
Nephrotic syndrome is a collection of symptoms due to kidney damage. This includes protein in the urine, low blood albumin levels, high blood lipids, and significant swelling. Other symptoms may include weight gain, feeling tired, and foamy urine. Complications may include blood clots, infections, and high blood pressure.
Renal agenesis is a medical condition in which one (unilateral) or both (bilateral) fetal kidneys fail to develop.

Podocytes are cells in Bowman's capsule in the kidneys that wrap around capillaries of the glomerulus. Podocytes make up the epithelial lining of Bowman's capsule, the third layer through which filtration of blood takes place. Bowman's capsule filters the blood, retaining large molecules such as proteins while smaller molecules such as water, salts, and sugars are filtered as the first step in the formation of urine. Although various viscera have epithelial layers, the name visceral epithelial cells usually refers specifically to podocytes, which are specialized epithelial cells that reside in the visceral layer of the capsule.
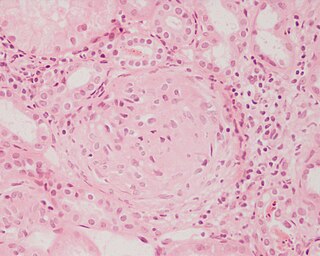
Glomerulonephritis (GN) is a term used to refer to several kidney diseases. Many of the diseases are characterised by inflammation either of the glomeruli or of the small blood vessels in the kidneys, hence the name, but not all diseases necessarily have an inflammatory component.

Membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN) is a slowly progressive disease of the kidney affecting mostly people between ages of 30 and 50 years, usually white people.

Cystinosis is a lysosomal storage disease characterized by the abnormal accumulation of cystine, the oxidized dimer of the amino acid cysteine. It is a genetic disorder that follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. It is a rare autosomal recessive disorder resulting from accumulation of free cystine in lysosomes, eventually leading to intracellular crystal formation throughout the body. Cystinosis is the most common cause of Fanconi syndrome in the pediatric age group. Fanconi syndrome occurs when the function of cells in renal tubules is impaired, leading to abnormal amounts of carbohydrates and amino acids in the urine, excessive urination, and low blood levels of potassium and phosphates.

Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a histopathologic finding of scarring (sclerosis) of glomeruli and damage to renal podocytes. This process damages the filtration function of the kidney, resulting in protein presence in the urine due to protein loss. FSGS is a leading cause of excess protein loss—nephrotic syndrome—in children and adults. Signs and symptoms include proteinuria and edema. Kidney failure is a common long-term complication of the disease. FSGS can be classified as primary, secondary, or genetic, depending on whether a particular toxic or pathologic stressor or genetic predisposition can be identified as the cause. Diagnosis is established by renal biopsy, and treatment consists of glucocorticoids and other immune-modulatory drugs. Response to therapy is variable, with a significant portion of patients progressing to end-stage kidney failure. An American epidemiological study 20 years ago demonstrated that FSGS is estimated to occur in 7 persons per million, with males and African-Americans at higher risk.

Galloway–Mowat syndrome is a very rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder, consisting of a variety of features including hiatal hernia, microcephaly and nephrotic syndrome.
Congenital nephrotic syndrome is a rare kidney disease which manifests in infants during the first 3 months of life, and is characterized by high levels of protein in the urine (proteinuria), low levels of protein in the blood, and swelling. This disease is primarily caused by genetic mutations which result in damage to components of the glomerular filtration barrier and allow for leakage of plasma proteins into the urinary space.

Nephrin is a protein necessary for the proper functioning of the renal filtration barrier. The renal filtration barrier consists of fenestrated endothelial cells, the glomerular basement membrane, and the podocytes of epithelial cells. Nephrin is a transmembrane protein that is a structural component of the slit diaphragm. They are present on the tips of the podocytes as an intricate mesh and convey strong negative charges which repel protein from crossing into the Bowman's space.

The glomerular basement membrane of the kidney is the basal lamina layer of the glomerulus. The glomerular endothelial cells, the glomerular basement membrane, and the filtration slits between the podocytes perform the filtration function of the glomerulus, separating the blood in the capillaries from the filtrate that forms in Bowman's capsule. The glomerular basement membrane is a fusion of the endothelial cell and podocyte basal laminas, and is the main site of restriction of water flow. Glomerular basement membrane is secreted and maintained by podocyte cells.
Podocin is a protein component of the filtration slits of podocytes. Glomerular capillary endothelial cells, the glomerular basement membrane and the filtration slits function as the filtration barrier of the kidney glomerulus. Mutations in the podocin gene NPHS2 can cause nephrotic syndrome, such as focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) or minimal change disease (MCD). Symptoms may develop in the first few months of life or later in childhood.
Nephrocystin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NPHP1 gene.

CD2-associated protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD2AP gene.

Synaptopodin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SYNPO gene.

Kin of IRRE-like protein 1, also known as NEPH1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIRREL gene.
Frasier syndrome is a urogenital anomaly associated with the WT1 gene.
Glomerulocystic kidney disease (GCKD) is a cystic disorder of the kidneys. GCKD involves cystic dilation of Bowman's capsule. It can occur with or without congenital abnormality.

Tetratricopeptide repeat domain 21B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TTC21B gene.
Karl Tryggvason is an Icelandic medical researcher.


















