Related Research Articles

Software is a collection of instructions and data that tell the computer how to work. This is in contrast to physical hardware, from which the system is built and actually performs the work. In computer science and software engineering, computer software is all information processed by computer systems, including programs and data. Computer software includes computer programs, libraries and related non-executable data, such as online documentation or digital media. Computer hardware and software require each other and neither can be realistically used on its own.
C is a general-purpose, procedural computer programming language supporting structured programming, lexical variable scope, and recursion, with a static type system. By design, C provides constructs that map efficiently to typical machine instructions. It has found lasting use in applications previously coded in assembly language. Such applications include operating systems and various application software for computer architectures that range from supercomputers to PLCs and embedded systems.

In physics, energy is the quantitative property that must be transferred to an object in order to perform work on, or to heat, the object. Energy is a conserved quantity; the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The SI unit of energy is the joule, which is the energy transferred to an object by the work of moving it a distance of 1 metre against a force of 1 newton.
Microsoft Windows, commonly referred to as Windows, is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families, all of which are developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. Active Microsoft Windows families include Windows NT and Windows IoT; these may encompass subfamilies,. Defunct Microsoft Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile, and Windows Phone.
macOS is a series of proprietary graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac computers. Within the market of desktop, laptop and home computers, and by web usage, it is the second most widely used desktop OS, after Microsoft Windows.

An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.

The International System of Units is the modern form of the metric system. It is the only system of measurement with an official status in nearly every country in the world. It comprises a coherent system of units of measurement starting with seven base units, which are the second, metre, kilogram, ampere, kelvin, mole, and candela. The system allows for an unlimited number of additional units, called derived units, which can always be represented as products of powers of the base units. Twenty-two derived units have been provided with special names and symbols. The seven base units and the 22 derived units with special names and symbols may be used in combination to express other derived units, which are adopted to facilitate measurement of diverse quantities. The SI system also provides twenty prefixes to the unit names and unit symbols that may be used when specifying power-of-ten multiples and sub-multiples of SI units. The SI is intended to be an evolving system; units and prefixes are created and unit definitions are modified through international agreement as the technology of measurement progresses and the precision of measurements improves.

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. The gametes produced by an organism define its sex: males produce small gametes while females produce large gametes. Individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Gametes can be identical in form and function, where male and female is generally not applied, but, in many cases, an asymmetry has evolved such that two different types of gametes (heterogametes) exist.
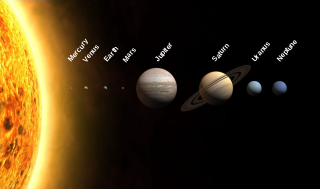
The Solar System is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it, either directly or indirectly. Of the objects that orbit the Sun directly, the largest are the eight planets, with the remainder being smaller objects, the dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies. Of the objects that orbit the Sun indirectly—the natural satellites—two are larger than the smallest planet, Mercury.

System of a Down is an Armenian-American heavy metal band formed in Glendale, California, in 1994. It currently consists of members Serj Tankian, Daron Malakian, Shavo Odadjian, and John Dolmayan (drums), who replaced original drummer Andy Khachaturian in 1997.

A geographic coordinate system (GCS) is a coordinate system associated with positions on Earth. A GCS can give positions:

The circulatory system, also called the cardiovascular system or the vascular system, is an organ system that permits blood to circulate and transport nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood cells to and from the cells in the body to provide nourishment and help in fighting diseases, stabilize temperature and pH, and maintain homeostasis. An organ system of human beings(and other animals) which is responsible for the transport of materials inside the body is called circulatory system. It is further divided into blood circulatory system and lymph circulatory system.

The Elo rating system is a method for calculating the relative skill levels of players in zero-sum games such as chess. It is named after its creator Arpad Elo, a Hungarian-American physics professor.

The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire is a British order of chivalry, rewarding contributions to the arts and sciences, work with charitable and welfare organisations, and public service outside the civil service. It was established on 4 June 1917 by King George V and comprises five classes across both civil and military divisions, the most senior two of which make the recipient either a knight if male or dame if female. There is also the related British Empire Medal, whose recipients are affiliated with, but not members of the order.
A multiplayer video game is a video game in which more than one person can play in the same game environment at the same time, either locally or online over the internet. Multiplayer games usually require players to share the resources of a single game system or use networking technology to play together over a greater distance; players may compete against one or more human contestants, work cooperatively with a human partner to achieve a common goal, or supervise other players' activity. Multiplayer games allow players interaction with other individuals in partnership, competition, or rivalry, providing them with social communication absent from single-player games.

A digital object identifier (DOI) is a persistent identifier or handle used to identify objects uniquely, standardized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). An implementation of the Handle System, DOIs are in wide use mainly to identify academic, professional, and government information, such as journal articles, research reports, data sets, and official publications. However, they also have been used to identify other types of information resources, such as commercial videos.
The English football league system, also known as the football pyramid, is a series of interconnected leagues for men's association football clubs in England, with five teams from Wales, one from Guernsey, one from Jersey and one from the Isle of Man also competing. The system has a hierarchical format with promotion and relegation between leagues at different levels, allowing even the smallest club the theoretical possibility of ultimately rising to the very top of the system. There are more than 140 individual leagues, containing more than 480 divisions.

Linux is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged in a Linux distribution.
High-definition television (HD) describes a television system providing an image resolution of substantially higher resolution than the previous generation of technologies. The term has been used since 1936, but in modern times refers to the generation following standard-definition television (SDTV), often abbreviated to HDTV or HD-TV. It is the current de facto standard video format used in most broadcasts: terrestrial broadcast television, cable television, satellite television and Blu-ray Discs.

Unix is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, development starting in the 1970s at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others.
References
- ↑ "GlobIZ search". Global Information System on Pyraloidea. Retrieved 2014-07-15.
- ↑ BOLD Systems
| This Omiodes-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |