
The 144th Guards Yelnya Red Banner Order of Suvorov Motor Rifle Division is a motorized infantry division of the Russian Ground Forces, reestablished in 2016 with its headquarters at Yelnya, Smolensk Oblast.

Vovchansk is a city in Chuhuiv Raion, Kharkiv Oblast, northeastern Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Vovchansk urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Population: 17,459, about 300 (2024). The city was largely destroyed during the 2024 Kharkiv offensive.

The Order of Lenin Leningrad Military District is a military district of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation. The district was awarded the Order of Lenin in 1968. In 2010, it was merged with the Moscow Military District, the Northern Fleet and the Baltic Fleet to form the new Western Military District. In December 2022, Defense Minister Sergey Shoigu proposed to reestablish it along with the Moscow Military District, a decision confirmed in June 2023 by Deputy Chief of the General Staff Yevgeny Burdinsky. On December 17, 2023, Russian President Vladimir Putin announced plans to recreate the Leningrad Military District as a reaction to Finland joining NATO. The district was formally reconstituted on 26 February 2024 by a Presidential Decree No.141, transferring the Northern Fleet under its command.

The 6th Red Banner Combined Arms Army is a field army of the Red Army and the Soviet Army that was active with the Russian Ground Forces until 1998 and has been active since 2010 as the 6th Combined Arms Army. Military Unit number в/ч 31807.

The 19th Voronezh-Shumlinskaya Red Banner Order of Suvorov and Red Banner of Labor Motor Rifle Division, is a division of the Russian Ground Forces. It appears to have been formed originally in July 1922 at Tambov in the Moscow Military District as a territorial formation. In 1923 it was awarded the 'Tambov' placename and renamed the 19th Voronezh Rifle Division. The division was downsized to a brigade in 2009 and reestablished as a division in 2020.

The 138th Guards Separate Motor Rifle Brigade is a formation of the Russian Ground Forces. It is stationed in the Leningrad Military District, in the village of Kamenka, Vyborgsky District, Leningrad Oblast. It is Military unit No. 02511. It includes various components: air defense, artillery battalion, infantry and tank battalions.

The Western Military District was a military district of Russia, in existence from 2010 until its abolishment as a unitary military command on February 26, 2024, succeeded by the newly reconstituted Moscow Military District and Leningrad Military District.

The 27th Guards Omsk-Novoburgskaya Red Banner Order of Bogdan Khmelnitskiy Motorised Rifle Division is a Guards mechanised infantry division of the Russian Ground Forces. It was a Red Army rifle division in World War II which later became a Soviet Ground Forces motor rifle division. In 2009, it was reformed into the 21st Guards Motor Rifle Brigade. In the spring of 2024, the 27th Guards Motorized Rifle Division was revived.

The 47th Czestochowa Red Banner Order of Kutuzov Tank Division is a formation of the Russian Ground Forces. The late 6th Tank Brigade fought in the war in Donbas of 2014–2015. In 2022, the brigade was reorganized into the 47th Tank Division, retaining its historical form, awards, and combat glory.

The 14th Army Corps is a tactical formation of the Russian Navy formed in 2017 as part of the Northern Fleet and the Leningrad Military District. It is the tactical command of the Northern Fleet's coastal defence troops.

The 11th Army Corps, is a tactical formation of the Coastal Troops of the Russian Navy, formed in 2016 as part of the Baltic Fleet, currently in the Leningrad Military District.
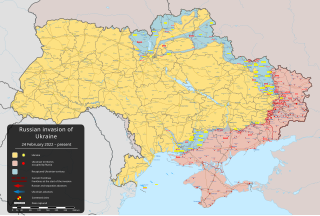
This is the order of battle for the Russian invasion of Ukraine. It should not be considered completely up to date nor accurate, being based on open-source press reporting.

Ukraine's easternmost oblasts, Donetsk, Luhansk, and Kharkiv, have been the site of an ongoing theatre of operation since the start of the Russian invasion of Ukraine in February 2022.

The 3rd Army Corps is a military formation of the Russian Ground Forces formed in June 2022 to participate in the Russian invasion of Ukraine. The 3rd Corps was raised in response to the depletion of trained manpower during the early months of the invasion. It was formed exclusively by volunteers, as at that point Russia had not yet begun the process of partial mobilization and preferred to avoid or delay doing so. Recruitment was on a regional basis, with federal subject administrations and local authorities conducting recruitment campaigns. Its planned strength was estimated to comprise 15,000–60,000 personnel, but as of January 2023, it only had 10,000–15,000. It originally belonged to the Western Military District, before moving under the command of the Central Military District in 2023.

The 51st Donetsk Combined Arms Army is a military formation of the Russian Ground Forces as part of the Southern Military District, formerly the 1st Army Corps of the Donetsk People's Republic. It was officially incorporated into the Russian Federation on 31 December 2022, after Russia annexed the occupied territory of Donetsk, and then reformed into a Combined Arms Army in 2024.
On 10 May 2024, the Russian Armed Forces began an offensive operation in Ukraine's Kharkiv Oblast, shelling and attempting to breach the defenses of the Ukrainian Armed Forces in the direction of Vovchansk and Kharkiv. The Guardian reported that the offensive has led to Russia's biggest territorial gains in 18 months. By early June the Russian offensive stalled, with The Guardian reporting that the situation on the frontline had been "stabilized." Ukrainian forces then began a concerted counterattack, which liberated its first settlement on 19 June.
The 2023 Ukrainian counteroffensive was a major offensive against Russian forces occupying Ukrainian territory with the goal of breaching the front lines. Efforts were made in many directions, primarily in the Donetsk and Zaporizhzhia oblasts. In total, Ukraine recaptured 14 villages with a total pre-war population of around 5,000 but suffered heavy casualties in the process. Western officials have said that such losses were not unexpected for attacking forces. The counteroffensive was widely regarded as a crucial moment in the war but also as a failure for Ukrainian forces.
Tykhe is a village in Vovchansk urban hromada, Chuhuiv Raion, Kharkiv Oblast, eastern Ukraine. It is located 60.48 kilometres (37.58 mi) northeast by east (NEbE) of the centre of Kharkiv city, about 4.09 kilometres (2.54 mi) south of the Russia–Ukraine border.
The 272nd Motor Rifle Regiment, is an active regiment of the Russian Ground Forces. It is a part of the Moscow Military District, the 1st Guards Tank Army anf the 47th Tank Division.
On 18 July 2024, Russian forces began an offensive with the goal of capturing the strategically important city of Pokrovsk. Pokrovsk serves as an important supply route and as a transportation hub for the Ukrainian Armed Forces.
 Russian Airborne Forces
Russian Airborne Forces  83rd Guards Air Assault Brigade - Guards Colonel Aleksandr Kornev [3]
83rd Guards Air Assault Brigade - Guards Colonel Aleksandr Kornev [3]  98th Guards Airborne Division - Guards Colonel Viktor Igoryevich Gunaza[ citation needed ]
98th Guards Airborne Division - Guards Colonel Viktor Igoryevich Gunaza[ citation needed ] 217th Guards Airborne Regiment - Guards Lieutenant Colonel Viktor Vasilyevich Droedov[ citation needed ]
217th Guards Airborne Regiment - Guards Lieutenant Colonel Viktor Vasilyevich Droedov[ citation needed ] Russian Aerospace Forces [4]
Russian Aerospace Forces [4]  Russian Ground Forces
Russian Ground Forces  Moscow Military District
Moscow Military District  1st Guards Tank Army
1st Guards Tank Army  20th Guards Combined Arms Army - Major General Sukhrab Akhmedov
20th Guards Combined Arms Army - Major General Sukhrab Akhmedov  3rd Motor Rifle Division - Major General Aleksei Vyacheslavovich Avdeyev[ citation needed ]
3rd Motor Rifle Division - Major General Aleksei Vyacheslavovich Avdeyev[ citation needed ] 144th Guards Motor Rifle Division - Colonel Aleksey Alekseyevich Polyakov [11]
144th Guards Motor Rifle Division - Colonel Aleksey Alekseyevich Polyakov [11]  Southern Military District
Southern Military District  8th Guards Combined Arms Army
8th Guards Combined Arms Army  51st Combined Arms Army
51st Combined Arms Army  Leningrad Military District
Leningrad Military District  6th Combined Arms Army - Alexander Vasilyevich Peryazev [14]
6th Combined Arms Army - Alexander Vasilyevich Peryazev [14]  25th Separate Guards Motor Rifle Brigade - Colonel Andrei Arkhipov [15]
25th Separate Guards Motor Rifle Brigade - Colonel Andrei Arkhipov [15]  138th Separate Guards Motor Rifle Brigade - Guards Colonel Sergei Maksimov [16]
138th Separate Guards Motor Rifle Brigade - Guards Colonel Sergei Maksimov [16]  Central Military District
Central Military District  90th Guards Tank Division - Colonel Ramil Rakhmatulovich Ibatullin[ citation needed ]
90th Guards Tank Division - Colonel Ramil Rakhmatulovich Ibatullin[ citation needed ] Storm-Z - Yevgeny Burdinsky [24]
Storm-Z - Yevgeny Burdinsky [24]  Russian Navy
Russian Navy  Black Sea Fleet
Black Sea Fleet  Baltic Fleet
Baltic Fleet  Leningrad Military District
Leningrad Military District  Pacific Fleet
Pacific Fleet  Kadyrovites [32]
Kadyrovites [32] ![]() Main Directorate of the General Staff
Main Directorate of the General Staff  2nd Guards Spetsnaz Brigade - Konstantin Bushuev [34]
2nd Guards Spetsnaz Brigade - Konstantin Bushuev [34] 












