
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearings or bushings are provided at the mounting points where the axle is supported. In the latter case, a bearing or bushing sits inside a central hole in the wheel to allow the wheel or gear to rotate around the axle. Sometimes, especially on bicycles, the latter type of axle is referred to as a spindle.
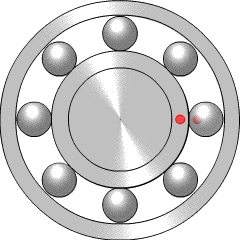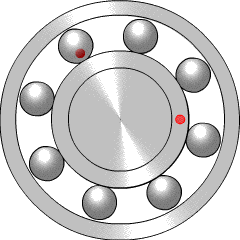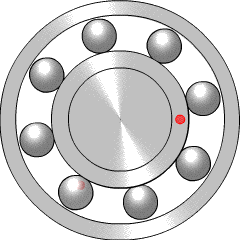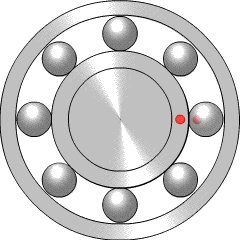
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races.
Fluid bearings are bearings in which the load is supported by a thin layer of rapidly moving pressurized liquid or gas between the bearing surfaces. Since there is no contact between the moving parts, there is no sliding friction, allowing fluid bearings to have lower friction, wear and vibration than many other types of bearings. Thus, it is possible for some fluid bearings to have near-zero wear if operated correctly.

A bearing is a machine element that constrains relative motion to only the desired motion and reduces friction between moving parts. The design of the bearing may, for example, provide for free linear movement of the moving part or for free rotation around a fixed axis; or, it may prevent a motion by controlling the vectors of normal forces that bear on the moving parts. Most bearings facilitate the desired motion by minimizing friction. Bearings are classified broadly according to the type of operation, the motions allowed, or the directions of the loads (forces) applied to the parts.

Inline speed skating is the roller sport of racing on inline skates. The sport may also be called inline racing by participants. Although it primarily evolved from racing on traditional roller skates, the sport is similar enough to ice speed skating that many competitors are known to switch between inline and ice speed skating according to the season.

The bottom bracket on a bicycle connects the crankset (chainset) to the bicycle and allows the crankset to rotate freely. It contains a spindle to which the crankset attaches, and the bearings that allow the spindle and crankset to rotate. The chainrings and pedals attach to the cranks. Bottom bracket bearings fit inside the bottom bracket shell, which connects the seat tube, down tube and chain stays as part of the bicycle frame.

A plain bearing, or more commonly sliding contact bearing and slide bearing, is the simplest type of bearing, comprising just a bearing surface and no rolling elements. Therefore, the journal slides over the bearing surface. The simplest example of a plain bearing is a shaft rotating in a hole. A simple linear bearing can be a pair of flat surfaces designed to allow motion; e.g., a drawer and the slides it rests on or the ways on the bed of a lathe.

In mechanical engineering, a rolling-element bearing, also known as a rolling bearing, is a bearing which carries a load by placing rolling elements between two concentric, grooved rings called races. The relative motion of the races causes the rolling elements to roll with very little rolling resistance and with little sliding.

A thrust bearing is a particular type of rotary bearing. Like other bearings they permanently rotate between parts, but they are designed to support a predominantly axial load.

In the context of an internal combustion engine, a rocker arm is a valvetrain component that typically transfers the motion of a pushrod to the corresponding intake/exhaust valve.

Tapered roller bearings are rolling element bearings that can support axial forces as well as radial forces.
A linear-motion bearing or linear slide is a bearing designed to provide free motion in one direction. There are many different types of linear motion bearings.
Brinelling is the permanent indentation of a hard surface. It is named after the Brinell scale of hardness, in which a small ball is pushed against a hard surface at a preset level of force, and the depth and diameter of the mark indicates the Brinell hardness of the surface. Brinelling is permanent plastic deformation of a surface, and usually occurs while two surfaces in contact are stationary and the material yield strength has been exceeded.

To "slew" means to turn without change of place.
In mechanical engineering, a cam follower, also known as a track follower, is a specialized type of roller or needle bearing designed to follow cam lobe profiles. Cam followers come in a vast array of different configurations, however the most defining characteristic is how the cam follower mounts to its mating part; stud style cam followers use a stud while the yoke style has a hole through the middle.

The yaw bearing is the most crucial and cost intensive component of a yaw system found on modern horizontal axis wind turbines. The yaw bearing must cope with enormous static and dynamic loads and moments during the wind turbine operation, and provide smooth rotation characteristics for the orientation of the nacelle under all weather conditions. It has also to be corrosion and wear resistant and extremely long lasting. It should last for the service life of the wind turbine) while being cost effective.
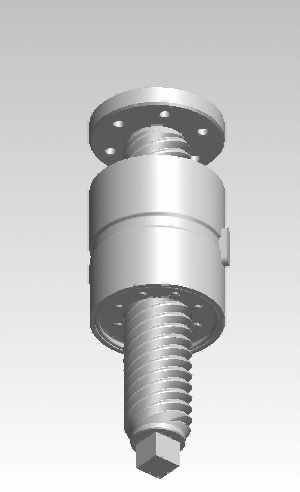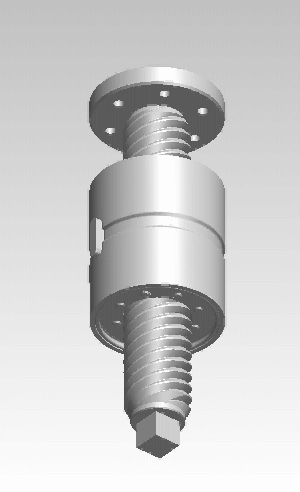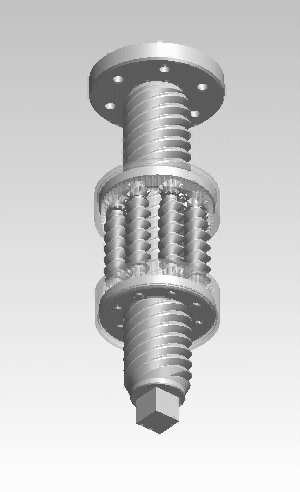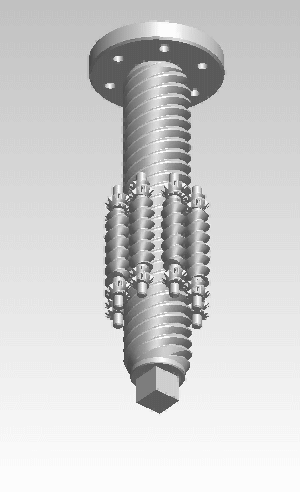
A roller screw, also known as a planetary roller screw or satellite roller screw, is a low-friction precision screw-type actuator, a mechanical device for converting rotational motion to linear motion, or vice versa. Planetary roller screws are used as the actuating mechanism in many electro-mechanical linear actuators. Due to its complexity the roller screw is a relatively expensive actuator, but may be suitable for high-precision, high-speed, heavy-load, long-life and heavy-use applications.

NTN Corporation is one of the most prominent manufacturers of bearings in Japan, second domestically only to NSK Ltd. The company is one of the largest exporters worldwide of friction-reducing products such as constant-velocity joints.
A tunnel crankcase, tunnel crankshaft or disc-webbed crankshaft engine is a design feature of a diesel engine or petrol engine where the crankshaft is designed so that the main bearings are enlarged in diameter, such that they are now larger than the crank webs. They thus form the largest diameter of any part of the crankshaft. Rather than a conventional crankcase that has webs across it to support the narrow bearings of a conventional crankcase, the crankcase now has a large tunnel through it, hence the name.

Air bearings are bearings that use a thin film of pressurized gas to provide a low friction load-bearing interface between surfaces. The two surfaces do not touch, thus avoiding the traditional bearing-related problems of friction, wear, particulates, and lubricant handling, and offer distinct advantages in precision positioning, such as lacking backlash and static friction, as well as in high-speed applications. Space craft simulators now most often use air bearings and 3-D printers are now used to make air-bearing-based attitude simulators for CubeSat satellites.















