Related Research Articles

The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. It is involved in data gathering and analysis, research, field projects, advocacy, and education. IUCN's mission is to "influence, encourage and assist societies throughout the world to conserve nature and to ensure that any use of natural resources is equitable and ecologically sustainable".

The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biological species. It uses a set of precise criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of thousands of species and subspecies. These criteria are relevant to all species and all regions of the world. With its strong scientific base, the IUCN Red List is recognized as the most authoritative guide to the status of biological diversity. A series of Regional Red Lists are produced by countries or organizations, which assess the risk of extinction to species within a political management unit.

The Canadian Rocky Mountain Parks World Heritage Site is located in the Canadian Rockies. It consists of seven contiguous parks including four national parks:

The tamaraw or Mindoro dwarf buffalo is a small hoofed mammal belonging to the family Bovidae. It is endemic to the island of Mindoro in the Philippines, and is the only endemic Philippine bovine. It is believed, however, to have once also thrived on the larger island of Luzon. The tamaraw was originally found all over Mindoro, from sea level up to the mountains, but because of human habitation, hunting, and logging, it is now restricted to only a few remote grassy plains and is now a critically endangered species.

A tadpole is the larval stage in the biological life cycle of an amphibian. Most tadpoles are fully aquatic, though some species of amphibians have tadpoles that are terrestrial. Tadpoles have some fish-like features that may not be found in adult amphibians such as a lateral line, gills and swimming tails. As they undergo metamorphosis, they start to develop functional lungs for breathing air, and the diet of tadpoles changes drastically.

Oryx is a genus consisting of four large antelope species called oryxes. Their pelage is pale with contrasting dark markings in the face and on the legs, and their long horns are almost straight. The exception is the scimitar oryx, which lacks dark markings on the legs, only has faint dark markings on the head, has an ochre neck, and has horns that are clearly decurved.

Dianchi Lake, also known as Lake Dian and Kunming Lake, is a large lake located on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau close to Kunming, Yunnan, China. Its nickname is the "Sparkling Pearl Embedded in a Highland" and it was the model for the Kunming Lake in the Summer Palace in Beijing. Its name is the source of Yunnan's Chinese abbreviation 滇.

Elasmobranchii is a subclass of Chondrichthyes or cartilaginous fish, including sharks, rays, skates, and sawfish. Members of this subclass are characterised by having five to seven pairs of gill clefts opening individually to the exterior, rigid dorsal fins and small placoid scales on the skin. The teeth are in several series; the upper jaw is not fused to the cranium, and the lower jaw is articulated with the upper. The details of this jaw anatomy vary between species, and help distinguish the different elasmobranch clades. The pelvic fins in males are modified to create claspers for the transfer of sperm. There is no swim bladder; instead, these fish maintain buoyancy with large livers rich in oil.

The Ethiopian wolf, also called the Simien jackal and Simien fox, is a canine native to the Ethiopian Highlands. In southeastern Ethiopia it is also known as the horse jackal. It is similar to the coyote in size and build, and is distinguished by its long and narrow skull, and its red and white fur. Unlike most large canids, which are widespread, generalist feeders, the Ethiopian wolf is a highly specialised feeder of Afroalpine rodents with very specific habitat requirements. It is one of the world's rarest canids, and Africa's most endangered carnivore.
Local extinction, also extirpation, is the termination of a species in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinctions.

The conservation status of a group of organisms indicates whether the group still exists and how likely the group is to become extinct in the near future. Many factors are taken into account when assessing conservation status: not simply the number of individuals remaining, but the overall increase or decrease in the population over time, breeding success rates, and known threats. Various systems of conservation status exist and are in use at international, multi-country, national and local levels as well as for consumer use.

The Malabar large-spotted civet, also known as the Malabar civet, is a viverrid endemic to the Western Ghats of India. It is listed as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List as the population is estimated to number fewer than 250 mature individuals. It has not been recorded during surveys carried out between 1990 and 2014. In the early 1990s, isolated populations still survived in less disturbed areas of South Malabar but were seriously threatened by habitat destruction and hunting outside protected areas.

The Indian elephant is one of three extant recognised subspecies of the Asian elephant and native to mainland Asia.

A least-concern species is a species that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as evaluated as not being a focus of species conservation because the specific species is still plentiful in the wild. They do not qualify as threatened, near threatened, or conservation dependent.

An IUCN Red List Critically Endangered species is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as facing an extremely high risk of extinction in the wild. As of 2021, of the 120,372 species currently tracked by the IUCN, there are 8,404 species that are considered to be Critically Endangered.

A species that is extinct in the wild (EW) is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as known only by living members kept in captivity or as a naturalized population outside its historic range due to massive habitat loss.
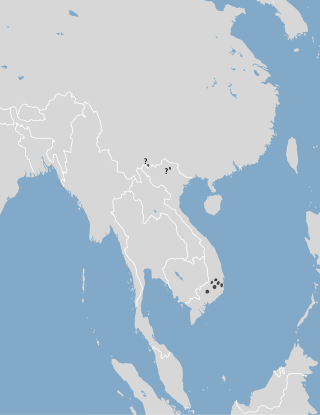
The small-toothed mole is a species of mammal in the family Talpidae. It is found in Di Linh, in southern Vietnam, and Rakho near the border of Vietnam and China, and in southern Yunnan, China, near the Vietnamese border. It is likely that it has a broader distribution, especially in places between the currently known locations.

The Lombok flying fox is a species of megabat in the genus Pteropus. It is endemic to Indonesia. This species has been listed on Appendix II of CITES since 1990, along with most others in the genus Pteropus. It was classified as "Least Concern" by the IUCN in 1996, but was changed to "Data Deficient" in 2008 due to uncertainty of the abundance and possible threats from hunting and habitat destruction.

Koslov's pika or Kozlov's pika is a species of mammal in the family Ochotonidae. It is endemic to China. Its natural habitat is tundra. It is threatened by habitat loss. Kozlov's pika are herbivores, they are known as "ecosystem engineers" as they're known to promote diversity of different plants species. Specifically, this species of Pikas has been enlisted as "endangered" in China. Kozlov Pikas are estimated to be within the Northern edge of the Arkatag Range in China.

The hawksbill sea turtle is a critically endangered sea turtle belonging to the family Cheloniidae. It is the only extant species in the genus Eretmochelys. The species has a global distribution, that is largely limited to tropical and subtropical marine and estuary ecosystems.
References
- ↑ Centre, World Conservation Monitoring (1990). 1990 IUCN Red List of Threatened Animals. IUCN. p. 157. ISBN 978-2-8317-0031-1.