 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
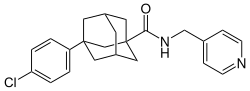
| Formula | C23H25ClN2O |
| Molar mass | 380.92 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Opaganib (ABC294640) is a drug which acts as an inhibitor of the enzyme sphingosine kinase 2, dihydroceramide desaturase (DES1), and glucosylceramide synthase (GCS). [1] It is under development as a potential treatment agent for several different kinds of cancer. [2] [3] Opaganib has also demonstrated antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 and has shown a reduction in mortality among patients with moderately severe COVID-19 in a multinational Phase 2/3 clinical trial and also appeared to exhibiting anti-inflammatory effects by reducing levels of IL-6 and TNF-alpha. [1] [4]