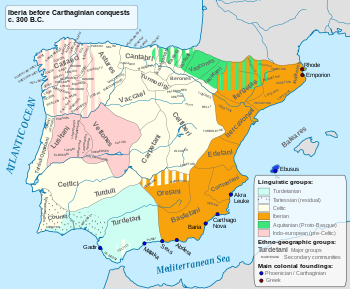
The Turboletae or Turboleti (Greek: Torboletoi or Torboletes) [1] [2] were an obscure pre-Roman people from ancient Spain, which lived in the northwest Teruel province since the early 3rd Century BC.

The Turboletae or Turboleti (Greek: Torboletoi or Torboletes) [1] [2] were an obscure pre-Roman people from ancient Spain, which lived in the northwest Teruel province since the early 3rd Century BC.
Their ethnical and linguistical affiliation is difficult to determine, though it seems that they were of part-Celtic, part-Illyrian ancestry, being confused by some ancient authors with either the Iberian Turdetani of Baetica [3] or the Turduli. [4] [5]
Their capital was the town of Turda, Turba, Turbola or Turbula, [6] [7] [8] whose precise location is unknown, with some archeologists tentatively placing it at the Iron Age site of Alto Chácon (Muela de San Juan), in the vicinity of modern Teruel. [9] No other pre-Roman sites connected with this people have been identified though recent archeological surveys at some Iron Age settlements in the Teruel region show that they were culturally affiliated with the Celtiberians. It has also been attributed to them the celtiberian inscription of Peñalva de Villastar. [10]
A warlike people whose tribal name later became a byword for unruly behaviour, the Turboletae were a constant source of trouble to most of their neighbours. Not only they harassed the Celtiberian Belli and Titii, but also raided the southeastern Iberian peoples throughout most of the 3rd century BC, in particularly the Edetanian city-state of Saguntum. [11] As allies of Carthage the Turboletae actively participated in the incident that triggered the Second Punic War, [12] the siege of Saguntum in 219-218 BC, where they assisted the Carthaginian troops in the final assault and looting of the city, slaughtering a great deal of its inhabitants. The backlash came in 212 BC when the Romans and their Edetani allies invaded Turboletania, seized the capital Turba and razed it to the ground, selling his residents to slavery. [13]
In 205 BC the exhausted Turboletae sued for peace, on which the Roman Senate forced them to pay a huge compensation to the surviving citizens of Saguntum. However, the resentment fuelled by the heavy tribute imposed, coupled with the destruction of their capital city in the previous years may account for the Tuboletae revolt of 196 BC, under the apparent leadership of two generals named Budares and Baesadines. [14] [15] After being crushed by Quintus Minucius Thermus, Praetor of Hispania Citerior in a pitched battle near the ruins of Turba, [16] [17] the remaining Turboletae population appears to have been either obliterated or simply reduced to subject status and their devastated lands divided among the Bastetani and Edetani, resulting in their total disappearance from the historical record.

The Cantabri or Ancient Cantabrians were a pre-Roman people and large tribal federation that lived in the northern coastal region of ancient Iberia in the second half of the first millennium BC. These peoples and their territories were incorporated into the Roman Province of Hispania Tarraconensis in 19 BC, following the Cantabrian Wars.

The Vaccaei or Vaccei were a pre-Roman Celtic people of Spain, who inhabited the sedimentary plains of the central Duero valley, in the Meseta Central of northern Hispania.

The Oretani or Oretanii were a pre-Roman ancient Iberian people of the Iberian Peninsula, that lived in northeastern Andalusia, in the upper Baetis (Guadalquivir) river valley, eastern Marianus Mons, and the southern area of present-day La Mancha.

The Edetani were an ancient Iberian (Pre-Roman) people of the Iberian Peninsula. They are believed to have spoken a form of the Iberian language.

The Lusones were an ancient Celtiberian (Pre-Roman) people of the Iberian Peninsula, who lived in the high Tajuña River valley, northeast of Guadalajara. They were eliminated by the Romans as a significant threat in the end of the 2nd century BC.
Marcus Fabius Buteo was a Roman politician during the 3rd century BC. He served as consul in 245 BC, and as censor, and in 216 BC, being the oldest living ex-censor, he was appointed dictator, legendo senatui, for the purpose of filling vacancies in the senate after the Battle of Cannae. He was appointed by the consul Varro, and, with M. Junius Pera, he was the only dictator to serve a simultaneous term with another. He resigned from the post immediately after he revised the censors' lists and enrolled the new Senate members.

The Carpetani, also named Karpesioi by Polybius, were one of the Celtic peoples inhabiting the Iberian Peninsula prior to the Roman conquest. Their core domain was constituted by the lands between the Tagus and the Anas, in the southern Meseta. Agriculture is thought to have had a greater importance in the Carpetanian economy than other neighboring peoples'.

The Arevaci or Aravaci, were a Celtic people who settled in the central Meseta of northern Hispania and dominated most of Celtiberia from the 4th to late 2nd centuries BC. The Vaccaei were their allies.

The Lobetani, were a small pre-Roman Iberian people of ancient Spain mentioned only once by Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD, situated around the mountainous Albarracín area of the southwest Province of Teruel.

The Olcades were an ancient stock-raising pre-Roman people from Hispania, who lived to the west of the Turboletae in the southeastern fringe of the Iberian system mountains.

The Germani were an obscure pre-Roman ancient people of the Iberian Peninsula which settled around the 4th century BC in western Oretania, an ancient region corresponding to the south of Ciudad Real and the eastern tip of Badajoz provinces.

The Berones were a pre-Roman Celtic people of ancient Spain, although they were not part of the Celtiberians. They lived north of the latter and close to the Cantabrian Conisci in the middle Ebro region between the Tirón and Alhama rivers.

The Titii or Tithii were a small and obscure Celtiberian people, whose lands were located along the middle Jalón and upper Tajuña valleys, somewhere between Alhama de Aragón in Zaragoza and Molina de Aragón in Guadalajara provinces.

The Pellendones, also designated Pelendones Celtiberorum and Cerindones, were an ancient pre-Roman Celtic people living on the Iberian Peninsula. From the early 4th century BC they inhabited the region near the source of the river Duero in what today is north-central Spain, an area comprising the north of Soria, the southeast of Burgos and the southwest of La Rioja provinces.

The Belli, also designated Beli or Belaiscos, were an ancient pre-Roman Celtic Celtiberian people who lived in the modern Spanish province of Zaragoza from the 3rd Century BC.

The Uraci or Duraci were a little-known Celtic people of pre-Roman Iberia who dwelt to the east of the Vaccaei and the Carpetani, occupying the southern Soria, northern Guadalajara and western Zaragoza provinces since the 4th century BC.

The Cratistii were an ancient pre-Roman, stock-raising people whose lands were situated along the upper Tagus valley, in the elevated plateau region of the western Cuenca and northeast Province of Teruel.
This section of the timeline of Hispania concerns Spanish and Portuguese history events from the Carthaginian conquests to before the barbarian invasions.

The Bergistani or Bargusii,, were an ancient Iberian or Pre-Roman people of the Iberian Peninsula. They were related to the Ilergetes and were not numerous. They inhabited the valley of the Saiarra river in the upper course of the Llobregat in the northern Tarraconense.
The Celtiberian confederacy was a tribal federation formed around the mid-3rd century BC, by the Arevaci, Lusones, Belli and Titii, with the Arevacian city of Numantia as the confederate capital.