| Part of a series on |
| Traditional African religions |
|---|
 |
Olapa, goddess of the moon, is married to Enkai (Ngai), god of the sun in Maasai mythology.
| Part of a series on |
| Traditional African religions |
|---|
 |
Olapa, goddess of the moon, is married to Enkai (Ngai), god of the sun in Maasai mythology.
The two fought one day, and Olapa, being a short tempered woman, inflicted Enkai with a wound. To hide his shame, he took to shining very brightly, so that no one could look straight at him. In revenge, Enkai hit Olapa back and struck out one of her eyes. This can be seen today, when the moon is full.
The word for moon and month (olapa) carries the masculine gender form 'ol' in the prefix.

Maasai Mara, also sometimes spelled Masai Mara and locally known simply as The Mara, is a large national game reserve in Narok, Kenya, contiguous with the Serengeti National Park in Tanzania. It is named in honor of the Maasai people, the ancestral inhabitants of the area, who migrated to the area from the Nile Basin. Their description of the area when looked at from afar: "Mara" means "spotted" in the local Maasai language, due to the many short bushy trees which dot the landscape.

The Maasai are a Nilotic ethnic group inhabiting northern, central and southern Kenya and northern Tanzania. They are among the best known local populations internationally due to their residence near the many game parks of the African Great Lakes, and their distinctive customs and dress. The Maasai speak the Maa language, a member of the Nilotic language family that is related to the Dinka, Kalenjin and Nuer languages. Except for some elders living in rural areas, most Maasai people speak the official languages of Kenya and Tanzania, Swahili and English. The Maasai population has been reported as numbering 1,189,522 in Kenya in the 2019 census, compared to 377,089 in the 1989 census.

The Serengeti ecosystem is a geographical region in Africa, spanning northern Tanzania. The protected area within the region includes approximately 30,000 km2 (12,000 sq mi) of land, including the Serengeti National Park and several game reserves. The Serengeti hosts the second largest terrestrial mammal migration in the world, which helps secure it as one of the Seven Natural Wonders of Africa, and as one of the ten natural travel wonders of the world.

The Kalenjin are a group of Southern Nilotic peoples indigenous to East Africa, residing mainly in what was formerly the Rift Valley Province in Kenya. They number 6,358,113 individuals as per the Kenyan 2019 census. They are divided into 11 culturally and linguistically related tribes: Kipsigis, Nandi, Keiyo, Marakwet, Sabaot, Pokots, Tugen, Terik, Sengwer, Lembus, and Ogiek. They speak Kalenjin languages, which belong to the Nilotic language family.
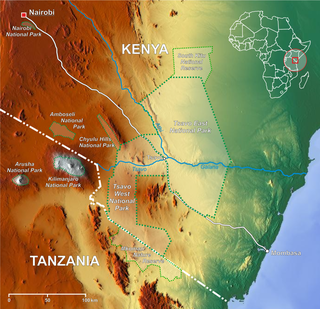
Amboseli National Park, formerly Maasai Amboseli Game Reserve, is a national park in Kajiado South Constituency in Kajiado County, Kenya. The park is 39,206 hectares in size at the core of an 8,000 km2 (3,100 sq mi) ecosystem that spreads across the Kenya-Tanzania border. The local people are mainly Maasai, but people from other parts of the country have settled there attracted by the successful tourist-driven economy and intensive agriculture along the system of swamps that makes this low-rainfall area, average 350 mm (14 in), one of the best wildlife-viewing experiences in the world with 400 species of birds including water birds like pelicans, kingfishers, crakes, hamerkop and 47 raptor species.

The Ngorongoro Conservation Area is a protected area and a World Heritage Site located 180 km (110 mi) west of Arusha in the Crater Highlands area of Tanzania. The area is named after Ngorongoro Crater, a large volcanic caldera within the area. The conservation area is administered by the Ngorongoro Conservation Area Authority, an arm of the Tanzanian government, and its boundaries follow the boundary of the Ngorongoro Division of the Arusha Region.
Ogiek is a Southern Nilotic language of the Kalenjin family spoken or once spoken by the Ogiek peoples, scattered groups of hunter-gatherers in Southern Kenya and Northern Tanzania. Most if not all Ogiek speakers have assimilated to cultures of surrounding peoples: the Akiek in northern Tanzania now speak Maasai and the Akiek of Kinare, Kenya now speak Gikuyu. Ndorobo is a term considered derogatory, occasionally used to refer to various groups of hunter-gatherers in this area, including the Ogiek.

Maasai (Masai) or Maa is an Eastern Nilotic language spoken in Southern Kenya and Northern Tanzania by the Maasai people, numbering about 800,000. It is closely related to the other Maa varieties: Samburu, the language of the Samburu people of central Kenya, Chamus, spoken south and southeast of Lake Baringo ; and Parakuyu of Tanzania. The Maasai, Samburu, il-Chamus and Parakuyu peoples are historically related and all refer to their language as ɔl Maa. Properly speaking, "Maa" refers to the language and the culture and "Maasai" refers to the people "who speak Maa."
Yaaku is an endangered Afroasiatic language spoken in Kenya. It is Cushitic, but its position within that family is unclear. Speakers are all older adults.
The Maasai mythology or Maasai religion are the traditional beliefs of the Maasai people of Kenya and Tanzania. In Maasai culture, nature and its elements are important facets of their religion. Ngai is the androgynous Supreme Creator, possessing both feminine and masculine principles. The Maasai refer to Ngai's primordial dwelling as "Ol Doinyo Lengai" which literally means "The Mountain of God", which they believe is located in Northern Tanzania.

Roosevelt in Africa is a film by Cherry Kearton, released in 1910. It is a documentary about the Smithsonian–Roosevelt African Expedition, featuring Theodore Roosevelt in Africa. It is shot in silent black and white.

The Okiek, sometimes called the Ogiek or Akiek, are a Southern Nilotic ethnic group native to Tanzania and Southern Kenya, and Western Kenya. In 2019 the ethnic Okiek population was 52,596, although the number of those speaking the Akiek language was as low as 500.
Le-eyo is a primal ancestor in Maasai mythology.
The earliest account of Nairobi's history dates back to 1899 when a railway depot was built in a brackish African swamp occupied only by a pastoralist people, the Maasai, the sedentary Akamba people, as well as the agriculturalist Kikuyu people who were all displaced by the colonialists. The railway complex and the building around it rapidly expanded and urbanized until it became the largest city of Kenya and the country's capital. The name "Nairobi" comes from the Maasai phrase Enkare Nyirobi, which translates to "the place of cool waters". However, Nairobi is popularly known as the "Green City in the Sun."

Olapa is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Francis Walker in 1855.

Assegai is Wilbur Smith's thirty-second novel, it follows The Triumph of the Sun in which the author brought the Courtney and Ballantyne series together. Assegai tells the story of Leon Courtney and is set in 1906 in Kenya. The events in the story are linked to and precede the outbreak of World War One.

Ongata Rongai is a town located in Kajiado County, Kenya. The town, situated 17 km (10.6 mi) south of the Nairobi Central Business District and East of the Ngong hills, lies 1,731 meters (5,682 feet) above sea level. According to the 2019 Census, it is the most populous town in Kajiado County and eleventh largest urban centre by population in Kenya.
Maasai may refer to:
Olapa tavetensis is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by William Jacob Holland in 1892.
Neiterkob is a figure from the mythology of the Maa-speaking communities, most notably the Maasai in the present day. He is perceived as having a superior intelligence and as having the ability to intercede with Engai or Enkai on behalf of man.