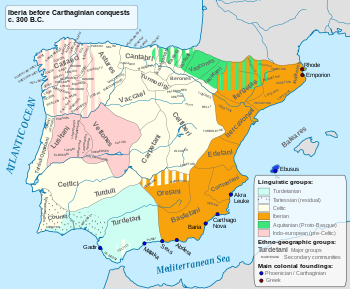
The Bardili were a small, pre-Roman tribe of the Iberian Peninsula, and an offshoot of the widespread Turduli people, who lived in what is now southwestern Portugal in the 5th-1st centuries BC.

The Bardili were a small, pre-Roman tribe of the Iberian Peninsula, and an offshoot of the widespread Turduli people, who lived in what is now southwestern Portugal in the 5th-1st centuries BC.
Migrating in conjunction with the Celtici, [1] [2] [3] they settled the present Setúbal peninsula along the Tagus river mouth and the lower Sardum [4] (Sado; Kallipos in the Greek sources [5] ) river valley around the 5th Century BC, where they founded several coastal towns. The exact location of the Bardili capital Bardo remains uncertain, though the towns of Equabona/Aquabona (Coina-a-Velha), Caetobriga/Cetobriga (Monte da Rotura, near Setúbal) and Salacia (Alcácer do Sal; Iberian-type mint: Ketuvion) have all been identified. [6]
In the mid-3rd century BC the Bardili were forced to acknowledge the suzerainty of Carthage at the latter part of the century. However, their history after the Second Punic War is unclear; they seem to have played no role in the Lusitanian Wars and subsequent conflicts during the 2nd-1st Centuries BC. It is almost certain that the Bardili recovered their independence, which they enjoyed for nearly a century before being included into Hispania Ulterior province by the Praetor Publius Licinius Crassus in the wake of his campaign against the Lusitani and Celtici in 93 BC. [7] Later during the Sertorian Wars in 79 BC, Proconsul Quintus Caecilius Metellus Pius established a permanent military base at Caeciliana (near Setúbal), in order to prevent the Bardili from lending their support to Quintus Sertorius. [8]
Increasingly Romanized after the Ulterior Propraetor Julius Caesar campaigns against the Lusitani, Turduli Oppidani, and Turduli Veteres in 61-60 BC, [9] they were aggregated to the new Lusitania province by Emperor Augustus in 27-13 BC.

Lusitania was an ancient Iberian Roman province encompassing most of modern-day Portugal and a large portion of western Spain. Romans named the region after the Lusitanians, an Indo-European tribe inhabiting the lands.
The Lusitanians were an Indo-European-speaking people living in the far west of the Iberian Peninsula, in present-day central Portugal and Extremadura and Castilla y Leon of Spain. After its conquest by the Romans, the land was subsequently incorporated as a Roman province named after them (Lusitania).

The Vettones were an Iron Age pre-Roman people of the Iberian Peninsula.

The Cynetes or Conii were one of the pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula, living in today's Algarve and Lower Alentejo regions of southern Portugal, and the southern part of Badajoz and the northwestern portions of Córdoba and Ciudad Real provinces in Spain before the 6th century BC. According to Justin's epitome, the mythical Gargoris and Habis were their founding kings.
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Pius was a general and statesman of the Roman Republic. His father Metellus Numidicus was banished from Rome through the machinations of Gaius Marius. He, because of his constant and unbending attempts to have his father officially recalled from exile, was given the agnomen (nickname) Pius.

The Celtici were a Celtic tribe or group of tribes of the Iberian Peninsula, inhabiting three definite areas: in what today are the regions of Alentejo and the Algarve in Portugal; in the Province of Badajoz and north of Province of Huelva in Spain, in the ancient Baeturia; and along the coastal areas of Galicia. Classical authors give various accounts of the Celtici's relationships with the Gallaeci, Celtiberians and Turdetani.

The Paesuri or Paesures were an ancient pre-Roman people of Lusitania, akin to the Lusitani, to whom they were a dependent tribe.

The Tapoli or Tapori were an ancient Celtic tribe of Lusitania, akin to the Lusitanians, to whom they were a dependent tribe, living just north of the river Tagus, around the border area of modern-day Portugal and Spain.

The Turduli or Turtuli were an ancient pre-Roman people of the southwestern Iberian Peninsula.

The Turduli Veteres, translated as "Ancient Turduli" or "Old Turduli" were an ancient pre-Roman tribe of present day Portugal, akin to the Calaicians or Gallaeci and Lusitanians.

The Turduli Oppidani or Turdulorum Oppida, were a pre-Roman coastal people in present-day Portugal, related to the Turduli Veteres and akin to the Callaeci-Lusitanians.
This is a historical timeline of Portugal.

The Vaccaei or Vaccei were a pre-Roman Celtic people of Spain, who inhabited the sedimentary plains of the central Duero valley, in the Meseta Central of northern Hispania.

The Gallaeci were a Celtic tribal complex who inhabited Gallaecia, the north-western corner of Iberia, a region roughly corresponding to what is now the Norte Region in northern Portugal, and the Spanish regions of Galicia, western Asturias and western León before and during the Roman period. They spoke a Q-Celtic language related to Northeastern Hispano-Celtic, called Gallaecian or Northwestern Hispano-Celtic. The region was annexed by the Romans in the time of Caesar Augustus during the Cantabrian Wars, a war which initiated the assimilation of the Gallaeci into Latin culture.
The Battle of the Baetis River was fought between an army of the Roman Republic and a rebel army at the Baetis river in Spain. The battle took place in 80 BC at the start of the Sertorian War. The Romans were led by Lucius Fufidius, while the rebels were led by the Roman rebel Quintus Sertorius. The rebel army was victorious, gaining Sertorius control over Hispania Ulterior.

The Sertorian War was a civil war in the Roman Republic fought from 80 to 72 BC between two Roman factions, one led by Quintus Sertorius and another led by the senate as constituted in the aftermath of Sulla's civil war. The war was fought on the Iberian peninsula and was one of the Roman civil wars of the first century BC. The Sertorians comprised many Roman exiles from the Sullan proscriptions led by Sertorius, who fashioned himself proconsul, and native Celts, Aquitanians, and Iberians.
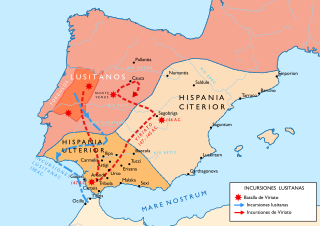
The Lusitanian War, called Pyrinos Polemos in Greek, was a war of resistance fought by the Lusitanian tribes of Hispania Ulterior against the advancing legions of the Roman Republic from 155 to 139 BC. The Lusitanians revolted in 155 BC, and again in 146 BC and were pacified. In 154 BC, a long war in Hispania Citerior, known as the Numantine War, was begun by the Celtiberians. It lasted until 133 and is an important event in the integration of what would become Portugal into the Roman and Latin-speaking world.

The Arevaci or Aravaci, were a Celtic people who settled in the central Meseta of northern Hispania and dominated most of Celtiberia from the 4th to late 2nd centuries BC. The Vaccaei were their allies.