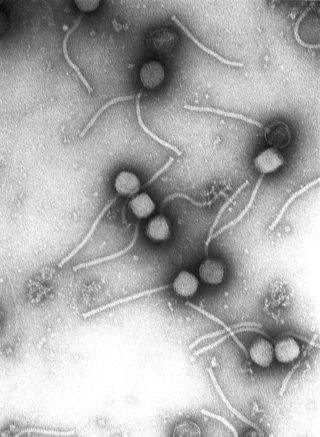
Virology is the scientific study of biological viruses. It is a subfield of microbiology that focuses on their detection, structure, classification and evolution, their methods of infection and exploitation of host cells for reproduction, their interaction with host organism physiology and immunity, the diseases they cause, the techniques to isolate and culture them, and their use in research and therapy.

Filoviridae is a family of single-stranded negative-sense RNA viruses in the order Mononegavirales. Two members of the family that are commonly known are Ebola virus and Marburg virus. Both viruses, and some of their lesser known relatives, cause severe disease in humans and nonhuman primates in the form of viral hemorrhagic fevers.

Hepatitis A is an infectious disease of the liver caused by Hepatovirus A (HAV); it is a type of viral hepatitis. Many cases have few or no symptoms, especially in the young. The time between infection and symptoms, in those who develop them, is two–six weeks. When symptoms occur, they typically last eight weeks and may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, jaundice, fever, and abdominal pain. Around 10–15% of people experience a recurrence of symptoms during the 6 months after the initial infection. Acute liver failure may rarely occur, with this being more common in the elderly.

The genus Ebolavirus is a virological taxon included in the family Filoviridae, order Mononegavirales. The members of this genus are called ebolaviruses, and encode their genome in the form of single-stranded negative-sense RNA. The six known virus species are named for the region where each was originally identified: Bundibugyo ebolavirus, Reston ebolavirus, Sudan ebolavirus, Taï Forest ebolavirus, Zaire ebolavirus, and Bombali ebolavirus. The last is the most recent species to be named and was isolated from Angolan free-tailed bats in Sierra Leone. Each species of the genus Ebolavirus has one member virus, and four of these cause Ebola virus disease (EVD) in humans, a type of hemorrhagic fever having a very high case fatality rate. The Reston virus has caused EVD in other primates. Zaire ebolavirus has the highest mortality rate of the ebolaviruses and is responsible for the largest number of outbreaks of the six known species of the genus, including the 1976 Zaire outbreak and the outbreak with the most deaths (2014).

Bunyavirales is an order of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses with mainly tripartite genomes. Member viruses infect arthropods, plants, protozoans, and vertebrates. It is the only order in the class Ellioviricetes. The name Bunyavirales derives from Bunyamwera, where the original type species Bunyamwera orthobunyavirus was first discovered. Ellioviricetes is named in honor of late virologist Richard M. Elliott for his early work on bunyaviruses.
Bwamba orthobunyavirus (BWAV) belongs to the genus Orthobunyavirus and the order Bunyavirales RNA viruses. BWAV is present in large parts of Africa, endemic in Mozambique, Tanzania and Uganda. It is transmitted to humans through mosquito bites and results in a brief benign generalised infection with headache, skin rash, diarrhea and joint pain and lasts 4–5 days. The animal reservoir of the virus includes birds, monkeys and donkeys.

Crimean–Congo hemorrhagic fever (CCHF) is a viral disease. Symptoms of CCHF may include fever, muscle pains, headache, vomiting due to loss of net saline of basal cells, diarrhea, and bleeding into the skin. Onset of symptoms is less than two weeks following exposure. Complications may include liver failure. Survivors generally recover around two weeks after onset.
Orbivirus is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses in the family Reoviridae and subfamily Sedoreovirinae. Unlike other reoviruses, orbiviruses are arboviruses. They can infect and replicate within a wide range of arthropod and vertebrate hosts. Orbiviruses are named after their characteristic doughnut-shaped capsomers.

The little collared fruit bat is a species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae found in Angola, Cameroon, the Central African Republic, the Republic of the Congo, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Liberia, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, South Sudan, Togo, and Uganda. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests and moist savanna.
Bunyamwera orthobunyavirus (BUNV) is a negative-sense, single-stranded enveloped RNA virus. It is assigned to the Orthobunyavirus genus, in the Bunyavirales order.

Herpes simplex, often known simply as herpes, is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Herpes infections are categorized by the area of the body that is infected. The two major types of herpes are oral herpes and genital herpes, though other forms also exist.

The primate T-lymphotropic viruses (PTLVs) are a group of retroviruses that infect primates, using their lymphocytes to reproduce. The ones that infect humans are known as human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV), and the ones that infect Old World monkeys are called simian T-lymphotropic viruses (STLVs). PTLVs are named for their ability to cause adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma, but in the case of HTLV-1 it can also cause a demyelinating disease called tropical spastic paraparesis. On the other hand, newer PTLVs are simply placed into the group by similarity and their connection to human disease remains unclear.
The epidemiology of herpes simplex is of substantial epidemiologic and public health interest. Worldwide, the rate of infection with herpes simplex virus—counting both HSV-1 and HSV-2—is around 90%. Although many people infected with HSV develop labial or genital lesions, the majority are either undiagnosed or display no physical symptoms—individuals with no symptoms are described as asymptomatic or as having subclinical herpes.

Marburg virus (MARV) is a hemorrhagic fever virus of the Filoviridae family of viruses and a member of the species Marburg marburgvirus, genus Marburgvirus. It causes Marburg virus disease in primates, a form of viral hemorrhagic fever. The World Health Organization (WHO) rates it as a Risk Group 4 Pathogen. In the United States, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases ranks it as a Category A Priority Pathogen and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention lists it as a Category A Bioterrorism Agent. It is also listed as a biological agent for export control by the Australia Group.
Ravn virus is a close relative of Marburg virus (MARV). RAVV causes Marburg virus disease in humans and nonhuman primates, a form of viral hemorrhagic fever. RAVV is a Select agent, World Health Organization Risk Group 4 Pathogen, National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Category A Priority Pathogen, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Category A Bioterrorism Agent, and listed as a Biological Agent for Export Control by the Australia Group.
Equine encephalosis virus (EEV) is a species of virus the Orbivirus genus, and a member of the Reoviridae family, related to African horse sickness virus (AHSV) and Bluetongue virus (BTV).
Infections of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) in children and pregnant women are less understood than those in other adults. Worldwide, the prevalence of HCV infection in pregnant women and children has been estimated to 1-8% and 0.05-5% respectively. The vertical transmission rate has been estimated to be 3-5% and there is a high rate of spontaneous clearance (25-50%) in the children. Higher rates have been reported for both vertical transmission. and prevalence in children (15%).
Oyewale Tomori is a Nigerian professor of virology, educational administrator, and former vice chancellor of Redeemer's University. In 2024, he became the chair of West Africa National Academy of Scientists.
Lubombo virus (LUBV) is an orbivirus that infects vertebrates and culicine mosquitoes, thought to be its arthropod vector. It is classified in the genus Orbivirus and the family Reoviridae. It is studied at biosafety level 2.











