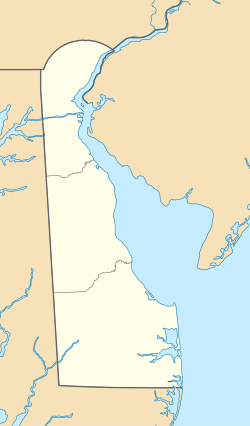
Donegal Mills Plantation is a historic grist mill complex located at East Donegal Township, Lancaster County, Pennsylvania. The complex consists of the mill, mansion, miller's house, and bake house. The mill was built in 1775, and is a three-story building. The original section of mansion was built before 1790, and is a two-story, stuccoed stone building with a gable roof. The mansion was expanded about 1820, with a frame kitchen wing, and about 1830, with a stone two-story addition. It features a full length, two-story, porch supported by five brick and stucco columns. The miller's house was originally built about, and is a 3 1/2-story, stuccoed stone building with a gable roof. It was expanded to its present size about 1830. The bake house is a two-story, gable roofed frame building. The property was auctioned in May 2010.

Colerain Forges Mansion is a historic home located at Franklin Township in Huntingdon County, Pennsylvania. It was built in four stages between the late-18th century and mid- to late-19th century. It appears as a two-story, five bay, "T"-shaped dwelling with a one-story, full-length porch in the Federal style. The oldest section is the two-story, plastered midsection. The frame portion to the east dates to the 1830s, and the brick section to the west to the 1840s. The rear section dates to the 1860s-1870s, and is a two-story board-and-batten structure. Also on the property is a 2 1/2-story, gable roofed stone outbuilding and a small board-and-batten shed. The house was built as the ironmaster's mansion at Colerain Forge.

Amos Palmer House is a historic farmhouse located in Lower Makefield Township, Bucks County, Pennsylvania. The original section was built about 1760, and is a two-story, double pile brick structure on a stone foundation. The house subsequently had four additions: a 2 1/2-story, single pile stone structure built about 1810; a 1 1/2-story, stone and rubble structure and frame shed roofed kitchen added about 1870; a two-story, frame kitchen addition built about 1900; and a small frame shed dated between about 1940 and 1980. The house is in the Georgian style.

David Leedom Farm, also known as "Pleasant Retreat," is a historic home and farm located at Newtown Township, Bucks County, Pennsylvania. The house was built in four stages, with the oldest dated to the late 18th century and consisting of a one-story, one roof stone structure. A large, 2 1/2-story stone addition was built in the late-18th century. In 1802, a three-story, stone "mansion" section was added. A two-story, frame addition was built in the early 1800s. The house features a series of piazzas and the interior of the mansion section has a three-story staircase. Also on the property are a variety of contributing farm-related buildings. The house was featured in one of four Newtown farmscape paintings by noted artist Edward Hicks (1780-1849).

Gardiner Wright Mansion, also known as The Marsh House, is a historic mansion located at Georgetown, Sussex County, Delaware. It was built in 1841, and is a two-story, three-bay, double pile, stuccoed brick dwelling. It is in the Regency style, with Second Empire and Italianate style design elements. The plan consists of two double-pile, single-bay, parallel rectangular sections, with a two-story brick central hall running between them. It was extensively renovated in the late-1940s. Also on the property are a contributing wood shed and two-level milk house.

Richards Mansion, also known as The Mansion House, is a historic mansion located at Georgetown, Sussex County, Delaware. The oldest section was built between 1796 and 1799, and is a two-story, four bay, single pile Federal style structure that is now the rear wing. The main house was built between 1835 and 1845, and is a three-story, five bay, frame structure in the Greek Revival style. The third floor was added in 1883, with the addition of a mansard roof in the Second Empire style.
Norwood House is a historic home located near Lewes, Sussex County, Delaware. It was built about 1850, and is two-story, three-bay, single-pile, frame house. It has a rectangular plan and sits on a brick foundation. The house is sheathed in weatherboard with cornerboards and has a shingled gable roof. A single story section extends down the entire length of the rear of the house and there is an earlier one-story section located on the north rear. Also on the property is a contributing privy. It is a virtually unaltered survivor of Belltown, a 19th-century "free colored" community.

Hopkins Covered Bridge Farm is a historic home and farm located near Lewes, Sussex County, Delaware. The house was built about 1868, and is a rectangular, two-story, five bay, single-pile, center-hall passage, frame dwelling with vernacular Gothic style details. It has a rectangular, two-story, three-bay, single pile, center passage, frame ell or wing. Both sections have gable roofs. The front facade has a three-bay, hipped roof porch. Also on the property are a contributing dairy barn designed by Rodney O'Neil, milk house (1925), and silo.

Jesse Robinson House was a historic home located at Seaford, Sussex County, Delaware, United States. It consisted of two sections: the rear wing, built about 1820 as a single-pile, one-room-plan frame house, and the front section, added about 1860 as a two-story single-pile, center-hall-plan frame structure. Five bays in width and resting on a brick foundation, it had design elements that mixed the Greek Revival and Italianate styles.

William Stevens House, also known as Peach Mansion, is a historic home located at Kenton, Kent County, Delaware. The house was built about 1860, and is a three-story, five bay, single pile frame dwelling in the Italianate style. It has a low hipped roof and a projecting box cornice with decorative brackets. The original house, built about 1811, forms the gable-roofed, three-bay, two-story, rear wing. Also on the property is a contributing 19th century springhouse.

Ivyside Farm is a historic home and farm located at Claymont, New Castle County, Delaware. It was built in three sections with the earliest dated to about 1795. The earliest section is a 2 1/2-story, two bay, single pile structure built of Brandywine granite. The second section was constructed in 1853, and is a two-story, three-bay, side-hall, double pile structure of Brandywine granite. It is in the Greek Revival style. In 1907, a two-story, gabled, shingle-sided section was added to the 1795 original structure and a two-story frame addition was built on the second section. Also on the property are a contributing large frame barn, wagon or carriage house, a corncrib and a chicken house.

Achmester is a historic home and national historic district located near Middletown, New Castle County, Delaware. It encompasses four contributing buildings and two contributing structures. Achmester was built in 1829, and is a 1 1/2-story, single pile "Peach Mansion." It consists of a five bay frame main block with a five bay gable end addition, and five bay rear service ell. It has a gable roof with dormers and sits on a stone foundation. The facade features simple box cornices and dormers decorated at a later date with Gothic Revival sawnwork trim, pendents, and vergeboards. The contributing outbuildings consist of a cow barn, shed, milk house, granary, and smokehouse. It was built by Richard Mansfield, a founder of Middletown Academy.

Abner Cloud House, also known as Sawmill Farm, Mansion Farm, and the John S. Petitdemange House, is a historic home located near Wilmington, New Castle County, Delaware. It was built about 1822, and consists of a two-story, side-gable, double-pile main section, a two-story, gable-roof, original kitchen wing; and a one-story, 20th century modern kitchen wing. It is constructed of stone and is in a vernacular Federal style. Also on the property is a 1 1/2-story gable-roof, frame and stone outbuilding.

Cobham Park, or Cobham Park Estate, is a historic estate located near Cobham, in Albemarle County and Louisa County, Virginia. The mansion was built in 1856, and is a rectangular 2 1/2-story, five bay, double pile structure covered by a hipped roof with three hipped roof dormers on each of the main slopes, and one dormer on each end. The house is an unusual example of ante-bellum period Georgian style architecture. It features front and rear, simple Doric order porches supported on square Ionic order columns. Also on the property are two smokehouses, one brick and one frame, a frame dependency, and a simple two-story frame dwelling. It was the summer home of William Cabell Rives, Jr., (1825-1890), second son of the noted United States senator and minister to France William Cabell Rives.

Ingleside is a historic home located near Amelia Courthouse, Amelia County, Virginia. The main section was built about 1824, and is a 2 1⁄2-story, single-pile frame building. It has a two-story, single-pile frame addition added about 1840. The house is in a late Federal style. Also on the property are a contributing two-story frame hay barn sheathed in weatherboard and a 2 1⁄2-story frame tobacco barn.

Spring Green is a historic home located near Mechanicsville, Hanover County, Virginia. It was built about 1800 and encompasses an earlier dwelling dated to about 1764. It is a 1 1/2-story, five bay, center hall, single pile frame dwelling in the Federal style. The oldest section includes the hall, east parlor with the old kitchen. The house sits on a brick foundation, has a gable roof with dormers, and exterior end chimneys. Also on the property is a contributing smokehouse.

Chester Plantation is a historic plantation house located at Disputanta, Prince George County, Virginia. The central section of the mansion was built circa 1845, as a two-story, single-pile, center hall-plan, Greek Revival style frame dwelling by Colonel Williamson Simmons. Chester remained in the Simmons family until 1918. The front facade features a two-story full-width porch, with full-height Doric order columns. A two-story rear wing was added in 1854, and flanking 1 1/2-story Colonial Revival style wings were added in 1949. Also on the property are the contributing icehouse and well house built in the 1840s, a secondary dwelling built in the 1920s, an open cart shed and concession building both constructed in the 1940s, and a swimming pool and pool house, dating from the 1940s when the estate was owned by prominent Petersburg businessman and politician Remmie L. Arnold.

Melrose, also known as the Williamson House, is a historic plantation house located near Yanceyville, Caswell County, North Carolina. It consists of two two-story, frame blocks connected by a 1 1/2-story breezeway. The original section dated to about 1780 and is a two-story, frame single pile block with Federal style details. The later section was built about 1840, and is a two-story, frame single pile block with Greek Revival style details. The later section features a portico supported by four unfluted Doric order columns. Also on the property is an octagonal, Williamsburg-style pump house with a conical roof.

The Lord Mansion is a historic house at 20 Summer Street in Kennebunk, Maine. The multi-part house includes a 1760 Georgian house as an ell to its main element, an 1801 Federal period structure. The house was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1973 for its architectural significance; it is also a contributing element to the Kennebunk Historic District.

The Hatheway House, also known as the Phelps-Hatheway House & Garden is a historic house museum at 55 South Main Street in Suffield, Connecticut. The sprawling house has sections built as early as 1732, with significant alterations made in 1795 to a design by Asher Benjamin for Oliver Phelps, a major land speculator. The house provides a window into a wide variety of 18th-century home construction methods. It is now maintained by Connecticut Landmarks, and is open seasonally between May and October. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1975.