
The South Pole–Aitken basin is an immense impact crater on the far side of the Moon. At roughly 2,500 km (1,600 mi) in diameter and between 6.2 and 8.2 km (3.9–5.1 mi) deep, it is one of the largest known impact craters in the Solar System. It is the largest, oldest, and deepest basin recognized on the Moon. It is estimated that it was formed approximately 4.2 to 4.3 billion years ago, during the Pre-Nectarian epoch. It was named for two features on opposite sides of the basin: the lunar South Pole at one end and the crater Aitken on the northern end. The outer rim of this basin can be seen from Earth as a huge mountain chain located on the Moon's southern limb, sometimes informally called "Leibnitz mountains".

A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the drainage divide, made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern.
Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as their creating process, shape, elevation, slope, orientation, rock exposure, and soil type.
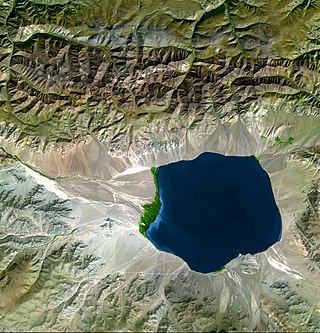
An endorheic basin is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water ; instead, the water drainage flows into permanent and seasonal lakes and swamps that equilibrate through evaporation. Endorheic basins are also called closed basins, terminal basins, and internal drainage systems.

A summit is a point on a surface that is higher in elevation than all points immediately adjacent to it. The topographic terms acme, apex, peak, and zenith are synonymous.

Badwater Basin is an endorheic basin in Death Valley National Park, Death Valley, Inyo County, California, noted as the lowest point in North America and the United States, with a depth of 282 ft (86 m) below sea level. Mount Whitney, the highest point in the contiguous United States, is only 84.6 miles (136 km) to the northwest.
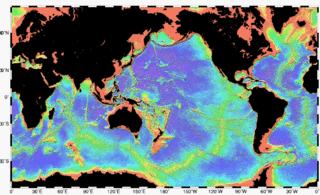
Bathymetry is the study of underwater depth of ocean floors, lake floors, or river floors. In other words, bathymetry is the underwater equivalent to hypsometry or topography. The first recorded evidence of water depth measurements are from Ancient Egypt over 3000 years ago.

In geology, a depression is a landform sunken or depressed below the surrounding area. Depressions form by various mechanisms.

A plunge pool is a deep depression in a stream bed at the base of a waterfall or shut-in. It is created by the erosional forces of cascading water on the rocks at the formation's base where the water impacts. The term may refer to the water occupying the depression, or the depression itself.

The White Tank Mountains are a mountain range in Maricopa County, Arizona. The mountains are on the western periphery of the Phoenix metropolitan area, primarily flanked by the suburban cities of Buckeye to the southwest, and Surprise to the northeast. The mountain range is home to the White Tank Mountain Regional Park and is a regional recreation hub.

The Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA), formerly the Interim Marine and Coastal Regionalisation for Australia, is a biogeographic regionalisation of the oceanic waters of Australia's exclusive economic zone (EEZ). As of 2008, the most recent version is IMCRA Version 4.0.

A lake is an often naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from the ocean, although they may be connected with the ocean by rivers. Most lakes are freshwater and account for almost all the world's surface freshwater, but some are salt lakes with salinities even higher than that of seawater. Lakes vary significantly in surface area and volume of water.

The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission is a satellite altimeter jointly developed and operated by NASA and CNES, the French space agency, in partnership with the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and UK Space Agency (UKSA). The objectives of the mission are to make the first global survey of the Earth's surface water, to observe the fine details of the ocean surface topography, and to measure how terrestrial surface water bodies change over time.

The most conspicuous feature of Mars is a sharp contrast, known as the Martian dichotomy, between the Southern and the Northern hemispheres. The two hemispheres' geography differ in elevation by 1 to 3 km. The average thickness of the Martian crust is 45 km, with 32 km in the northern lowlands region, and 58 km in the southern highlands.

The Noachis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Noachis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-27.

Inverted relief, inverted topography, or topographic inversion refers to landscape features that have reversed their elevation relative to other features. It most often occurs when low areas of a landscape become filled with lava or sediment that hardens into material that is more resistant to erosion than the material that surrounds it. Differential erosion then removes the less resistant surrounding material, leaving behind the younger resistant material, which may then appear as a ridge where previously there was a valley. Terms such as "inverted valley" or "inverted channel" are used to describe such features. Inverted relief has been observed on the surfaces of other planets as well as on Earth. For example, well-documented inverted topographies have been discovered on Mars.
Ledoyom is a term proposed by the Russian geologist Vasily Nekhoroshev for intermontane depressions which might get completely filled by glaciers from the surrounding mountains at the maxima of glaciation.
This glossary of geography terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in geography and related fields, including Earth science, oceanography, cartography, and human geography, as well as those describing spatial dimension, topographical features, natural resources, and the collection, analysis, and visualization of geographic data. It is split across two articles:

The gravity of Mars is a natural phenomenon, due to the law of gravity, or gravitation, by which all things with mass around the planet Mars are brought towards it. It is weaker than Earth's gravity due to the planet's smaller mass. The average gravitational acceleration on Mars is 3.72076 m/s2 and it varies.
















