Related Research Articles

Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. It covers an area of 8,515,767 square kilometres (3,287,956 sq mi), with a population of over 211 million. Brazil is the world's fifth-largest and sixth-most populous country, composed of 26 states and the Federal District. It is the largest country to have Portuguese as an official language and the only one in the Americas. Brazil is one of the world's most multicultural and ethnically diverse nations, due to over a century of mass immigration from around the world. It is also the most populous Roman Catholic-majority country, and its capital is Brasília, while the largest city is São Paulo.

Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America. It is bounded on the north by the Caribbean Sea, the northwest by Panama, the south by Ecuador and Peru, the east by Venezuela, the southeast by Brazil, and the west by the Pacific Ocean. Colombia is composed of 32 departments and the Capital District of Bogotá, the country's largest city. It covers an area of 1,418,748 square kilometres (547,782 sq mi), with a population of 50 million. Colombia's rich cultural heritage reflects influences by various Amerindian civilizations, European settlement, forced African labor, and immigration from Europe and the Middle East. Spanish is the nation's official language, besides which over 70 languages are spoken.

The Dominican Republic is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with Haiti, making Hispaniola one of only two Caribbean islands, along with Saint Martin, that are shared by two sovereign states. The Dominican Republic is the second-largest nation in the Antilles by area at 48,671 square kilometers (18,792 sq mi), and third-largest by population, with approximately 10.8 million people, of whom approximately 3.3 million live in the metropolitan area of Santo Domingo, the capital city. The official language of the country is Spanish.

El Salvador, officially the Republic of El Salvador, is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south by the Pacific Ocean. El Salvador's capital and largest city is San Salvador. As of 2021, the country had a population of approximately 6,825,935.
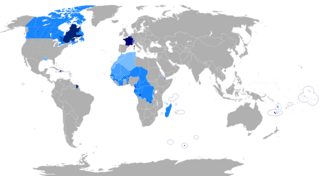
French is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the (Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French.

North America is a continent entirely within the Northern Hemisphere and almost all within the Western Hemisphere. It can also be described as the northern subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. Because it is on the North American Tectonic Plate, Greenland is included as part of North America geographically.

Paris is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,175,601 residents as of 2018, in an area of more than 105 square kilometres. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of Europe's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, science and arts. The City of Paris is the centre and seat of government of the region and province of Île-de-France, or Paris Region, which has an estimated population of 12,174,880, or about 18 percent of the population of France as of 2017. The Paris Region had a GDP of €709 billion in 2017. According to the Economist Intelligence Unit Worldwide Cost of Living Survey in 2018, Paris was the second most expensive city in the world, after Singapore and ahead of Zürich, Hong Kong, Oslo and Geneva. Another source ranked Paris as most expensive, on a par with Singapore and Hong Kong, in 2018.

Paraguay, officially the Republic of Paraguay, is a country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to the east and northeast, and Bolivia to the northwest. It has a population of 7 million, nearly 3 million of which live in the capital and largest city of Asunción, and its surrounding metro. Although one of only two landlocked countries in South America, the country has coasts, beaches and ports on the Paraguay and Paraná rivers that give exit to the Atlantic Ocean through the Paraná-Paraguay Waterway.

South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern subcontinent of the Americas. The reference to South America instead of other regions has increased in recent decades due to changing geopolitical dynamics.

Mestizo is a racial classification used to refer to a person of a combined White and Indigenous American ancestry. The term was used as an ethnic/racial category for mixed-race castas that evolved during the Spanish Empire. Although, broadly speaking, mestizo means someone of mixed European/indigenous heritage, the term did not have a fixed meaning in the colonial period. It was a formal label for individuals in official documentation, such as censuses, parish registers, Inquisition trials, and other matters. Priests and royal officials might label individuals as mestizos, but the term was also used for self-identification.
White is a racialized classification of people and a skin color specifier, generally used for people of European origin; although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, and point of view. This term has at times been expanded to encompass persons of South Asian, West Asian, and North African descent, persons who are often considered "non-white" in other contexts in the United States. It has also been alleged that, in the United States, people of Southern European and even Irish descent have been excluded from this category, although this idea has been contested. The usage of "white people" or a "white race" for a large group of mainly or exclusively European populations, defined by their light skin, among other physical characteristics, and contrasting with "black", "red", "brown", "yellow", and other "colored" people or "persons of color", originated in the 17th century. Prior to this, Europeans also described people from East Asia as being "white". It was only during the 19th century that this vague category was transformed in a pseudo-scientific system of race and skin color relations.

An urban area, or built-up area, is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities, towns, conurbations or suburbs. In urbanism, the term contrasts to rural areas such as villages and hamlets; in urban sociology or urban anthropology it contrasts with natural environment. The creation of early predecessors of urban areas during the urban revolution led to the creation of human civilization with modern urban planning, which along with other human activities such as exploitation of natural resources led to a human impact on the environment. "Agglomeration effects" are in the list of the main consequences of increased rates of firm creation since. This is due to conditions created by a greater level of industrial activity in a given region. However, a favorable environment for human capital development would also be generated simultaneously.

The indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.

Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and to the east by the Gulf of Mexico. Mexico covers 1,972,550 square kilometers (761,610 sq mi), making it the world's 13th-largest country by area; with approximately 126,014,024 inhabitants, it is the 10th-most-populous country and has the most Spanish-speakers. Mexico is organized as a federation comprising 31 states and Mexico City, its capital and largest metropolis. Other major urban areas include Guadalajara, Monterrey, Puebla, Toluca, Tijuana, Ciudad Juárez, and León.

Overseas France consists of all the French-administered territories outside Europe, mostly remains of the French colonial empire. It includes island territories in the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans, French Guiana on the South American continent, and several peri-Antarctic islands as well as a claim in Antarctica. Excluding the district of Adélie Land, where French sovereignty is effective de jure by French law, but where the French exclusive claim on this part of Antarctica is frozen by the Antarctic Treaty, overseas France covers a land area of 119,396 km2 (46,099 sq mi) and accounts for 18.0% of the French Republic's land territory. Its exclusive economic zone (EEZ) of 9,825,538 km2 (3,793,661 sq mi) accounts for 96.7% of the EEZ of the French Republic.
References
- ↑ TROISIEME RECENSEMENT GENERAL DE LA POPULATION ET DE L’HABITATION
