derived from infra- meaning below and temporal which refers to the temporalis muscle.