
The darters, anhingas, or snakebirds are mainly tropical waterbirds in the family Anhingidae, which contains a single genus, Anhinga. There are four living species, three of which are very common and widespread while the fourth is rarer and classified as near-threatened by the IUCN. The term snakebird is usually used without any additions to signify whichever of the completely allopatric species occurs in any one region. It refers to their long thin neck, which has a snake-like appearance when they swim with their bodies submerged, or when mated pairs twist it during their bonding displays. "Darter" is used with a geographical term when referring to particular species. It alludes to their manner of procuring food, as they impale fishes with their thin, pointed beak. The American darter is more commonly known as the anhinga. It is sometimes called "water turkey" in the southern United States; though the anhinga is quite unrelated to the wild turkey, they are both large, blackish birds with long tails that are sometimes hunted for food.

The Anatidae are the biological family of water birds that includes ducks, geese, and swans. The family has a cosmopolitan distribution, occurring on all the world's continents except Antarctica. These birds are adapted for swimming, floating on the water surface, and, in some cases, diving in at least shallow water. The family contains around 174 species in 43 genera.

The bird family Sulidae comprises the gannets and boobies. Collectively called sulids, they are medium-large coastal seabirds that plunge-dive for fish and similar prey. The 10 species in this family are often considered congeneric in older sources, placing all in the genus Sula. However, Sula and Morus (gannets) can be readily distinguished by morphological, behavioral, and DNA sequence characters. Abbott's booby (Papasula) is given its own genus, as it stands apart from both in these respects. It appears to be a distinct and ancient lineage, maybe closer to the gannets than to the true boobies.

The Cryptobranchidae are a family of large salamanders that are fully aquatic. The family includes some of the largest living amphibians. They are native to China, Japan, and the eastern United States. Giant salamanders constitute one of two living families—the other being the Asiatic salamanders belonging to the family Hynobiidae—within the Cryptobranchoidea, one of two main divisions of living salamanders.

Plethodontidae, or lungless salamanders, are a family of salamanders. With over 500 species, lungless salamanders are by far the largest family of salamanders in terms of their diversity. Most species are native to the Western Hemisphere, from British Columbia to Brazil. Only two extant genera occur in the Eastern Hemisphere: Speleomantes and Karsenia.

The family Proteidae is a group of aquatic salamanders found today in the Balkan Peninsula and North America. The range of the genus Necturus runs from southern central Canada, through the midwestern United States, east to North Carolina and south to Georgia and Mississippi. The range of the olm, the only extant member of the genus Proteus, is limited to the Western Balkans. The fossil record of the family extends back to the Late Cretaceous, with Paranecturus being known from the Maastrichtian of North America, and Bishara from the Santonian-Campanian of Central Asia.

Anas is a genus of dabbling ducks. It includes the pintails, most teals, and the mallard and its close relatives. It formerly included additional species but following the publication of a molecular phylogenetic study in 2009 the genus was split into four separate genera. The genus now contains 31 living species. The name Anas is the Latin for "duck".

The olm or proteus is an aquatic salamander which is the only species in the genus Proteus of the family Proteidae and the only exclusively cave-dwelling chordate species found in Europe; the family's other extant genus is Necturus. In contrast to most amphibians, it is entirely aquatic, eating, sleeping, and breeding underwater. Living in caves found in the Dinaric Alps, it is endemic to the waters that flow underground through the extensive limestone bedrock of the karst of Central and Southeastern Europe in the basin of the Soča River near Trieste, Italy, southern Slovenia, southwestern Croatia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina. Introduced populations are found near Vicenza, Italy, and Kranj, Slovenia. It was first mentioned in 1689 by the local naturalist Valvasor in his Glory of the Duchy of Carniola, who reported that, after heavy rains, the olms were washed up from the underground waters and were believed by local people to be a cave dragon's offspring.

Oriental giant squirrels are cat-sized tree squirrels from the genus Ratufa in the subfamily Ratufinae. They are a distinctive element of the fauna of south and southeast Asia.

Scapanorhynchus is an extinct genus of goblin shark that lived during the Cretaceous period, from the Aptian to the end of the Maastrichtian. Later records, such as those from the Miocene assigned to the species S. subulatus, are highly dubious and may be misidentified sand sharks.

Öhningen is a municipality on the western edge of Lake Constance where it forms the border between Switzerland and the district of Konstanz in Baden-Württemberg in Germany.

Andrias scheuchzeri is an extinct species of giant salamander belonging to the genus Andrias, which also contains the closely related living Asian giant salamanders. It is known from Oligocene to Pliocene aged deposits primarily from Central Europe, but possibly as far east as Western Siberia and eastern Kazakhstan.

Chelotriton is an extinct genus of prehistoric salamanders that lived in Europe and Central Asia during the Neogene. It closely resembles the extant genera Tylototriton and Echinotriton.
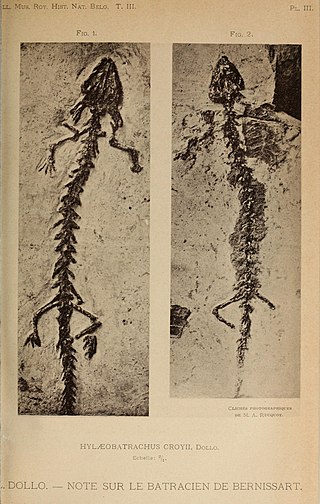
Hylaeobatrachus is an extinct genus of prehistoric salamander, known from the Early Cretaceous of Europe. The type species H. croyii is known from the Sainte-Barbe Clays Formation at the Iguanodon locality of Belgium, and was described by Louis Dollo. An unnamed Hylaeobatrachus-like taxon has also been reported from Las Hoyas, Spain. Both localities are of Barremian age. Hylaeobatrachus belongs to the crown group of modern salamanders, though its exact relationship with modern salamander groups is uncertain. It was neotenic, llike some modern salamanders.
Koalliella is an extinct genus of prehistoric salamander. It is the oldest known salamandrid.

Mioproteus is an extinct genus of prehistoric salamanders from Neogene Europe. Its living relatives are the olm and the mudpuppies. The species M. caucasicus is from the Middle Miocene. The species M. wezei first appears in the fossil record during the Pliocene, then disappears during the Middle Pleistocene.

The Ville Formation is a geologic formation in Germany. It preserves fossils dating back to the Neogene period. Lignite of the Ville Formation is excavated in North Rhine-Westphalia.
Batrachosauroididae is an extinct family of prehistoric salamanders with holarctic distribution. They were paedomorphic and presumably aquatic. They are possibly the sister taxon of Proteidae, an extant family of aquatic salamanders. They are definitively known from the Late Cretaceous to Miocene of North America and Europe. Remains from the earliest Cretaceous (Berriasian) Lulworth Formation of England have tenatively been attributed to this family.















