The Coral Sea Islands Territory is an external territory of Australia which comprises a group of small and mostly uninhabited tropical islands and reefs in the Coral Sea, north-east of Queensland, Australia. The only inhabited island is Willis Island. The territory covers 780,000 km2 (301,160 sq mi), most of which is ocean, extending east and south from the outer edge of the Great Barrier Reef and includes Heralds Beacon Island, Osprey Reef, the Willis Group and fifteen other reef/island groups. Cato Island is the highest point in the Territory.
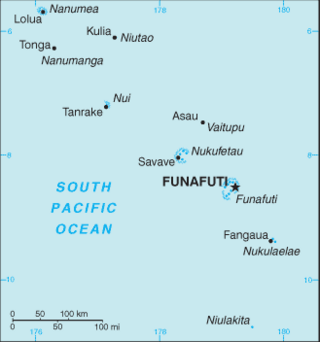
The Western Pacific nation of Tuvalu, formerly known as the Ellice Islands, is situated 4,000 kilometers (2,500 mi) northeast of Australia and is approximately halfway between Hawaii and Australia. It lies east-northeast of the Santa Cruz Islands, southeast of Nauru, south of Kiribati, west of Tokelau, northwest of Samoa and Wallis and Futuna and north of Fiji. It is a very small island country of 26 km2 (10 sq mi). Due to the spread out islands it has the 38th largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 749,790 km2 (289,500 sq mi).

An atoll is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical parts of the oceans and seas where corals can develop. Most of the approximately 440 atolls in the world are in the Pacific Ocean.

Vanua Levu, formerly known as Sandalwood Island, is the second largest island of Fiji. Located 64 kilometres to the north of the larger Viti Levu, the island has an area of 5,587.1 square kilometres (2,157.2 sq mi) and a population of 135,961 as of 2007.

Fongafale is the largest of Funafuti's islets in Tuvalu. It is a long narrow sliver of land, 12 kilometres long and between 10 and 400 metres wide, with the South Pacific Ocean and reef on the east and the protected lagoon on the west. The north part is the Tengako peninsula, and Funafuti International Airport runs from northeast to southwest on the widest part of the island, with the village and administrative centre of Vaiaku on the lagoon side.

The New Caledonian barrier reef is a barrier reef located in New Caledonia in the South Pacific, being the longest continuous barrier reef in the world and the third largest after the Great Barrier Reef of Australia and the Mesoamerican Barrier Reef.
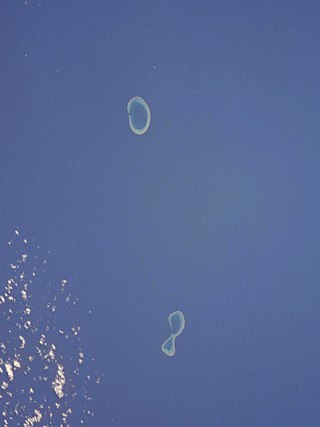
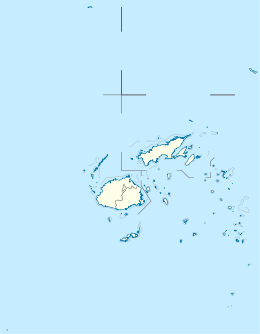
The Minerva Reefs are a group of two submerged atolls located in the Pacific Ocean between Fiji, Niue and Tonga. The islands are the subject of a territorial dispute between Fiji and Tonga, and in addition were briefly claimed by American Libertarians as the centre of a micronation, the Republic of Minerva.
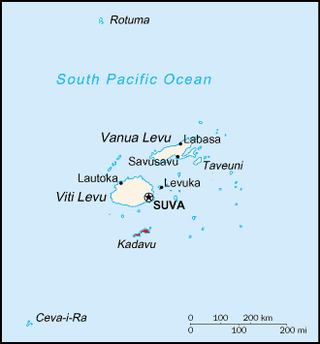
Kadavu, with an area of 411 square kilometres (159 sq mi), is the fourth largest island in Fiji, and the largest island in the Kadavu Group, a volcanic archipelago consisting of Kadavu, Ono, Galoa and a number of smaller islands in the Great Astrolabe Reef. Its main administrative centre is Vunisea, which has an airport, a high school, a hospital, and a government station, on the Namalata Isthmus where the island is almost cut in two. Suva, Fiji's capital, lies 88 kilometres to the north of Kadavu. The population of the island province was 10,167 at the most recent census in 2007.

Taveuni is the third-largest island in Fiji, after Viti Levu and Vanua Levu, with a total land area of 434 square kilometres. The cigar-shaped island, a massive shield volcano which rises from the floor of the Pacific Ocean, is situated 6.5 kilometres east of Vanua Levu, across the Somosomo Strait. It belongs to the Vanua Levu Group of islands and is part of Fiji's Cakaudrove Province within the Northern Division.
The Lau Islands of Fiji are situated in the southern Pacific Ocean, just east of the Koro Sea. Of this chain of about sixty islands and islets, about thirty are inhabited. The Lau Group covers a land area of 188 square miles, and had a population of 10,683 at the most recent census in 2007. While most of the northern Lau Group are high islands of volcanic origin, those of the south are mostly carbonate low islands.

Vatoa is an outlier of Fiji's Lau Group.

Fulaga is a crescent-shaped reef-limestone island in Fiji's Southern Lau Group.
Ogea Levu is a coral island on a barrier reef in Fiji's Southern Lau archipelago. With an area of 13.3 square kilometres, it is situated at 19.18° South and 178.47° West, 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) east of Fulaga. It has a maximum altitude of 82 metres (270 ft).

Vanua Balavu is the third largest island in Fiji's Lau archipelago, and the main island of the Northern Lau Group.
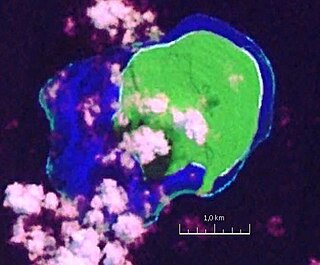
Vatu Vara Island is a Fijian island in the northwest sector of the Lau Group of islands.

Monuriki is a small, uninhabited island situated off the coast of Viti Levu in the Fiji Islands, in Melanesia in the South Pacific Ocean. Monuriki is part of the Atolls islands, and related to a group of three islets in the larger group of islands known as the Mamanuca Islands. This coral and volcanic island is the smallest islet and the southernmost of a small group of three islets, west of Tavua.

Funafuti is the capital of the island nation of Tuvalu. It has a population of 6,320 people, and so it has more people than the rest of Tuvalu combined, with approximately 60% of the population. It consists of a narrow sweep of land between 20 and 400 metres wide, encircling a large lagoon 18 km long and 14 km wide. The average depth of the Funafuti lagoon is about 20 fathoms. With a surface area of 275 square kilometres (106.2 sq mi), it is by far the largest lagoon in Tuvalu. The land area of the 33 islets around the atoll of Funafuti totals 2.4 square kilometres (0.9 sq mi); taken together, they constitute less than one percent of the total area of the atoll. Cargo ships can enter Funafuti's lagoon and dock at the port facilities on Fongafale.

The coral reefs of Tuvalu consist of three reef islands and six atolls, containing approximately 710 km2 (270 sq mi) of reef platforms. The islands of the Tuvalu archipelago are spread out between the latitude of 5° to 10° south and longitude of 176° to 180°, west of the International Date Line. The islands of Tuvalu are volcanic in origin. On the atolls, an annular reef rim surrounds the lagoon, and may include natural reef channels. The reef islands have a different structure to the atolls, and are described as reef platforms as they are smaller tabular reef platforms that do not have a salt-water lagoon, although they may have a completely closed rim of dry land, with the remnants of a lagoon that has no direct connection to the open sea or that may be drying up.

The Coral reefs of the Solomon Islands consists of six major islands and over 986 smaller islands, in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and northwest of Vanuatu. The Solomon Islands lie between latitudes 5° and 13°S, and longitudes 155° and 169°E. The distance between the westernmost and easternmost islands is about 1,500 km (930 mi). The Santa Cruz Islands are situated north of Vanuatu and are especially isolated at more than 200 km (120 mi) from the other islands. The Solomon Islands has the 22nd largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 1,589,477 km2 (613,701 sq mi) of the Pacific Ocean.