
The Grovii or Gravii were an ancient Gallaeci tribe who inhabited the low valley of the Minho river, present day Portugal and Galicia (Spain), and also along the coast near the rivers Avo, Celadus, Nebis and Limia, northern Portugal.

The Grovii or Gravii were an ancient Gallaeci tribe who inhabited the low valley of the Minho river, present day Portugal and Galicia (Spain), and also along the coast near the rivers Avo, Celadus, Nebis and Limia, northern Portugal.
Pomponius Mela stated that all the people living along the coast of Gallaecia were Celtic, with the exception of the Grovii, while Pliny wrote that they had a Greek origin. Anyhow, E.R. Luján, studying their onomastics, couldn't conclude on their non-Celtiness, since their anthroponyms and toponyms could be Celtic. [1]
Their main settlement was Tude, present day Tui, Pontevedra, by the border with Portugal along the Minho river. [2] The non-localized oppidum of Avobriga and Lambriaca were located near the Grovii lands. [3]
Lusitanian mythology is the mythology of the Lusitanians, an Indo-European speaking people of western Iberia, in what was then known as Lusitania. In present times, the territory comprises the central part of Portugal and small parts of Extremadura and Salamanca.
The Lusitanians were an Indo-European-speaking people living in the far west of the Iberian Peninsula, in present-day central Portugal and Extremadura and Castilla y Leon of Spain. After its conquest by the Romans, the land was subsequently incorporated as a Roman province named after them (Lusitania).

Lusitanian was an Indo-European Paleohispanic language. There has been support for either a connection with the ancient Italic languages or Celtic languages. It is known from only six sizeable inscriptions, dated from c. 1 CE, and numerous names of places (toponyms) and of gods (theonyms). The language was spoken in the territory inhabited by Lusitanian tribes, from the Douro to the Tagus rivers, territory that today falls in central Portugal and western Spain.

The Astures or Asturs, also named Astyrs, were the Hispano-Celtic inhabitants of the northwest area of Hispania that now comprises almost the entire modern autonomous community of the Principality of Asturias, the modern province of León, and the northern part of the modern province of Zamora, and eastern Trás os Montes in Portugal. They were a horse-riding highland cattle-raising people who lived in circular huts of stone drywall construction. The Albiones were a major tribe from western Asturias. Isidore of Seville gave an etymology as coming from a river Astura, identified by David Magie as the Órbigo River in the plain of León, and by others as the modern Esla River.

The Celtici were a Celtic tribe or group of tribes of the Iberian Peninsula, inhabiting three definite areas: in what today are the regions of Alentejo and the Algarve in Portugal; in the Province of Badajoz and north of Province of Huelva in Spain, in the ancient Baeturia; and along the coastal areas of Galicia. Classical authors give various accounts of the Celtici's relationships with the Gallaeci, Celtiberians and Turdetani.
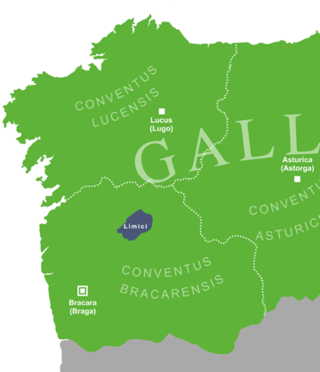
The Limici were an ancient Celtic tribe of Gallaecia, living in the swamps of the river Lima, in the border region between Minho (Portugal) and Galicia (Spain).
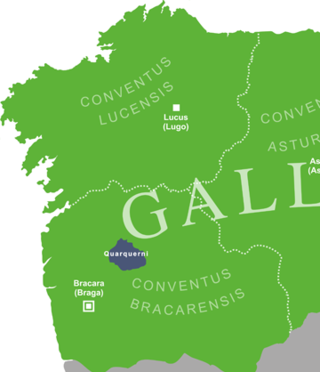
The Quaquerni or Querquerni were an ancient tribe of Gallaecia, living in the Baixa Limia region of southern Galicia, where the Roman fort of Aquis Querquennis has been found.

The Gallaeci were a Celtic tribal complex who inhabited Gallaecia, the north-western corner of Iberia, a region roughly corresponding to what is now the Norte Region in northern Portugal, and the Spanish regions of Galicia, western Asturias and western León before and during the Roman period. They spoke a Q-Celtic language related to Northeastern Hispano-Celtic, called Gallaecian or Northwestern Hispano-Celtic. The region was annexed by the Romans in the time of Caesar Augustus during the Cantabrian Wars, a war which initiated the assimilation of the Gallaeci into Latin culture.

Castro culture is the archaeological term for the material culture of the northwestern regions of the Iberian Peninsula from the end of the Bronze Age until it was subsumed by Roman culture. It is the culture associated with the Gallaecians and Astures.

The Minho or Miño is the longest river in the autonomous community of Galicia in Spain, with a length of 340 kilometres (210 mi). It forms a part of the international border between Spain and Portugal. By discharge volume, it is the fourth largest river of the Iberian Peninsula after the Douro, Ebro, and Tagus rivers.

Galicians are a Romance-speaking European ethnic group from northwestern Spain; they are closely related to the northern Portuguese people and have their historic homeland in Galicia, in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. Two Romance languages are widely spoken and official in Galicia: the native Galician and Spanish.

Cividade de Terroso was an ancient city of the Castro culture in North-western coast of the Iberian Peninsula, situated near the present bed of the Ave river, in the suburbs of present-day Póvoa de Varzim, Portugal.
Portus Cale was an ancient town and port in present-day northern Portugal, in the area of today's Porto and Vila Nova de Gaia. The name of the town eventually influenced the name of the subsequent country of Portugal, from the 9th century onwards.

The Citânia de Briteiros is an archaeological site of the Castro culture located in the Portuguese civil parish of Briteiros São Salvador e Briteiros Santa Leocádia in the municipality of Guimarães; important for its size, "urban" form and developed architecture, it is one of the more excavated sites in northwestern Iberian Peninsula. Although primarily known as the remains of an Iron Age proto-urban hill fort, the excavations at the site have revealed evidence of sequential settlement, extending from the Bronze to Middle Ages.
Gallaecian or Northwestern Hispano-Celtic is an extinct Celtic language of the Hispano-Celtic group. It was spoken by the Gallaeci in the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula around the start of the 1st millennium. The region became the Roman province of Gallaecia, which is now divided between the Spanish regions of Galicia, western Asturias, the west of the Province of León, and Northern Portugal.
This section of the timeline of Iberian history concerns events from before the Carthaginian conquests.