The glissando illusion is an auditory illusion, created when a sound with a fixed pitch, such as a synthesized oboe tone, is played together with a sine wave gliding up and down in pitch, and they are both switched back and forth between stereo loudspeakers. The effect is that the oboe is heard as switching between loudspeakers while the sine wave is heard as joined together seamlessly, and as moving around in space in accordance with its pitch motion. Right-handers often hear the glissando as traveling from left to right as its pitch glides from low to high, and then back from right to left as its pitch glides from high to low.

The parietal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus.

Brodmann area 9, or BA9, refers to a cytoarchitecturally defined portion of the frontal cortex in the brain of humans and other primates. It contributes to the dorsolateral and medial prefrontal cortex.

The mammillary bodies are a pair of small round bodies, located on the undersurface of the brain that, as part of the diencephalon, form part of the limbic system. They are located at the ends of the anterior arches of the fornix. They consist of two groups of nuclei, the medial mammillary nuclei and the lateral mammillary nuclei.

The pulvinar nuclei or nuclei of the pulvinar are the nuclei located in the thalamus. As a group they make up the collection called the pulvinar of the thalamus, usually just called the pulvinar.

The Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST) is a neuropsychological test of set-shifting, which is the capability to show flexibility when exposed to changes in reinforcement. The WCST was written by David A. Grant and Esta A. Berg. The Professional Manual for the WCST was written by Robert K. Heaton, Gordon J. Chelune, Jack L. Talley, Gary G. Kay, and Glenn Curtiss.
Beta waves, or beta rhythm, are a neural oscillation (brainwave) in the brain with a frequency range of between 12.5 and 30 Hz. Beta waves can be split into three sections: Low Beta Waves ; Beta Waves ; and High Beta Waves. Beta states are the states associated with normal waking consciousness.
The two-streams hypothesis is a model of the neural processing of vision as well as hearing. The hypothesis, given its initial characterisation in a paper by David Milner and Melvyn A. Goodale in 1992, argues that humans possess two distinct visual systems. Recently there seems to be evidence of two distinct auditory systems as well. As visual information exits the occipital lobe, and as sound leaves the phonological network, it follows two main pathways, or "streams". The ventral stream leads to the temporal lobe, which is involved with object and visual identification and recognition. The dorsal stream leads to the parietal lobe, which is involved with processing the object's spatial location relative to the viewer and with speech repetition.

In neuroanatomy, the parieto-occipital sulcus is a deep sulcus in the cerebral cortex that marks the boundary between the cuneus and precuneus, and also between the parietal and occipital lobes. Only a small part can be seen on the lateral surface of the hemisphere, its chief part being on the medial surface.
The perirhinal cortex is a cortical region in the medial temporal lobe that is made up of Brodmann areas 35 and 36. It receives highly processed sensory information from all sensory regions, and is generally accepted to be an important region for memory. It is bordered caudally by postrhinal cortex or parahippocampal cortex and ventrally and medially by entorhinal cortex.
Somatoparaphrenia is a type of monothematic delusion where one denies ownership of a limb or an entire side of one's body. Even if provided with undeniable proof that the limb belongs to and is attached to their own body, the patient produces elaborate confabulations about whose limb it really is or how the limb ended up on their body. In some cases, delusions become so elaborate that a limb may be treated and cared for as if it were a separate being.

Giacomo Rizzolatti is an Italian neurophysiologist who works at the University of Parma. Born in Kyiv, UkSSR, he is the Senior Scientist of the research team that discovered mirror neurons in the frontal and parietal cortex of the macaque monkey, and has written many scientific articles on the topic. He also proposed the premotor theory of attention. He is a past president of the European Brain and Behaviour Society. Rizzolatti was the 2007 co-recipient, with Leonardo Fogassi and Vittorio Gallese, for the University of Louisville Grawemeyer Award for Psychology. He is an elected member of the Academia Europaea, National Academy of Sciences, and Royal Society In 2020 he adheres to Empathism.
Kent Cochrane, also known as Patient K.C., was a widely studied Canadian memory disorder patient who has been used as a case study in over 20 neuropsychology papers over the span of 25 years. In 1981, Cochrane was involved in a motorcycle accident that left him with severe anterograde amnesia, as well as temporally graded retrograde amnesia. Like other amnesic patients, Cochrane had his semantic memory intact, but lacked episodic memory with respect to his entire past. As a case study, Cochrane has been linked to the breakdown of the single-memory single-locus hypothesis regarding amnesia, which states that an individual memory is localized to a single location in the brain.

Vestibular cortex is the portion of the cerebrum which responds to input from the vestibular system.
The Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery (CANTAB), originally developed at the University of Cambridge in the 1980s but now provided in a commercial capacity by Cambridge Cognition, is a computer-based cognitive assessment system consisting of a battery of neuropsychological tests, administered to subjects using a touch screen computer. The CANTAB tests were co-invented by Professor Trevor Robbins and Professor Barbara Sahakian. The 25 tests in CANTAB examine various areas of cognitive function, including:
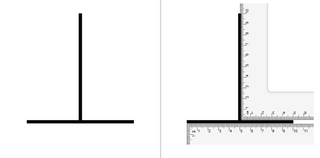
The vertical–horizontal illusion is the tendency for observers to overestimate the length of a vertical line relative to a horizontal line of the same length. This involves a bisecting component that causes the bisecting line to appear longer than the line that is bisected. People often overestimate or underestimate the length of the bisecting line relative to the bisected line of the same length. This even happens if people are aware that the lines are of the same length.
Michael Steven Anthony Graziano is an American scientist and novelist who is currently a professor of Psychology and Neuroscience at Princeton University. His scientific research focuses on the brain basis of awareness. He has proposed the "attention schema" theory, an explanation of how, and for what adaptive advantage, brains attribute the property of awareness to themselves. His previous work focused on how the cerebral cortex monitors the space around the body and controls movement within that space. Notably he has suggested that the classical map of the body in motor cortex, the homunculus, is not correct and is better described as a map of complex actions that make up the behavioral repertoire. His publications on this topic have had a widespread impact among neuroscientists but have also generated controversy. His novels rely partly on his background in psychology and are known for surrealism or magic realism. Graziano also composes music including symphonies and string quartets.
Michael Charles Corballis was a New Zealand and Canadian psychologist and author. He was Emeritus Professor at the Department of Psychology at the University of Auckland. His fields of research were cognitive psychology and cognitive neuroscience, encompassing visual perception, visual imagery, attention, memory, and the evolution of language.
In psychology, the numerical Stroop effect demonstrates the relationship between numerical values and physical sizes. When digits are presented visually, they can be physically large or small, irrespective of their actual values. Congruent pairs occur when size and value correspond while incongruent pairs occur when size and value are incompatible. It was found that when people are asked to compare digits, their reaction time tends to be slower in the case of incongruent pairs. This reaction time difference between congruent and incongruent pairs is termed the numerical Stroop effect
John Aggleton is a British behavioural neuroscientist.