
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceans, with an area of about 106,460,000 km2 (41,100,000 sq mi). It covers approximately 20 percent of Earth's surface and about 29 percent of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" from the "New World" in the European perception of the World.

The Gulf Coast of the United States is the coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The coastal states that have a shoreline on the Gulf of Mexico are Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, and these are known as the Gulf States.

The North Atlantic Current (NAC), also known as North Atlantic Drift and North Atlantic Sea Movement, is a powerful warm western boundary current within the Atlantic Ocean that extends the Gulf Stream northeastward.

The Gulf of Guinea is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez in Gabon, north and west to Cape Palmas in Liberia. The intersection of the Equator and Prime Meridian is in the gulf.

The Gulf of Saint Lawrence is the outlet of the North American Great Lakes via the Saint Lawrence River into the Atlantic Ocean. The gulf is a semi-enclosed sea, covering an area of about 226,000 square kilometres (87,000 sq mi) and containing about 34,500 cubic kilometres (8,300 cu mi) of water, which results in an average depth of 152 metres (499 ft).

The east coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, the Atlantic Coast, and the Atlantic Seaboard, is the coastline along which the eastern United States meets the North Atlantic Ocean. Regionally, the term refers to the coastal states and area east of the Appalachian Mountains that have shoreline on the Atlantic Ocean, from north to south, Maine, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia and Florida.

The Intracoastal Waterway (ICW) is a 3,000-mile (4,800 km) inland waterway along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coasts of the United States, running from Boston, Massachusetts, southward along the Atlantic Seaboard and around the southern tip of Florida, then following the Gulf Coast to Brownsville, Texas. Some sections of the waterway consist of natural inlets, saltwater rivers, bays, and sounds, while others are artificial canals. It provides a navigable route along its length without many of the hazards of travel on the open sea.
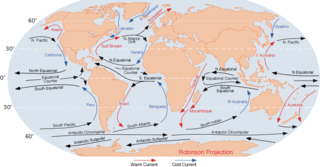
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents are primarily horizontal water movements.

A coastal plain is flat, low-lying land adjacent to a sea coast. Some of the largest coastal plains are in Alaska and the southeastern United States. The Gulf Coastal Plain of North America extends northwards from the Gulf of Mexico along the Lower Mississippi River to the Ohio River, which is a distance of about 981 miles (1,579 km).

The Gulf of Maine is a large gulf of the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast of North America. It is bounded by Cape Cod at the eastern tip of Massachusetts in the southwest and by Cape Sable Island at the southern tip of Nova Scotia in the northeast. The gulf includes the entire coastlines of the U.S. states of New Hampshire and Maine, as well as Massachusetts north of Cape Cod, and the southern and western coastlines of the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, respectively.

A U.S. National Marine Sanctuary is a zone within United States waters where the marine environment enjoys special protection. The program began in 1972 in response to public concern about the plight of marine ecosystems.

The Labrador Current is a cold current in the North Atlantic Ocean which flows from the Arctic Ocean south along the coast of Labrador and passes around Newfoundland, continuing south along the east coast of Canada near Nova Scotia. Near Nova Scotia, this cold water current meets the warm northward moving Gulf Stream. The combination of these two currents produces heavy fogs and has also created one of the richest fishing grounds in the world.

An Atlantic hurricane or tropical storm is a tropical cyclone that forms in the Atlantic Ocean, primarily between the months of June and November. A hurricane differs from a cyclone or typhoon only on the basis of location. A hurricane is a storm that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean and northeastern Pacific Ocean, a typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, and a cyclone occurs in the south Pacific or Indian Ocean.

The Tropical Atlantic realm is one of twelve marine realms that cover the world's coastal seas and continental shelves.

The Gulf of Mexico is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southwest and south by the Mexican states of Tamaulipas, Veracruz, Tabasco, Campeche, Yucatan, and Quintana Roo; and on the southeast by Cuba. The US states of Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, which border the Gulf on the north, are often referred to as the "Third Coast" of the United States.
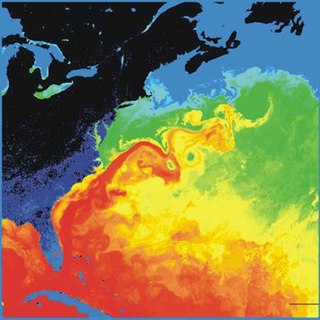
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and stretches to the tip of Florida, and follows the eastern coastlines of the United States and Newfoundland before crossing the Atlantic Ocean as the North Atlantic Current. The process of western intensification causes the Gulf Stream to be a northwards accelerating current off the east coast of North America. At about 40°0′N30°0′W, it splits in two, with the northern stream, the North Atlantic Drift, crossing to Northern Europe and the southern stream, the Canary Current, recirculating off West Africa.

The Florida Gulf Coast Eagles refer to the fifteen sports teams representing Florida Gulf Coast University in Fort Myers, Florida in intercollegiate athletics, including men and women's basketball, cross country, golf, soccer, and tennis; women's-only: softball, swimming and diving, indoor volleyball, and beach volleyball; and men's-only: baseball. The Eagles compete in the NCAA Division I and are members of the Atlantic Sun Conference (ASUN). FGCU is also notable as the youngest institution competing in NCAA Division I, having been officially founded in 1991 and started classes in 1997. Their mascot is Azul the Eagle.

The Florida Gulf Coast Eagles men's basketball team is the men's basketball team that represents Florida Gulf Coast University in Fort Myers, Florida, United States. The school's team currently competes in the Atlantic Sun Conference.

The Florida Gulf Coast Eagles men's soccer team represents Florida Gulf Coast University in Fort Myers, Florida in all NCAA Division I men's soccer competitions. The Eagles compete in the Atlantic Sun Conference. The soccer team is one of several varsity sports teams that represent the Florida Gulf Coast Eagles.


















