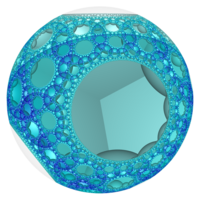
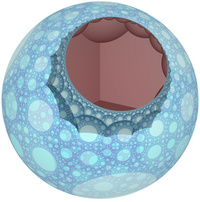
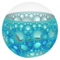
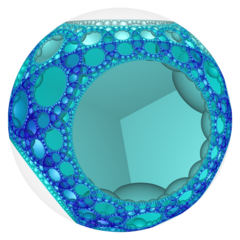
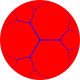
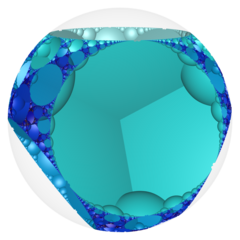
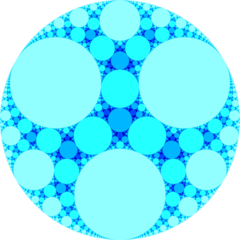
In the field of hyperbolic geometry, the order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb arises as one of 11 regular paracompact honeycombs in 3-dimensional hyperbolic space. It is paracompact because it has cells composed of an infinite number of faces. Each cell is a hexagonal tiling whose vertices lie on a horosphere: a flat plane in hyperbolic space that approaches a single ideal point at infinity.
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-7 dodecahedral honeycomb is a regular space-filling tessellation.

In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-3-7 hexagonal honeycomb or a regular space-filling tessellation with Schläfli symbol {6,3,7}.
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the heptagonal tiling honeycomb or 7,3,3 honeycomb a regular space-filling tessellation. Each infinite cell consists of a heptagonal tiling whose vertices lie on a 2-hypercycle, each of which has a limiting circle on the ideal sphere.
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-7 cubic honeycomb is a regular space-filling tessellation. With Schläfli symbol {4,3,7}, it has seven cubes {4,3} around each edge. All vertices are ultra-ideal with infinitely many cubes existing around each vertex in an order-7 triangular tiling vertex arrangement.
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-3-5 heptagonal honeycomb a regular space-filling tessellation. Each infinite cell consists of a heptagonal tiling whose vertices lie on a 2-hypercycle, each of which has a limiting circle on the ideal sphere.
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-3-6 heptagonal honeycomb a regular space-filling tessellation. Each infinite cell consists of a heptagonal tiling whose vertices lie on a 2-hypercycle, each of which has a limiting circle on the ideal sphere.
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-3-7 heptagonal honeycomb a regular space-filling tessellation with Schläfli symbol {7,3,7}.
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-5 octahedral honeycomb is a regular space-filling tessellation with Schläfli symbol {3,4,5}. It has five octahedra {3,4} around each edge. All vertices are ultra-ideal with infinitely many octahedra existing around each vertex in an order-5 square tiling vertex arrangement.
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-4 icosahedral honeycomb is a regular space-filling tessellation with Schläfli symbol {3,5,4}.
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-6-4 triangular honeycomb is a regular space-filling tessellation with Schläfli symbol {3,6,4}.
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-4-3 pentagonal honeycomb or 5,4,3 honeycomb is a regular space-filling tessellation. Each infinite cell is an order-4 pentagonal tiling whose vertices lie on a 2-hypercycle, each of which has a limiting circle on the ideal sphere.
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-4-4 pentagonal honeycomb a regular space-filling tessellation. Each infinite cell consists of a pentagonal tiling whose vertices lie on a 2-hypercycle, each of which has a limiting circle on the ideal sphere.
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-5-3 square honeycomb or 4,5,3 honeycomb a regular space-filling tessellation. Each infinite cell consists of a pentagonal tiling whose vertices lie on a 2-hypercycle, each of which has a limiting circle on the ideal sphere.
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-5-4 square honeycomb a regular space-filling tessellation with Schläfli symbol {4,5,4}.
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-7-3 triangular honeycomb is a regular space-filling tessellation with Schläfli symbol {3,7,3}.
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-6-3 square honeycomb or 4,6,3 honeycomb is a regular space-filling tessellation. Each infinite cell consists of a hexagonal tiling whose vertices lie on a 2-hypercycle, each of which has a limiting circle on the ideal sphere.
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-6-4 square honeycomb a regular space-filling tessellation with Schläfli symbol {4,6,4}.
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-8-3 triangular honeycomb is a regular space-filling tessellation with Schläfli symbol {3,8,3}.
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-infinite-3 triangular honeycomb is a regular space-filling tessellation with Schläfli symbol {3,∞,3}.