
A metallocene is a compound typically consisting of two cyclopentadienyl anions (C
5H−
5, abbreviated Cp) bound to a metal center (M) in the oxidation state II, with the resulting general formula (C5H5)2M. Closely related to the metallocenes are the metallocene derivatives, e.g. titanocene dichloride or vanadocene dichloride. Certain metallocenes and their derivatives exhibit catalytic properties, although metallocenes are rarely used industrially. Cationic group 4 metallocene derivatives related to [Cp2ZrCH3]+ catalyze olefin polymerization.
Ferrocene is an organometallic compound with the formula Fe(C5H5)2. The molecule is a complex consisting of two cyclopentadienyl rings sandwiching a central iron atom. It is an orange solid with a camphor-like odor that sublimes above room temperature, and is soluble in most organic solvents. It is remarkable for its stability: it is unaffected by air, water, strong bases, and can be heated to 400 °C without decomposition. In oxidizing conditions it can reversibly react with strong acids to form the ferrocenium cation Fe(C5H5)+2. Ferrocene and the ferrocenium cation are sometimes abbreviated as Fc and Fc+ respectively.

Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the formula (CH3CO)2O. Commonly abbreviated Ac2O, it is the simplest isolable anhydride of a carboxylic acid and is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is a colorless liquid that smells strongly of acetic acid, which is formed by its reaction with moisture in the air.

Cobaltocene, known also as bis(cyclopentadienyl)cobalt(II) or even "bis Cp cobalt", is an organocobalt compound with the formula Co(C5H5)2. It is a dark purple solid that sublimes readily slightly above room temperature. Cobaltocene was discovered shortly after ferrocene, the first metallocene. Due to the ease with which it reacts with oxygen, the compound must be handled and stored using air-free techniques.

tert-Butyllithium is a chemical compound with the formula (CH3)3CLi. As an organolithium compound, it has applications in organic synthesis since it is a strong base, capable of deprotonating many carbon molecules, including benzene. tert-Butyllithium is available commercially as solutions in hydrocarbons (such as pentane); it is not usually prepared in the laboratory.

Tebbe's reagent is the organometallic compound with the formula (C5H5)2TiCH2ClAl(CH3)2. It is used in the methylidenation of carbonyl compounds, that is it converts organic compounds containing the R2C=O group into the related R2C=CH2 derivative. It is a red solid that is pyrophoric in the air, and thus is typically handled with air-free techniques. It was originally synthesized by Fred Tebbe at DuPont Central Research.
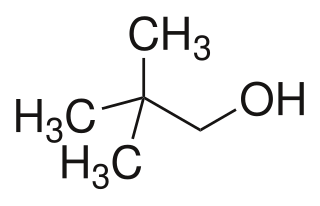
Neopentyl alcohol is a compound with formula (CH3)3CCH2OH. It is a colorless solid. The compound is one of the eight isomers of pentyl alcohol.
Diphenylmethane is an organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2CH2 (often abbreviated CH
2Ph
2). The compound consists of methane wherein two hydrogen atoms are replaced by two phenyl groups. It is a white solid.

In organometallic chemistry, a sandwich compound is a chemical compound featuring a metal bound by haptic, covalent bonds to two arene (ring) ligands. The arenes have the formula CnHn, substituted derivatives and heterocyclic derivatives. Because the metal is usually situated between the two rings, it is said to be "sandwiched". A special class of sandwich complexes are the metallocenes.

2,6-Lutidine is a natural heterocyclic aromatic organic compound with the formula (CH3)2C5H3N. It is one of several dimethyl-substituted derivative of pyridine, all of which are referred to as lutidines. It is a colorless liquid with mildly basic properties and a pungent, noxious odor.

Dimethylbenzylamine is the organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2N(CH3)2. The molecule consists of a benzyl group, C6H5CH2, attached to a dimethylamino functional group. It is a colorless liquid. It is used as a catalyst for the formation of polyurethane foams and epoxy resins.
Ruthenocene is an organoruthenium compound with the formula (C5H5)2Ru. This pale yellow, volatile solid is classified as a sandwich compound and more specifically, as a metallocene.
In organic chemistry, pentadiene is any hydrocarbon with an open chain of five carbons, connected by two single bonds and two double bonds. All those compounds have the same molecular formula C5H8. The inventory of pentadienes include:

1-Phenylethylamine (1-PEA or α-PEA), also known as α-methylbenzylamine, is the organic compound with the formula C6H5CH(NH2)CH3. This primary amine is a colorless liquid is often used in chiral resolutions. Like benzylamine, it is relatively basic and forms stable ammonium salts and imines.

Trimethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate (TMSOTf) is an organosilicon compound with the formula (CH3)3SiO3SCF3. It is a colorless moisture-sensitive liquid. It is the trifluoromethanesulfonate derivative of trimethylsilyl. It is mainly used to activate ketones and aldehydes in organic synthesis.
Silylation is the introduction of one or more (usually) substituted silyl groups (R3Si) to a molecule. Silylations are core methods for production of organosilicon chemistry. Silanization, while similar to silylation, usually refers to attachment of silyl groups to solids. Silyl groups are commonly used for: alcohol protection, enolate trapping, gas chromatography, electron-impact mass spectrometry (EI-MS), and coordinating with metal complexes.
1-Naphthol, or α-naphthol, is an organic compound with the formula C10H7OH. It is a fluorescent white solid. 1-Naphthol differs from its isomer 2-naphthol by the location of the hydroxyl group on the naphthalene ring. The naphthols are naphthalene homologues of phenol. Both isomers are soluble in simple organic solvents. They are precursors to a variety of useful compounds.
Organoiron chemistry is the chemistry of iron compounds containing a carbon-to-iron chemical bond. Organoiron compounds are relevant in organic synthesis as reagents such as iron pentacarbonyl, diiron nonacarbonyl and disodium tetracarbonylferrate. Although iron is generally less active in many catalytic applications, it is less expensive and "greener" than other metals. Organoiron compounds feature a wide range of ligands that support the Fe-C bond; as with other organometals, these supporting ligands prominently include phosphines, carbon monoxide, and cyclopentadienyl, but hard ligands such as amines are employed as well.

Ferrocenecarboxylic acid is the organoiron compound with the formula (C5H5)Fe(C5H4CO2H). It is the simplest carboxylic acid derivative of ferrocene. It can be prepared in two steps from ferrocene by acylation with a 2-chlorobenzoyl chloride followed by hydrolysis.
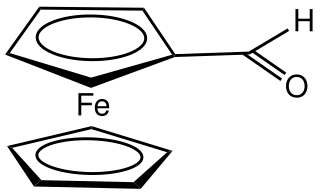
Ferrocenecarboxaldehyde is the organoiron compound with the formula (C5H5)Fe(C5HCHO). The molecule consists of ferrocene substituted by an formyl group on one of the cyclopentadienyl rings. It is an orange, air-stable solid that is soluble in organic solvents.














