
The Semi-Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE) was a system of large computers and associated networking equipment that coordinated data from many radar sites and processed it to produce a single unified image of the airspace over a wide area. SAGE directed and controlled the NORAD response to a possible Soviet air attack, operating in this role from the late 1950s into the 1980s. Its enormous computers and huge displays remain a part of cold war lore, and after decommissioning were common props in movies such as Dr. Strangelove and Colossus, and on science fiction TV series such as The Time Tunnel.

The RCA 474L Ballistic Missile Early Warning System was a United States Air Force Cold War early warning radar, computer, and communications system, for ballistic missile detection. The network of twelve radars, which was constructed beginning in 1958 and became operational in 1961, was built to detect a "mass ballistic missile attack launched on northern approaches [for] 15 to 25 minutes' warning time" also provided Project Space Track satellite data.

The AN/FSQ-7 Combat Direction Central, referred to as the Q7 for short, was a computerized command and control system for Cold War ground-controlled interception used in the USAF Semi-Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE) air defense network.

The Southeast Air Defense Sector (SEADS), was a unit of the US Air Force located at Tyndall Air Force Base near Panama City, Florida. It provided air defense and surveillance of the southeastern region of the US. SEADS closed in winter 2005, giving up surveillance and control of their airspace to the Eastern Air Defense Sector (EADS) and the former Northeast Air Defense Sector (NEADS).

Aerospace Defense Command was a major command of the United States Air Force, responsible for continental air defense. It was activated in 1968 and disbanded in 1980. Its predecessor, Air Defense Command, was established in 1946, briefly inactivated in 1950, reactivated in 1951, and then redesignated Aerospace rather than Air in 1968. Its mission was to provide air defense of the Continental United States (CONUS). It directly controlled all active measures, and was tasked to coordinate all passive means of air defense.

Ground Equipment Facility J-33 is a Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) radar station of the Joint Surveillance System's Western Air Defense Sector (WADS) with an Air Route Surveillance Radar (ARSR-4). The facility was previously a USAF general surveillance radar station during the Cold War.

The 26th Air Division is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with Air Defense Tactical Air Command, assigned to First Air Force, being stationed at March Air Force Base, California. It was inactivated on 30 September 1990.
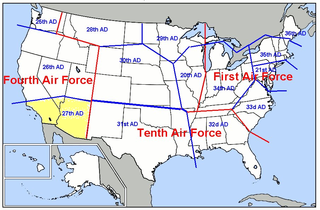
The 27th Air Division was a United States Air Force numbered air division and the geographic Air Defense Command region controlled by the 27th AD. Its last assignment was with Air Defense Command (ADC)'s Tenth Air Force, at Luke Air Force Base, Arizona. It was inactivated on 19 November 1969.
Thomasville Air Force Station is a closed United States Air Force General Surveillance Radar station. It is located 1.9 miles (3.1 km) north-northwest of Thomasville, Alabama. It was closed in 1969.
The SAGE radar stations of Air Defense Command were the military installations operated by USAF squadrons using the 1st automated air defense environment and networked by the SAGE System, a computer network. Most of the radar stations used the Burroughs AN/FST-2 Coordinate Data Transmitting Set (CDTS) to automate the operator environment and provide radar tracks to sector command posts at SAGE Direction Centers (DCs), e.g., the Malmstrom Z-124 radar station was co-located with DC-20. The sector/division radar stations were networked by DCs and Manual Control Centers to provide command, control, and coordination for ground-controlled interception of enemy aircraft by interceptors such as the F-106 developed to work with the SAGE System.
Oakdale Air Force Station is a United States Air Force General Surveillance Radar station. It is located 1.3 miles (2.1 km) east of the Pittsburgh suburb of Oakdale, Pennsylvania. It was closed in 1969.
Omaha Air Force Station is a closed United States Air Force General Surveillance Radar station. It is located 7.5 miles (12.1 km) north of Omaha, Nebraska. It was closed in 1968.
Olathe Air Force Station is a former United States Air Force radar station that was located in Gardner, Kansas. It was located next to Naval Air Station Olathe, now the grounds of New Century AirCenter.
The Martin AN/FSG-1 Antiaircraft Defense System, better known as Missile Master, was an electronic fire distribution center to computerize Cold War air defense (AD) command posts from manual plotting board operations to automated command and control of remote surface-to-air missile (SAM) launch batteries. The 10 United States Army C3 systems used radar netting ("electronic umbrella") at Missile Master military installations for coordinating ground-controlled interception by Nike and MIM-23 Hawk missiles. The vacuum tube fire control logic reduced the time to designate the appropriate missile battery to launch if an enemy target had intruded into a defense area where an AN/FSG-1 system was deployed.
The Permanent System was a 1950s radar network used for the CONUS "manual air defense system" and which had a USAF aircraft control and warning (AC&W) organization of personnel and military installations with radars to allow Air Defense Command ground-controlled interception of Cold War bombers attacking the United States.

The Fort Heath radar station was a USAF radar site and US Army Missile Master installation of the joint-use site system (JUSS) for North American Air Defense at a former coastal defense site. The Cold War radar station had 2 USAF AN/FPS-6B height finding radars, 2 Army AN/FPS-6A height finders, an FAA ARSR-1 radar emplaced 1958-9, and an Army nuclear bunker. Arctic Towers were the pedestals for the FPS antennas and radomes, while the Air Route Surveillance Radar was on a 50-foot extension temperate tower adjacent to the Federal Aviation Administration building.
The GE AN/GPA-37 Course Directing Group was a USAF Cold War air defense command, control, and coordination system for weapons direction. During Air Defense Command's "Control Capability Improvement Program" to improve command guidance of manned aircraft, the AN/GPA-37 was "developed by the General Electric Heavy Military Electronic Equipment Department at Syracuse in conjunction with...Rome Air Development Center and the Electronics Research Laboratories of Columbia University." Used to process radar data, the system was to "track a potential enemy aircraft and direct intercepters [sic] into a position from which they can make their automatic firing runs", the system included the:
An Air Defense Direction Center (ADDC) was a type of United States command post for assessing Cold War radar tracks, assigning height requests to available height-finder radars, and for "Weapons Direction": coordinating command guidance of aircraft from more than 1 site for ground-controlled interception. As with the World War II Aircraft Warning Service CONUS defense network, a "manual air defense system" was used through the 1950s Along with 182 radar stations at "the end of 1957, ADC operated … 17 control centers", and the Ground Observation Corps was TBD on TBD. With the formation of NORAD, several types of ADDCs were planned by Air Defense Command:

The Denver Air Defense Sector was a United States Air Force geographic area designated during the Cold War for both air defense and air traffic control, as well as the name of the planned military unit for conducting radar surveillance and fighter-interceptor operations in the sector area. The Denver ADS spanned the entire state of Colorado, nearly all of Utah, most of Wyoming and western Nebraska, and small parts of Kansas, Oklahoma, New Mexico, Arizona, and Nevada. Potential targets in the sector included the military/industrial facilities and urban civilian populations of the metropolitan areas at Salt Lake City, Cheyenne, Denver, and Colorado Springs..

Continental Air Defense Command (CONAD) was a Unified Combatant Command of the United States Department of Defense, tasked with air defense for the Continental United States. It comprised Army, Air Force, and Navy components. It included Army Project Nike missiles anti-aircraft defenses and USAF interceptors. The primary purpose of continental air defense during the CONAD period was to provide sufficient attack warning of a Soviet bomber air raid to ensure Strategic Air Command could launch a counterattack without being destroyed. CONAD controlled nuclear air defense weapons such as the 10 kiloton W-40 nuclear warhead on the CIM-10B BOMARC. The command was disestablished in 1975, and Aerospace Defense Command became the major U.S. component of North American Air Defense Command (NORAD).










