Gildone is a hill town and comune in the province of Campobasso, in the Molise region. At its peak, the town consisted of 3,000 inhabitants, but the population now numbers about 750. The town is in a rural area surrounded by farms dotted with olive trees and sheep, and is located about 15 minutes southeast of the city of Campobasso.

Lauria is a town and comune of the province of Potenza, in Basilicata, southern Italy, situated near the borders of Calabria. It is a walled, medieval town on the steep side of a hill, with another portion of municipal territory in the plain below.

Moliterno is a town and comune in the province of Potenza, in the southern Italian region of Basilicata. It is bounded by the comuni of Castelsaraceno, Grumento Nova, Lagonegro, Lauria, Montesano sulla Marcellana, Sarconi, Tramutola.

Montescaglioso is a town and comune in the Province of Matera, Basilicata, southern Italy.

San Mauro Forte is a town and comune in the province of Matera, in the Southern Italian region of Basilicata.

Lagonegro is a town and comune in the province of Potenza, in the Southern Italy region of Basilicata. It is part of the Valle del Noce and has (2017) a population of 5,471.

Maratea is an Italian town and comune of Basilicata, in the province of Potenza. It is the only comune of the region on the Tyrrhenian coast, and is known as "the Pearl of the Tyrrhenian". Owing to the considerable number of its churches and chapels it has also been described as "the town with 44 churches". It is one of I Borghi più belli d'Italia.

Rivello is a town and comune in the province of Potenza, in the Southern Italian region of Basilicata. The population was 2,515 as of March 2024.

Teana is a town and comune in the province of Potenza, in the southern Italian region of Basilicata.

Montesano sulla Marcellana is a town and comune of the province of Salerno in the Campania region of south-west Italy.
Carosino is a town and comune in the province of Taranto, in the northern Salento, part of the Apulia region of southeast Italy. Carosino was historically an Arbëreshë settlement. Its economy is based on the production of wine, olive oil and grapes.

Riccia is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Campobasso in the Italian region of Molise, located about 15 kilometres (9 mi) southeast of Campobasso, with a population of about 5,600.

Santa Maria la Carità is a comune (municipality) of 11,617 inhabitants in the Metropolitan City of Naples, in the Italian region of Campania, located about 25 kilometres (16 mi) southeast of Naples. It is situated in the Stabiae-Vesuvian plain, in the Sarno valley.

Cilento is an Italian geographical region of Campania in the central and southern part of the province of Salerno and an important tourist area of southern Italy.

Santa Maria di Castellabate is a southern Italian town and hamlet (frazione) of Castellabate, a municipality in the province of Salerno, Campania. It is the most populated frazione of its comune and the seat of the town hall building.

Tortorella is a town and comune of the province of Salerno, Campania, in south-western Italy.

Our Lady of Graces or Saint Mary of Graces is a devotion to the Virgin Mary in the Roman Catholic Church. Several churches with this dedication often owe their foundation to thankfulness for graces received from the Virgin Mary, and are particularly numerous in Italy, India, Australia, United States, Portugal, France and the Italian-speaking region of Switzerland. Also it is related to the Marian apparitions in which was revealed the Miraculous Medal, also known as the Medal of Our Lady of Graces.
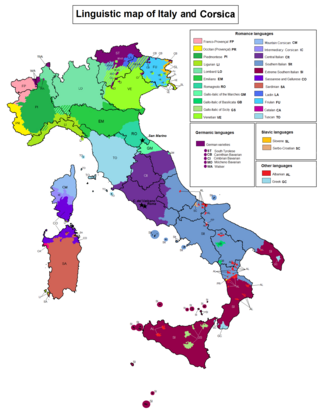
The Gallo-Italic of Basilicata is a group of Gallo-Italic dialects found in Basilicata in southern Italy, that could date back to migrations from Northern Italy during the time of the Normans.

San Rocco is a Roman Catholic church located in the city of Potenza in the region of Basilicata, Italy.

Lake Sirino is a small natural reservoir in Basilicata located in a karst sinkhole at the foot of the mountain of the same name, in the municipality of Nemoli, at an altitude of 788 meters above sea level.






















