Related Research Articles

In telecommunications, orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) is a type of digital transmission used in digital modulation for encoding digital (binary) data on multiple carrier frequencies. OFDM has developed into a popular scheme for wideband digital communication, used in applications such as digital television and audio broadcasting, DSL internet access, wireless networks, power line networks, and 4G/5G mobile communications.
In telecommunications and computer networks, a channel access method or multiple access method allows more than two terminals connected to the same transmission medium to transmit over it and to share its capacity. Examples of shared physical media are wireless networks, bus networks, ring networks and point-to-point links operating in half-duplex mode.

Power-line communication (PLC) is the carrying of data on a conductor that is also used simultaneously for AC electric power transmission or electric power distribution to consumers. The line that does so is known as a power-line carrier.

A wireless mesh network (WMN) is a communications network made up of radio nodes organized in a mesh topology. It can also be a form of wireless ad hoc network.
Broadband over power lines (BPL) is a method of power-line communication (PLC) that allows relatively high-speed digital data transmission over public electric power distribution wiring. BPL uses higher frequencies, a wider frequency range, and different technologies compared to other forms of power-line communications to provide high-rate communication over longer distances. BPL uses frequencies that are part of the radio spectrum allocated to over-the-air communication services; therefore, the prevention of interference to, and from, these services is a very important factor in designing BPL systems.
HomePlug is the family name for various power line communications specifications under the HomePlug designation, each with unique capabilities and compatibility with other HomePlug specifications.

Orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA) is a multi-user version of the popular orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) digital modulation scheme. Multiple access is achieved in OFDMA by assigning subsets of subcarriers to individual users. This allows simultaneous low-data-rate transmission from several users.
IEEE 1901 is a standard for high-speed communication devices via electric power lines, often called broadband over power lines (BPL). The standard uses transmission frequencies below 100 MHz. This standard is usable by all classes of BPL devices, including BPL devices used for the connection to Internet access services as well as BPL devices used within buildings for local area networks, smart energy applications, transportation platforms (vehicle), and other data distribution applications.

The WiMedia Alliance was a non-profit industry trade group that promoted the adoption, regulation, standardization and multi-vendor interoperability of ultra-wideband (UWB) technologies. It existed from about 2002 through 2009.
Single-carrier FDMA (SC-FDMA) is a frequency-division multiple access scheme. Originally known as Carrier Interferometry, it is also called linearly precoded OFDMA (LP-OFDMA). Like other multiple access schemes, it deals with the assignment of multiple users to a shared communication resource. SC-FDMA can be interpreted as a linearly precoded OFDMA scheme, in the sense that it has an additional DFT processing step preceding the conventional OFDMA processing.
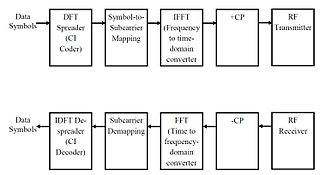
Carrier Interferometry(CI) is a spread spectrum scheme designed to be used in an Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) communication system for multiplexing and multiple access, enabling the system to support multiple users at the same time over the same frequency band.
IEEE 802.11a-1999 or 802.11a was an amendment to the IEEE 802.11 wireless local network specifications that defined requirements for an orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) communication system. It was originally designed to support wireless communication in the unlicensed national information infrastructure (U-NII) bands as regulated in the United States by the Code of Federal Regulations, Title 47, Section 15.407.
IEEE 802.11b-1999 or 802.11b is an amendment to the IEEE 802.11 wireless networking specification that extends throughout up to 11 Mbit/s using the same 2.4 GHz band. A related amendment was incorporated into the IEEE 802.11-2007 standard.
IEEE 802.11g-2003 or 802.11g is an amendment to the IEEE 802.11 specification that operates in the 2.4 GHz microwave band. The standard has extended link rate to up to 54 Mbit/s using the same 20 MHz bandwidth as 802.11b uses to achieve 11 Mbit/s. This specification, under the marketing name of Wi‑Fi, has been implemented all over the world. The 802.11g protocol is now Clause 19 of the published IEEE 802.11-2007 standard, and Clause 19 of the published IEEE 802.11-2012 standard.

In radio, multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) is a method for multiplying the capacity of a radio link using multiple transmission and receiving antennas to exploit multipath propagation. MIMO has become an essential element of wireless communication standards including IEEE 802.11n, IEEE 802.11ac, HSPA+ (3G), WiMAX, and Long Term Evolution (LTE). More recently, MIMO has been applied to power-line communication for three-wire installations as part of the ITU G.hn standard and of the HomePlug AV2 specification.
Gigabit Home Networking (G.hn) is a specification for wired home networking that supports speeds up to 2 Gbit/s and operates over four types of legacy wires: telephone wiring, coaxial cables, power lines and plastic optical fiber. Some benefits of a multi-wire standard are lower equipment development costs and lower deployment costs for service providers.

WiGig, alternatively known as 60 GHz Wi-Fi, refers to a set of 60 GHz wireless network protocols. It includes the current IEEE 802.11ad standard and also the IEEE 802.11ay standard.
IEEE 802.11ah is a wireless networking protocol published in 2017 called Wi-Fi HaLow as an amendment of the IEEE 802.11-2007 wireless networking standard. It uses 900 MHz license-exempt bands to provide extended-range Wi-Fi networks, compared to conventional Wi-Fi networks operating in the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz bands. It also benefits from lower energy consumption, allowing the creation of large groups of stations or sensors that cooperate to share signals, supporting the concept of the Internet of things (IoT). The protocol's low power consumption competes with Bluetooth, LoRa, and Zigbee, and has the added benefit of higher data rates and wider coverage range.

Wi-Fi 6, or IEEE 802.11ax, is an IEEE standard from the Wi-Fi Alliance, for wireless networks (WLANs). It operates in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, with an extended version, Wi-Fi 6E, that adds the 6 GHz band. It is an upgrade from Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac), with improvements for better performance in crowded places. Wi-Fi 6 covers frequencies in license-exempt bands between 1 and 7.125 GHz, including the commonly used 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, as well as the broader 6 GHz band.
Non-orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (N-OFDM) is a method of encoding digital data on multiple carrier frequencies with non-orthogonal intervals between frequency of sub-carriers. N-OFDM signals can be used in communication and radar systems.
References
- ↑ HD-PLC TECHNOLOGY
- ↑ "IEEE 1901 Working Group". IEEE SA. Retrieved 2023-10-13.
- ↑ "IEEE P1901c Standard for Broadband over Power Line Networks: Medium Access Control and Physical Layer Specifications Amendment 3: Enhanced Flexible Channel Wavelet (FCW) physical and media access control layers for use on any media". IEEE SA. Retrieved 2023-10-13.
- 1 2 "Panasonic Holdings' Technology Approved as a Technology Draft Standard for IEEE's Next-generation Communication Standard:Accelerating Global Development with a New Brand Name, Nessum". Panasonic Holdings Corporation. Retrieved 2023-10-13.
- ↑ "Nessum IP core". Panasonic Holdings Corporation. Retrieved 2023-10-20.
- ↑ "PLINE電力線通信タイプ". Toho Technology Corporation. Retrieved 2023-10-13.
- ↑ "Coaxial LAN converter". i-PRO . 3 September 2021. Retrieved 2023-10-20.
- ↑ "納入事例 名古屋大学 インターナショナル・レジデンス東山". Panasonic Corporation. Retrieved 2023-10-13.
- ↑ "What is Nessum?". Nessum Alliance. Retrieved 2023-10-20.
- ↑ "Nessum Technical Overview, Nessm PHY layer". Nessum Alliance. Retrieved 2023-10-20.
- ↑ "Nessum Latest Technology, Modes and channels". Nessum Alliance. Retrieved 2023-10-20.
- ↑ "Nessum Technical Overview, Nessum MAC layer". Nessum Alliance. Retrieved 2023-10-20.
- ↑ "特集PLC(電力線通信)". 電気総合誌OHM. 2020年7月号.
- ↑ "Installation and operation of Long Range "HD-PLC" multi-hop" (PDF).
- ↑ HD-PLC TECHNOLOGY
- ↑ 4th-generation HD-PLC Quatro Core Overview
- ↑ HD-PLC Use Cases
- ↑ Navid, Michael V. "HD-PLC Technology: A New Communication Standard Enabling Future Smart HVAC Systems In Smart Buildings". www.hvacinformed.com. Retrieved 2020-07-30.
- ↑ "HD-PLC Technology: A New Communication Standard Enabling Future Smart HVAC Systems In Smart Buildings". LonMark. 2020-07-06. Retrieved 2020-07-30.
- ↑ "Smart Building Network Based on HD-PLC". www.megachips.com. 15 March 2018. Retrieved 2020-07-30.
- ↑ "High-Speed Powerline Channel Earns ANSI/CTA Approval". LonMark. 2020-01-05. Retrieved 2020-07-30.
- ↑ "新長崎トンネル | 納入事例集 | 電気・建築設備 | Panasonic". www2.panasonic.biz. Retrieved 2020-07-30.
- ↑ "[DAIHEN] 新型大気用ウエハ搬送ロボット UTX/W-RM5700 - YouTube". www.youtube.com. 20 February 2017. Retrieved 2020-07-30.
- ↑ ""HD-PLC Alliance" is renamed "Nessum Alliance" as it enters a New Era of Wired and Wireless (Any Media) IoT Communication Applications!". businesswire (Press release). 4 October 2023. Retrieved 2023-10-13.