
A mirror, also known as a looking glass, is an object that reflects an image. Light that bounces off a mirror will show an image of whatever is in front of it, when focused through the lens of the eye or a camera. Mirrors reverse the direction of the image in an equal yet opposite angle from which the light shines upon it. This allows the viewer to see themselves or objects behind them, or even objects that are at an angle from them but out of their field of view, such as around a corner. Natural mirrors have existed since prehistoric times, such as the surface of water, but people have been manufacturing mirrors out of a variety of materials for thousands of years, like stone, metals, and glass. In modern mirrors, metals like silver or aluminium are often used due to their high reflectivity, applied as a thin coating on glass because of its naturally smooth and very hard surface.

Nonlinear optics (NLO) is the branch of optics that describes the behaviour of light in nonlinear media, that is, media in which the polarization density P responds non-linearly to the electric field E of the light. The non-linearity is typically observed only at very high light intensities (when the electric field of the light is >108 V/m and thus comparable to the atomic electric field of ~1011 V/m) such as those provided by lasers. Above the Schwinger limit, the vacuum itself is expected to become nonlinear. In nonlinear optics, the superposition principle no longer holds.

Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation, and other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties.

Photonics is a branch of optics that involves the application of generation, detection, and manipulation of light in form of photons through emission, transmission, modulation, signal processing, switching, amplification, and sensing. Photonics is closely related to quantum electronics, where quantum electronics deals with the theoretical part of it while photonics deal with its engineering applications. Though covering all light's technical applications over the whole spectrum, most photonic applications are in the range of visible and near-infrared light. The term photonics developed as an outgrowth of the first practical semiconductor light emitters invented in the early 1960s and optical fibers developed in the 1970s.
Mode locking is a technique in optics by which a laser can be made to produce pulses of light of extremely short duration, on the order of picoseconds (10−12 s) or femtoseconds (10−15 s). A laser operated in this way is sometimes referred to as a femtosecond laser, for example, in modern refractive surgery. The basis of the technique is to induce a fixed phase relationship between the longitudinal modes of the laser's resonant cavity. Constructive interference between these modes can cause the laser light to be produced as a train of pulses. The laser is then said to be "phase-locked" or "mode-locked".

In physics, a plasmon is a quantum of plasma oscillation. Just as light consists of photons, the plasma oscillation consists of plasmons. The plasmon can be considered as a quasiparticle since it arises from the quantization of plasma oscillations, just like phonons are quantizations of mechanical vibrations. Thus, plasmons are collective oscillations of the free electron gas density. For example, at optical frequencies, plasmons can couple with a photon to create another quasiparticle called a plasmon polariton.
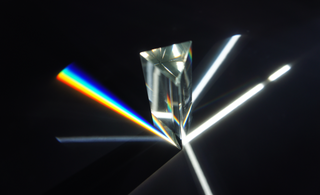
An optical prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that are designed to refract light. At least one surface must be angled — elements with two parallel surfaces are not prisms. The most familiar type of optical prism is the triangular prism, which has a triangular base and rectangular sides. Not all optical prisms are geometric prisms, and not all geometric prisms would count as an optical prism. Prisms can be made from any material that is transparent to the wavelengths for which they are designed. Typical materials include glass, acrylic and fluorite.

In the field of optics, transparency is the physical property of allowing light to pass through the material without appreciable scattering of light. On a macroscopic scale, the photons can be said to follow Snell's law. Translucency allows light to pass through but does not necessarily follow Snell's law; the photons can be scattered at either of the two interfaces, or internally, where there is a change in the index of refraction. In other words, a translucent material is made up of components with different indices of refraction. A transparent material is made up of components with a uniform index of refraction. Transparent materials appear clear, with the overall appearance of one color, or any combination leading up to a brilliant spectrum of every color. The opposite property of translucency is opacity. Other categories of visual appearance, related to the perception of regular or diffuse reflection and transmission of light, have been organized under the concept of cesia in an order system with three variables, including transparency, translucency and opacity among the involved aspects.

Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. Common examples include the reflection of light, sound and water waves. The law of reflection says that for specular reflection the angle at which the wave is incident on the surface equals the angle at which it is reflected.

An optical coating is one or more thin layers of material deposited on an optical component such as a lens, prism or mirror, which alters the way in which the optic reflects and transmits light. These coatings have become a key technology in the field of optics. One type of optical coating is an anti-reflective coating, which reduces unwanted reflections from surfaces, and is commonly used on spectacle and camera lenses. Another type is the high-reflector coating, which can be used to produce mirrors that reflect greater than 99.99% of the light that falls on them. More complex optical coatings exhibit high reflection over some range of wavelengths, and anti-reflection over another range, allowing the production of dichroic thin-film filters.
A collimator is a device which narrows a beam of particles or waves. To narrow can mean either to cause the directions of motion to become more aligned in a specific direction, or to cause the spatial cross section of the beam to become smaller.

Diamond turning is turning using a cutting tool with a diamond tip. It is a process of mechanical machining of precision elements using lathes or derivative machine tools equipped with natural or synthetic diamond-tipped tool bits. The term single-point diamond turning (SPDT) is sometimes applied, although as with other lathe work, the "single-point" label is sometimes only nominal. The process of diamond turning is widely used to manufacture high-quality aspheric optical elements from crystals, metals, acrylic, and other materials. Plastic optics are frequently molded using diamond turned mold inserts. Optical elements produced by the means of diamond turning are used in optical assemblies in telescopes, video projectors, missile guidance systems, lasers, scientific research instruments, and numerous other systems and devices. Most SPDT today is done with computer numerical control (CNC) machine tools. Diamonds also serve in other machining processes, such as milling, grinding, and honing. Diamond turned surfaces have a high specular brightness and require no additional polishing or buffing, unlike other conventionally machined surfaces.

Zinc telluride is a binary chemical compound with the formula ZnTe. This solid is a semiconductor material with a direct band gap of 2.26 eV. It is usually a p-type semiconductor. Its crystal structure is cubic, like that for sphalerite and diamond.
An optical waveguide is a physical structure that guides electromagnetic waves in the optical spectrum. Common types of optical waveguides include optical fiber waveguides, transparent dielectric waveguides made of plastic and glass, liquid light guides, and liquid waveguides.
Nanophotonics or nano-optics is the study of the behavior of light on the nanometer scale, and of the interaction of nanometer-scale objects with light. It is a branch of optics, optical engineering, electrical engineering, and nanotechnology. It often involves dielectric structures such as nanoantennas, or metallic components, which can transport and focus light via surface plasmon polaritons.
A hybrid silicon laser is a semiconductor laser fabricated from both silicon and group III-V semiconductor materials. The hybrid silicon laser was developed to address the lack of a silicon laser to enable fabrication of low-cost, mass-producible silicon optical devices. The hybrid approach takes advantage of the light-emitting properties of III-V semiconductor materials combined with the process maturity of silicon to fabricate electrically driven lasers on a silicon wafer that can be integrated with other silicon photonic devices.

Electro-optic rectification (EOR), also referred to as optical rectification, is a non-linear optical process that consists of the generation of a quasi-DC polarization in a non-linear medium at the passage of an intense optical beam. For typical intensities, optical rectification is a second-order phenomenon which is based on the inverse process of the electro-optic effect. It was reported for the first time in 1962, when radiation from a ruby laser was transmitted through potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) and potassium dideuterium phosphate (KDdP) crystals.

A photonic metamaterial (PM), also known as an optical metamaterial, is a type of electromagnetic metamaterial, that interacts with light, covering terahertz (THz), infrared (IR) or visible wavelengths. The materials employ a periodic, cellular structure.
A nonlinear metamaterial is an artificially constructed material that can exhibit properties not yet found in nature. Its response to electromagnetic radiation can be characterized by its permittivity and material permeability. The product of the permittivity and permeability results in the refractive index. Unlike natural materials, nonlinear metamaterials can produce a negative refractive index. These can also produce a more pronounced nonlinear response than naturally occurring materials.
Linear optics is a sub-field of optics, consisting of linear systems, and is the opposite of nonlinear optics. Linear optics includes most applications of lenses, mirrors, waveplates, diffraction gratings, and many other common optical components and systems.












