
Muscular dystrophies (MD) are a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare neuromuscular diseases that cause progressive weakness and breakdown of skeletal muscles over time. The disorders differ as to which muscles are primarily affected, the degree of weakness, how fast they worsen, and when symptoms begin. Some types are also associated with problems in other organs.
The muscular system is an organ system consisting of skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles. It permits movement of the body, maintains posture and circulates blood throughout the body. The muscular systems in vertebrates are controlled through the nervous system although some muscles can be completely autonomous. Together with the skeletal system in the human, it forms the musculoskeletal system, which is responsible for movement of the body.

Limb–girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD) is a genetically heterogeneous group of rare muscular dystrophies that share a set of clinical characteristics. It is characterised by progressive muscle wasting which affects predominantly hip and shoulder muscles. LGMD usually has an autosomal pattern of inheritance. It currently has no known cure or treatment.

Spinal muscular atrophies (SMAs) are a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare debilitating disorders characterised by the degeneration of lower motor neurons and subsequent atrophy (wasting) of various muscle groups in the body. While some SMAs lead to early infant death, other diseases of this group permit normal adult life with only mild weakness.
Weakness is a symptom of a number of different conditions. The causes are many and can be divided into conditions that have true or perceived muscle weakness. True muscle weakness is a primary symptom of a variety of skeletal muscle diseases, including muscular dystrophy and inflammatory myopathy. It occurs in neuromuscular junction disorders, such as myasthenia gravis.
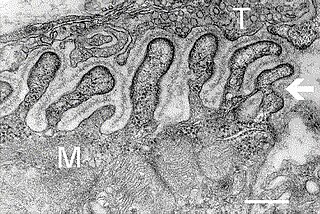
A neuromuscular junction is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.

Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe type of muscular dystrophy that primarily affects boys. Muscle weakness usually begins around the age of four, and worsens quickly. Muscle loss typically occurs first in the thighs and pelvis followed by the arms. This can result in trouble standing up. Most are unable to walk by the age of 12. Affected muscles may look larger due to increased fat content. Scoliosis is also common. Some may have intellectual disability. Females with a single copy of the defective gene may show mild symptoms.

Becker muscular dystrophy is an X-linked recessive inherited disorder characterized by slowly progressing muscle weakness of the legs and pelvis. It is a type of dystrophinopathy. This is caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene, which encodes the protein dystrophin. Becker muscular dystrophy is related to Duchenne muscular dystrophy in that both result from a mutation in the dystrophin gene, but has a milder course.
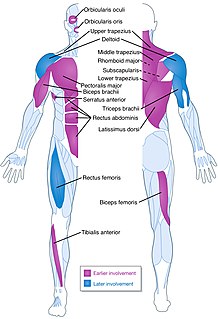
Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) is a type of muscular dystrophy, a group of heritable diseases that cause progressive impairment of muscles. FSHD preferentially weakens the skeletal muscles of the face, those that position the scapula (scapulo), and those in the upper arm, overlying the humerus bone (humeral). These areas can be spared, and others usually are affected, especially the chest, the trunk, and around the shin. Abnormally positioned scapulas and inability to lift the foot are common. The two sides of the body are often affected unequally. Weakness typically manifests at ages 15 – 30 years. FSHD can also cause hearing loss and blood vessel abnormalities in the back of the eye.
Muscle weakness is a lack of muscle strength. Its causes are many and can be divided into conditions that have either true or perceived muscle weakness. True muscle weakness is a primary symptom of a variety of skeletal muscle diseases, including muscular dystrophy and inflammatory myopathy. It occurs in neuromuscular junction disorders, such as myasthenia gravis. Muscle weakness can also be caused by low levels of potassium and other electrolytes within muscle cells. It can be temporary or long-lasting. The term myasthenia is from my- from Greek μυο meaning "muscle" + -asthenia ἀσθένεια meaning "weakness".

Neuromuscular disease is a broad term that encompasses many diseases and ailments that impair the functioning of the muscles, either directly, being pathologies of the voluntary muscle, or indirectly, being pathologies of nerves or neuromuscular junctions.
Electrical muscle stimulation (EMS), also known as neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) or electromyostimulation, is the elicitation of muscle contraction using electric impulses. EMS has received an increasing amount of attention in the last few years for many reasons: it can be utilized as a strength training tool for healthy subjects and athletes; it could be used as a rehabilitation and preventive tool for people who are partially or totally immobilized; it could be utilized as a testing tool for evaluating the neural and/or muscular function in vivo; it could be used as a post-exercise recovery tool for athletes. The impulses are generated by a device and are delivered through electrodes on the skin near to the muscles being stimulated. The electrodes are generally pads that adhere to the skin. The impulses mimic the action potential that comes from the central nervous system, causing the muscles to contract. The use of EMS has been cited by sports scientists as a complementary technique for sports training, and published research is available on the results obtained. In the United States, EMS devices are regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).

Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a rare neuromuscular disorder that results in the loss of motor neurons and progressive muscle wasting. It is usually diagnosed in infancy or early childhood and if left untreated it is the most common genetic cause of infant death. It may also appear later in life and then have a milder course of the disease. The common feature is progressive weakness of voluntary muscles, with arm, leg and respiratory muscles being affected first. Associated problems may include poor head control, difficulties swallowing, scoliosis, and joint contractures.
Congenital myopathy is a very broad term for any muscle disorder present at birth. This defect primarily affects skeletal muscle fibres and causes muscular weakness and/or hypotonia. Congenital myopathies account for one of the top neuromuscular disorders in the world today, comprising approximately 6 in 100,000 live births every year. As a whole, congenital myopathies can be broadly classified as follows:
Victor Dubowitz, FRCP, Hon FRCPCH is a British neurologist and professor emeritus at Imperial College London. He is principally known along with his wife Lilly Dubowitz for developing two clinical tests, the Dubowitz Score to estimate gestational age and the other for the systematic neurological examination of the newborn.
Neuromuscular ultrasound refers to a field in medicine in which ultrasound is used to diagnosis and guide treatment for people with neuromuscular diseases. Neuromuscular ultrasound is often combined with electrodiagnosis, and particularly nerve conduction studies and EMG, to improve the accuracy of diagnosis and add anatomic information to the functional information obtained with electrodiagnosis. It has been demonstrated that neuromuscular ultrasound adds value to the diagnosis of nerve disease in over 80% of cases.
Electrodiagnosis (EDX) is a method of medical diagnosis that obtains information about diseases by passively recording the electrical activity of body parts or by measuring their response to external electrical stimuli. The most widely used methods of recording spontaneous electrical activity are various forms of electrodiagnostic testing (electrography) such as electrocardiography (ECG), electroencephalography (EEG), and electromyography (EMG). Electrodiagnostic medicine is a medical subspecialty of neurology, clinical neurophysiology, cardiology, and physical medicine and rehabilitation. Electrodiagnostic physicians apply electrophysiologic techniques, including needle electromyography and nerve conduction studies to diagnose, evaluate, and treat people with impairments of the neurologic, neuromuscular, and/or muscular systems. The provision of a quality electrodiagnostic medical evaluation requires extensive scientific knowledge that includes anatomy and physiology of the peripheral nerves and muscles, the physics and biology of the electrical signals generated by muscle and nerve, the instrumentation used to process these signals, and techniques for clinical evaluation of diseases of the peripheral nerves and sensory pathways.
Mary M. Reilly FRCP is an Irish neurologist who works at National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery. She studies peripheral neuropathy. She is the President of the Association of British Neurologists.

Spinal muscular atrophy with lower extremity predominance 2A (SMALED2A) is a rare neuromuscular disorder characterised by muscle weakness predominantly in legs. The disorder is usually diagnosed shortly after birth; affected children have a delayed motor development, waddling gait, difficulties walking, sometimes develop spasticity. Sensation, swallowing and cognitive development are not affected. The disorder is slowly progressive throughout the lifetime.









