
A solvation shell or solvation sheath is the solvent interface of any chemical compound or biomolecule that constitutes the solute. When the solvent is water it is often referred to as a hydration shell or hydration sphere. The number of solvent molecules surrounding each unit of solute is called the hydration number of the solute.
Fucoxanthin is a xanthophyll, with formula C42H58O6. It is found as an accessory pigment in the chloroplasts of brown algae and most other heterokonts, giving them a brown or olive-green color. Fucoxanthin absorbs light primarily in the blue-green to yellow-green part of the visible spectrum, peaking at around 510-525 nm by various estimates and absorbing significantly in the range of 450 to 540 nm.

Interleukin 12 (IL-12) is an interleukin that is naturally produced by dendritic cells, macrophages, neutrophils, and human B-lymphoblastoid cells (NC-37) in response to antigenic stimulation. IL-12 belongs to the family of interleukin-12. IL-12 family is unique in comprising the only heterodimeric cytokines, which includes IL-12, IL-23, IL-27 and IL-35. Despite sharing many structural features and molecular partners, they mediate surprisingly diverse functional effects.
CD1 is a family of glycoproteins expressed on the surface of various human antigen-presenting cells. They are related to the class I MHC molecules, and are involved in the presentation of lipid antigens to T cells. However their precise function is unknown.

The interferon-gamma receptor (IFNGR) protein complex is the heterodimer of two chains: IFNGR1 and IFNGR2. It binds interferon-γ, the sole member of interferon type II.

Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) is a transcription factor which in humans is encoded by the STAT1 gene. It is a member of the STAT protein family.

Emodin (6-methyl-1,3,8-trihydroxyanthraquinone) is a chemical compound, of the anthraquinone family, that can be isolated from rhubarb, buckthorn, and Japanese knotweed. Emodin is particularly abundant in the roots of the Chinese rhubarb, knotweed and knotgrass as well as Hawaii ‘au‘auko‘i cassia seeds or coffee weed. It is specifically isolated from Rheum Palmatum L. It is also produced by many species of fungi, including members of the genera Aspergillus, Pyrenochaeta, and Pestalotiopsis, inter alia. The common name is derived from Rheum emodi, a taxonomic synonym of Rheum australe, and synonyms include emodol, frangula emodin, rheum emodin, 3-methyl-1,6,8-trihydroxyanthraquinone, Schuttgelb, and Persian Berry Lake.

Blakeslea trispora is a mould and member of the division Zygomycota. This species has been well studied for its ability to produce carotenoids, particularly, β-carotene and lycopene. β-carotene is a vitamin A precursor and both of β-carotene and lycopene play a significant role in the inhibition of oxidative stress. Blakeslea trispora is commonly isolated from soil samples throughout the Southern United States and Southern Asia. B. trispora is a pathogen of tropical plants. In vivo pathogenicity testing using animal models suggests this fungus is not a cause of animal or human disease.

Ganoderic acids are a class of closely related triterpenoids found in Ganoderma mushrooms. For thousands of years, the fruiting bodies of Ganoderma fungi have been used in traditional medicines in East Asia. Consequently, there have been efforts to identify the chemical constituents that may be responsible for the putative pharmacological effects. There are dozens of ganoderic acids that have been isolated and characterized, of which ganoderic acid A and ganoderic acid B are the most well characterized. Some ganoderic acids have been found to possess biological activities including hepatoprotection, anti-tumor effects, and 5-alpha reductase inhibition.

Protocatechuic acid (PCA) is a dihydroxybenzoic acid, a type of phenolic acid. It is a major metabolite of antioxidant polyphenols found in green tea. It has mixed effects on normal and cancer cells in in vitro and in vivo studies.

Cord factor, or trehalose dimycolate, is a glycolipid molecule found in the cell wall of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and similar species. It is the primary lipid found on the exterior of M. tuberculosis cells. Cord factor influences the arrangement of M. tuberculosis cells into long and slender formations, giving its name. Cord factor is virulent towards mammalian cells and critical for survival of M. tuberculosis in hosts, but not outside of hosts. Cord factor has been observed to influence immune responses, induce the formation of granulomas, and inhibit tumor growth. The antimycobacterial drug SQ109 is thought to inhibit TDM production levels and in this way disrupts its cell wall assembly.

Tetrandrine, a bis-benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, is a calcium channel blocker. It has anti-inflammatory, immunologic and antiallergenic effects. It inhibits the degranulation of mast cells. It has a quinidine-like anti-arrhythmic effect. It is isolated from the plant Stephania tetrandra, and other Chinese and Japanese herbs. It has vasodilatory properties and can therefore reduce blood pressure. Tetrandrine may have potential use for the treatment of liver disease and liver cancer. Tetrandrine has potential therapeutic value to prevent excess scarring/fibrosis in conjunctiva following trabeculectomy or in patients with severe conjunctival inflammation. Tetrandrine has anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrogenic actions, which make tetrandrine and related compounds potentially useful in the treatment of lung silicosis, liver cirrhosis, and rheumatoid arthritis. Tetrandrine has also been shown to inhibit entry of Ebola virus into host cells in vitro and showed therapeutic efficacy against Ebola in preliminary studies on mice. Tetrandrine has also been studied and patented as a possible treatment for tinnitus.

Renalase, FAD-dependent amine oxidase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RNLS gene. Renalase is a flavin adenine dinucleotide-dependent amine oxidase that is secreted into the blood from the kidney.

α-Cadinol or 10α-hydroxy-4-cadinene is an organic compound, a sesquiterpenoid alcohol.

Cerevisterol (5α-ergosta-7,22-diene-3β,5,6β-triol) is a sterol. Originally described in the 1930s from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, it has since been found in several other fungi and, recently, in deep water coral. Cerevisterol has some in vitro bioactive properties, including cytotoxicity to some mammalian cell lines.

Secalonic acids are a group of chiral dimeric tetrahydroxanthones closely related to ergoflavin and ergochrysin A that are collectively called ergochromes and belong to a class of mycotoxins initially isolated as major ergot pigments from the fungi Claviceps purpurea that grows parasitically on rye grasses. From early times and particularly in medieval Europe the consumption of grains containing ergot has repeatedly lead to mass poisonings known as ergotism which was caused by toxic ergot alkaloids and mycotoxins such as the ergochromes, due to contamination of flour by C. purpurea. A cluster of genes responsible for the synthesis of secalonic acids in C. purpurea has been identified. Secalonic acid D the enantiomer of secalonic acid A is a major environmental toxin, isolated from the fungus Penicillium oxalicum, and is a major microbial contaminant of freshly-harvested corn which causes toxicity through contamination of foodstuffs.

Phillyrin is an endophytic fungal isolate with anti-obesity activity. It can be produced by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, an endophytic fungus isolated from Forsythia suspensa. It can also be prepared directly from Forsythia suspensa.
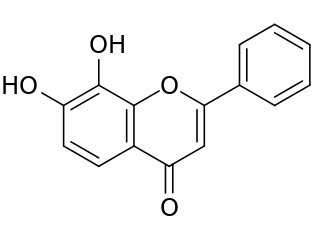
Tropoflavin, also known as 7,8-dihydroxyflavone, is a naturally occurring flavone found in Godmania aesculifolia, Tridax procumbens, and primula tree leaves. It has been found to act as a potent and selective small-molecule agonist of the tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB), the main signaling receptor of the neurotrophin brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Tropoflavin is both orally bioavailable and able to penetrate the blood–brain barrier. A prodrug of tropoflavin with greatly improved potency and pharmacokinetics, R13, is under development for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.

7,8,3′-Trihydroxyflavone (7,8,3'-THF) is a flavone and small-molecule agonist of TrkB, the main receptor of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), that was derived from tropoflavin (7,8-DHF). Relative to tropoflavin, 7,8,3'-THF is 2–3-fold more potent in vitro as a TrkB agonist. 7,3’-Dihydroxyflavone (7,3'-DHF) is also more potent than tropoflavin in vitro, indicating that a 3'-hydroxy group on the B-ring enhances TrkB agonistic activity. 7,8,3'-THF has been tested in vivo and was found to produce TrkB-dependent neuroprotective effects in mice similarly to tropoflavin.

Eutropoflavin (4'-Dimethylamino-7,8-dihydroxyflavone) is a synthetic flavone and selective small-molecule agonist of TrkB, the main receptor of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which was derived from structural modification of tropoflavin (7,8-DHF). Relative to tropoflavin, eutropoflavin possesses higher agonistic activity at TrkB, is significantly more potent than tropoflavin both in vitro and in vivo, and has a longer duration of action. The compound has been found to produce neuroprotective, neurogenic, and antidepressant-like effects in animals.


















