The Nerii were an ancient Gallaecian Celtic tribe, living in the north of modern Galicia, in the Costa da Morte region. Celtici Nerii are mentioned for the first time on a tombstone on the grave of a Galician nerio called Tássionos, in a Tartessian inscription from the Bronze Age.

Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia, northern Portugal, Asturias and Leon and the later Suebic Kingdom of Gallaecia. The Roman cities included the port Cale (Porto), the governing centers Bracara Augusta (Braga), Lucus Augusti (Lugo) and Asturica Augusta (Astorga) and their administrative areas Conventus bracarensis, Conventus lucensis and Conventus asturicensis.

The Celts are an Indo-European ethnolinguistic group of Europe identified by their use of Celtic languages and cultural similarities. The history of pre-Celtic Europe and the exact relationship between ethnic, linguistic and cultural factors in the Celtic world remains uncertain and controversial. The exact geographic spread of the ancient Celts is disputed; in particular, the ways in which the Iron Age inhabitants of Great Britain and Ireland should be regarded as Celts have become a subject of controversy. According to one theory, the common root of the Celtic languages, the Proto-Celtic language, arose in the Late Bronze Age Urnfield culture of Central Europe, which flourished from around 1200 BC.

Galicia is an autonomous community of Spain and historic nationality under Spanish law. Located in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula, it comprises the provinces of A Coruña, Lugo, Ourense and Pontevedra, being bordered by Portugal to the south, the Spanish autonomous communities of Castile and León and Asturias to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and the Cantabrian Sea to the north. It had a population of 2,718,525 in 2016 and has a total area of 29,574 km2 (11,419 sq mi). Galicia has over 1,660 km (1,030 mi) of coastline, including its offshore islands and islets, among them Cíes Islands, Ons, Sálvora, Cortegada, and—the largest and most populated—A Illa de Arousa.
[J.1.1] ‘Fonte Velha 6’ lokooboo niiraboo too araiai kaaltee lokoo|n ane narkee kaakiisiin|koolobo|o ii te’-e.ro-baar|e(be)e tea|siioonii ‘invoking the Lugoues of the Neri people, for a nobleman of the Celtae/Galtai Galicia: he rests still within; invoking every hero, the grave of Tasiioonos has received him.’ See John T. Koch A Case For Tartessian as a Celtic Language. ActPal X = PalHisp 9, 344.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
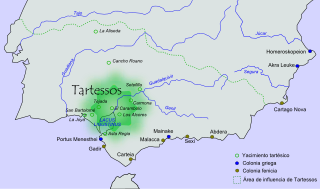
Tartessos or Tartessus, was a semi-mythical harbor city and the surrounding culture on the south coast of the Iberian Peninsula, at the mouth of the Guadalquivir River. Greeks believed that European civilization began in Tartessos. It appears in sources from Greece and the Near East starting during the first millennium BC. Herodotus, for example, describes it as beyond the Pillars of Heracles. Roman authors tend to echo the earlier Greek sources but from around the end of the millennium there are indications that the name Tartessos had fallen out of use and the city may have been lost to flooding, though several authors attempt to identify it with cities of other names in the area. Archaeological discoveries in the region have built up a picture of a more widespread culture, identified as Tartessian, that includes some 97 inscriptions in a Tartessian language.

The Lusitanians were an Indo-European people living in the west of the Iberian Peninsula, where Portugal is located nowadays, prior the conquest by the Roman Republic and the subsequent incorporation of the territory into the Roman province of Lusitania.

The Cynetes or Conii were one of the pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula, living in today's Algarve and Lower Alentejo regions of southern Portugal, and the southern part of Badajoz and the northwestern portions of Córdoba and Ciudad Real provinces in Spain before the 6th century BCE.

The Celtici were a Celtic tribe or group of tribes of the Iberian peninsula, inhabiting three definite areas: in what today are the regions of Alentejo and the Algarve in Portugal; in the Province of Badajoz and north of Province of Huelva in Spain, in the ancient Baeturia; and along the coastal areas of Galicia. Classical authors give various accounts of the Celtici's relationships with the Gallaeci, Celtiberians and Turdetani.
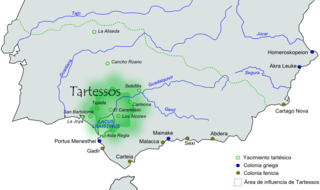
The Tartessian language is the extinct Paleohispanic language of inscriptions in the Southwestern script found in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula: mainly in the south of Portugal, and the southwest of Spain. There are 95 of these inscriptions, the longest having 82 readable signs. Around one-third of them were found in Early Iron Age necropolises or other Iron Age burial sites associated with rich complex burials. It is usual to date them to the 7th century BC and consider the southwestern script to be the most ancient Paleohispanic script, with characters most closely resembling specific Phoenician letter forms found in inscriptions dated to c. 825 BC. Five of the inscriptions occur on stelae with what has been interpreted as Late Bronze Age carved warrior gear from the Urnfield culture.

Galicians are a national, cultural and ethnic group whose historic homeland is Galicia, in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. Two Romance languages are widely spoken and official in Galicia: the native Galician and, mainly because of language shift, Castilian.

The prehistory of the Iberian Peninsula begins with the arrival of the first hominins 1.2 million years ago and ends with the Punic Wars, when the territory enters the domains of written history. In this long period, some of its most significant landmarks were to host the last stand of the Neanderthal people, to develop some of the most impressive Paleolithic art, alongside southern France, to be the seat of the earliest civilizations of Western Europe and finally to become a most desired colonial objective due to its strategic position and its many mineral riches.

The Paleohispanic languages were the languages of the Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula, excluding languages of foreign colonies, such as Greek in Emporion and Phoenician in Qart Hadast. After the Roman conquest of Hispania the Paleohispanic languages, with the exception of Proto-Basque, were replaced by Latin, the ancestor of the modern Iberian Romance languages.
Gallaecian, or Northwestern Hispano-Celtic, is an extinct Celtic language and was one of the Hispano-Celtic languages. It was spoken at the beginning of the 1st millennium in the northwest corner of the Iberian Peninsula that became the Roman province of Gallaecia and is now divided between the modern regions of Galicia, Norte Region, Portugal, western Asturias, and the Province of León, in Spain.
The Namarini were an ancient Gallaecian Celtic tribe, living in the north of modern Galicia, in the Foz's county.
The Capori were an ancient Gallaecian Celtic tribe, living in the west of modern Galicia, in the Padrón's county.
The Celtici Praestamarici were an ancient Gallaecian Celtic tribe, living in the west of modern Galicia, in the Barbanza's county.
The Louguei were an ancient Gallaecian Celtic tribe, living in the east of modern Galicia, in the Ancares's county.
The Seurri were an ancient Gallaecian Celtic tribe, living in the center-east of modern Galicia, in the Sarria's county.
This section of the timeline of Iberian history concerns events from before the Carthaginian conquests.









