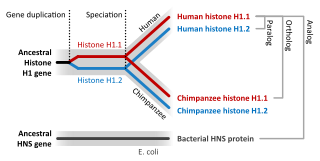
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal gene transfer event (xenologs).

Protein SSX2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SSX2 gene.

Nesprin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SYNE2 gene. The human SYNE2 gene consists of 116 exons and encodes nesprin-2, a member of the nuclear envelope (NE) spectrin-repeat (nesprin) family. Nesprins are modular proteins with a central extended spectrin-repeat (SR) rod domain and a C-terminal Klarsicht/ANC-1/Syne homology (KASH) transmembrane domain, which acts as a NE-targeting motif. Nesprin-2 (Nesp2) binds to cytoplasmic F-actin, tethering the nucleus to the cytoskeleton and maintaining the structural integrity of the nucleus.

WD repeat and SOCS box-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WSB1 gene.

Dimethylaniline monooxygenase [N-oxide-forming] 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FMO2 gene.

Ankyrin repeat and SOCS box protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ASB2 gene.

Pogo transposable element with ZNF domain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the POGZ gene.

Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ANKRD17 gene.

Leucine-rich repeat neuronal protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LRRN1 gene.

KN motif and ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KANK1 gene.

Myomegalin, also known as phosphodiesterase 4D-interacting protein or cardiomyopathy-associated protein 2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PDE4DIP gene. It has roles in the formation of microtubules from the centrosome. Its name derives from the fact that it is highly expressed in units of tubular myofibrils known as sarcomeres and is a large protein, at 2,324 amino acids. It was first characterised in 2000.

Ankyrin 1, also known as ANK-1, and erythrocyte ankyrin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ANK1 gene.

Ankyrin repeat and SOCS box protein 1 is a protein that is in humans, encoded by the ASB1 gene.

Ankyrin repeat and BTB/POZ domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABTB1 gene.

Neuroblastoma breakpoint family, member 15, also known as NBPF15, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the NBPF15 gene. The gene is 18762 bp long, with mRNA that is 3837 bp long. The gene is located on chromosome 1q21.1. Its sub-cellular location is predicted to be in the nucleus and cytoplasm. It contains what is known as the NBPF repeat, which is a two-exon stretch of sequence that is characteristic of all 21 members of the NBPF gene family. The repeat is considered the ancestral exons, and the NBPF family has been linked to primate evolution.

Neuroblastoma breakpoint family member 10 is a protein that in Homo sapiens is encoded by the NBPF10 gene.

Chromosome X open reading frame 36 (CXorf36) is a gene that in humans encodes a protein “hypothetical protein LOC79742”. This protein has a function that is not currently very well understood. Other known aliases are “FLJ14103, DKFZp313K0825, FLJ55198, PRO3743, FLJ55198, hCG1981635, bA435K1.1,” and “4930578C19Rik.”

Neuroblastoma breakpoint family, member 1, or NBPF1, is a protein that is encoded by the gene NBPF1 in humans. This protein is member of the neuroblastoma breakpoint family of proteins, a group of proteins that are thought to be involved in the development of the nervous system.

Neuroblastoma breakpoint family member 19, or NBPF19, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NBPF19 gene. This protein is included in the neuroblastoma breakpoint family of proteins.
The neuroblastoma breaking point family (NBPF) is a family of genes involved in neuronal development. The family is highly specific to primates, with minimal similarity or presence in other mammals and no presence in other animals, and its genes' content has been subject to a very high number of duplications in humans. It was described by Vandepoele et al. in 2005 and named as such because NBPF1 was found to be broken by a chromosomal translocation in a neuroblastoma patient.
















