
Aromatic compounds or arenes usually refers to organic compounds "with a chemistry typified by benzene" and "cyclically conjugated." The word "aromatic" originates from the past grouping of molecules based on odor, before their general chemical properties were understood. The current definition of aromatic compounds does not have any relation to their odor. Aromatic compounds are now defined as cyclic compounds satisfying Hückel's Rule. Aromatic compounds have the following general properties:

A fullerene is an allotrope of carbon whose molecules consist of carbon atoms connected by single and double bonds so as to form a closed or partially closed mesh, with fused rings of five to seven atoms. The molecules may have hollow sphere- and ellipsoid-like forms, tubes, or other shapes.

In chemistry, a hydrogen bond is primarily an electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bonded to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a lone pair of electrons—the hydrogen bond acceptor (Ac). Such an interacting system is generally denoted Dn−H···Ac, where the solid line denotes a polar covalent bond, and the dotted or dashed line indicates the hydrogen bond. The most frequent donor and acceptor atoms are the period 2 elements nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), and fluorine (F).
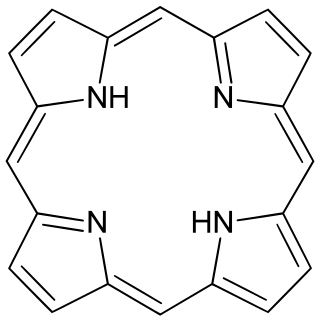
Porphyrins are a group of heterocyclic macrocycle organic compounds, composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at their α carbon atoms via methine bridges (=CH−). In vertebrates, an essential member of the porphyrin group is heme, which is a component of hemoproteins, whose functions include carrying oxygen in the bloodstream. In plants, an essential porphyrin derivative is chlorophyll, which is involved in light harvesting and electron transfer in photosynthesis.

Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a form of phototherapy involving light and a photosensitizing chemical substance used in conjunction with molecular oxygen to elicit cell death (phototoxicity).
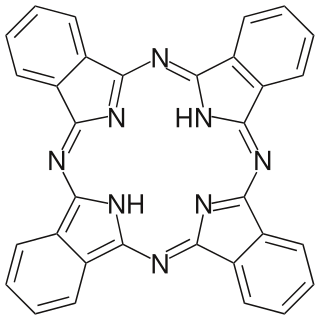
Phthalocyanine is a large, aromatic, macrocyclic, organic compound with the formula (C8H4N2)4H2 and is of theoretical or specialized interest in chemical dyes and photoelectricity.

Transmission Electron Aberration-Corrected Microscope (TEAM) is a collaborative research project between four US laboratories and two companies. The project's main activity is design and application of a transmission electron microscope (TEM) with a spatial resolution below 0.05 nanometers, which is roughly half the size of an atom of hydrogen.

Endohedral fullerenes, also called endofullerenes, are fullerenes that have additional atoms, ions, or clusters enclosed within their inner spheres. The first lanthanum C60 complex called La@C60 was synthesized in 1985. The @ (at sign) in the name reflects the notion of a small molecule trapped inside a shell. Two types of endohedral complexes exist: endohedral metallofullerenes and non-metal doped fullerenes.

Borazine, also known as borazole, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula B3H6N3. In this cyclic compound, the three BH units and three NH units alternate. The compound is isoelectronic and isostructural with benzene. For this reason borazine is sometimes referred to as “inorganic benzene”. Like benzene, borazine is a colourless liquid with an aromatic odor.
In chemistry, a non-covalent interaction differs from a covalent bond in that it does not involve the sharing of electrons, but rather involves more dispersed variations of electromagnetic interactions between molecules or within a molecule. The chemical energy released in the formation of non-covalent interactions is typically on the order of 1–5 kcal/mol. Non-covalent interactions can be classified into different categories, such as electrostatic, π-effects, van der Waals forces, and hydrophobic effects.
In the context of chemistry, molecular physics, physical chemistry, and molecular modelling, a force field is a computational model that is used to describe the forces between atoms within molecules or between molecules as well as in crystals. Force fields are a variety of interatomic potentials. More precisely, the force field refers to the functional form and parameter sets used to calculate the potential energy of a system on the atomistic level. Force fields are usually used in molecular dynamics or Monte Carlo simulations. The parameters for a chosen energy function may be derived from classical laboratory experiment data, calculations in quantum mechanics, or both. Force fields utilize the same concept as force fields in classical physics, with the main difference being that the force field parameters in chemistry describe the energy landscape on the atomistic level. From a force field, the acting forces on every particle are derived as a gradient of the potential energy with respect to the particle coordinates.

Pentacene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of five linearly-fused benzene rings. This highly conjugated compound is an organic semiconductor. The compound generates excitons upon absorption of ultra-violet (UV) or visible light; this makes it very sensitive to oxidation. For this reason, this compound, which is a purple powder, slowly degrades upon exposure to air and light.
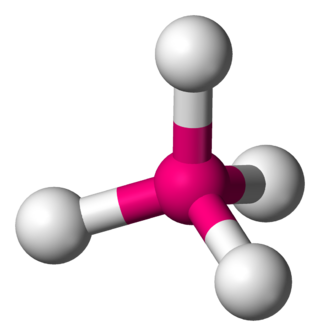
In a tetrahedral molecular geometry, a central atom is located at the center with four substituents that are located at the corners of a tetrahedron. The bond angles are cos−1(−1⁄3) = 109.4712206...° ≈ 109.5° when all four substituents are the same, as in methane as well as its heavier analogues. Methane and other perfectly symmetrical tetrahedral molecules belong to point group Td, but most tetrahedral molecules have lower symmetry. Tetrahedral molecules can be chiral.

A molecular solid is a solid consisting of discrete molecules. The cohesive forces that bind the molecules together are van der Waals forces, dipole–dipole interactions, quadrupole interactions, π–π interactions, hydrogen bonding, halogen bonding, London dispersion forces, and in some molecular solids, coulombic interactions. Van der Waals, dipole interactions, quadrupole interactions, π–π interactions, hydrogen bonding, and halogen bonding are typically much weaker than the forces holding together other solids: metallic, ionic, and network solids. Intermolecular interactions typically do not involve delocalized electrons, unlike metallic and certain covalent bonds. Exceptions are charge-transfer complexes such as the tetrathiafulvane-tetracyanoquinodimethane (TTF-TCNQ), a radical ion salt. These differences in the strength of force and electronic characteristics from other types of solids give rise to the unique mechanical, electronic, and thermal properties of molecular solids.
In chemistry, a halogen bond (XB) occurs when there is evidence of a net attractive interaction between an electrophilic region associated with a halogen atom in a molecular entity and a nucleophilic region in another, or the same, molecular entity. Like a hydrogen bond, the result is not a formal chemical bond, but rather a strong electrostatic attraction. Mathematically, the interaction can be decomposed in two terms: one describing an electrostatic, orbital-mixing charge-transfer and another describing electron-cloud dispersion. Halogen bonds find application in supramolecular chemistry; drug design and biochemistry; crystal engineering and liquid crystals; and organic catalysis.
Inelastic electron tunneling spectroscopy (IETS) is an experimental tool for studying the vibrations of molecular adsorbates on metal oxides. It yields vibrational spectra of the adsorbates with high resolution (< 0.5 meV) and high sensitivity (< 1013 molecules are required to provide a spectrum). An additional advantage is the fact that optically forbidden transitions may be observed as well. Within IETS, an oxide layer with molecules adsorbed on it is put between two metal plates. A bias voltage is applied between the two contacts. An energy diagram of the metal-oxide-metal device under bias is shown in the top figure. The metal contacts are characterized by a constant density of states, filled up to the Fermi energy. The metals are assumed to be equal. The adsorbates are situated on the oxide material. They are represented by a single bridge electronic level, which is the upper dashed line. If the insulator is thin enough, there is a finite probability that the incident electron tunnels through the barrier. Since the energy of the electron is not changed by this process, it is an elastic process. This is shown in the left figure.
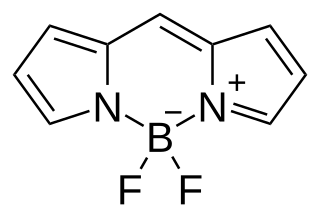
BODIPY is the technical common name of a chemical compound with formula C
9H
7BN
2F
2, whose molecule consists of a boron difluoride group BF
2 joined to a dipyrromethene group C
9H
7N
2; specifically, the compound 4,4-difluoro-4-bora-3a,4a-diaza-s-indacene in the IUPAC nomenclature. The common name is an abbreviation for "boron-dipyrromethene". It is a red crystalline solid, stable at ambient temperature, soluble in methanol.

Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon.

In organic chemistry, contorted aromatics, or more precisely contorted polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, are polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in which the fused aromatic molecules deviate from the usual planarity.

















