Related Research Articles

In electrical engineering, ground or earth may be a reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.
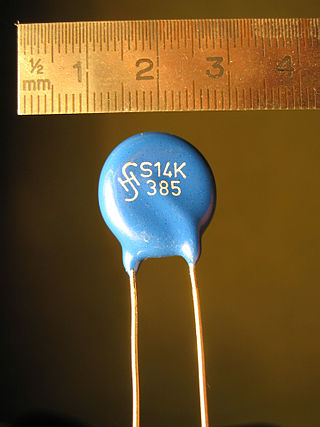
A varistor is a surge protecting electronic component with an electrical resistance that varies with the applied voltage. It has a nonlinear, non-ohmic current–voltage characteristic that is similar to that of a diode. Unlike a diode however, it has the same characteristic for both directions of traversing current. Traditionally, varistors were indeed constructed by connecting two rectifiers, such as the copper-oxide or germanium-oxide rectifier in antiparallel configuration. At low voltage the varistor has a high electrical resistance which decreases as the voltage is raised. Modern varistors are primarily based on sintered ceramic metal-oxide materials which exhibit directional behavior only on a microscopic scale. This type is commonly known as the metal-oxide varistor (MOV).

A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a result, power supplies are sometimes referred to as electric power converters. Some power supplies are separate standalone pieces of equipment, while others are built into the load appliances that they power. Examples of the latter include power supplies found in desktop computers and consumer electronics devices. Other functions that power supplies may perform include limiting the current drawn by the load to safe levels, shutting off the current in the event of an electrical fault, power conditioning to prevent electronic noise or voltage surges on the input from reaching the load, power-factor correction, and storing energy so it can continue to power the load in the event of a temporary interruption in the source power.

A short circuit is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with no or very low electrical impedance. This results in an excessive current flowing through the circuit. The opposite of a short circuit is an open circuit, which is an infinite resistance between two nodes.

A circuit breaker is an electrical safety device designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by current in excess of that which the equipment can safely carry (overcurrent). Its basic function is to interrupt current flow to protect equipment and to prevent fire. Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then must be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset to resume normal operation.

A surge protector (or spike suppressor, surge suppressor, surge diverter, surge protection device (SPD), transient voltage suppressor(TVS) or transient voltage surge suppressor (TVSS)) is an appliance or device intended to protect electrical devices in alternating current (AC) circuits from voltage spikes with very short duration measured in microseconds, which can arise from a variety of causes including lightning strikes in the vicinity.

A residual-current device (RCD), residual-current circuit breaker (RCCB) or ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) is an electrical safety device that interrupts an electrical circuit when the current passing through a conductor is not equal and opposite in both directions, therefore indicating leakage current to ground or current flowing to another powered conductor. The device's purpose is to reduce the severity of injury caused by an electric shock. This type of circuit interrupter cannot protect a person who touches both circuit conductors at the same time, since it then cannot distinguish normal current from that passing through a person.

In electronics and electrical engineering, a fuse is an electrical safety device that operates to provide overcurrent protection of an electrical circuit. Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows through it, thereby stopping or interrupting the current. It is a sacrificial device; once a fuse has operated, it is an open circuit, and must be replaced or rewired, depending on its type.
A distribution board is a component of an electricity supply system that divides an electrical power feed into subsidiary circuits while providing a protective fuse or circuit breaker for each circuit in a common enclosure. Normally, a main switch, and in recent boards, one or more residual-current devices (RCDs) or residual current breakers with overcurrent protection (RCBOs) are also incorporated.
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom is commonly understood to be an electrical installation for operation by end users within domestic, commercial, industrial, and other buildings, and also in special installations and locations, such as marinas or caravan parks. It does not normally cover the transmission or distribution of electricity to them.
The prospective short-circuit current (PSCC), available fault current, or short-circuit making current is the highest electric current which can exist in a particular electrical system under short-circuit conditions. It is determined by the voltage and impedance of the supply system. It is of the order of a few thousand amperes for a standard domestic mains electrical installation, but may be as low as a few milliamperes in a separated extra-low voltage (SELV) system or as high as hundreds of thousands of amps in large industrial power systems. The term is used in electrical engineering rather than electronics.

In electric power distribution, automatic circuit reclosers (ACRs) are a class of switchgear designed for use on overhead electricity distribution networks to detect and interrupt transient faults. Also known as reclosers or autoreclosers, ACRs are essentially rated circuit breakers with integrated current and voltage sensors and a protection relay, optimized for use as a protection asset. Commercial ACRs are governed by the IEC 62271-111/IEEE Std C37.60 and IEC 62271-200 standards. The three major classes of operating maximum voltage are 15.5 kV, 27 kV and 38 kV.
Power system protection is a branch of electrical power engineering that deals with the protection of electrical power systems from faults through the disconnection of faulted parts from the rest of the electrical network. The objective of a protection scheme is to keep the power system stable by isolating only the components that are under fault, whilst leaving as much of the network as possible in operation. The devices that are used to protect the power systems from faults are called protection devices.
In electric power systems and industrial automation, ANSI Device Numbers can be used to identify equipment and devices in a system such as relays, circuit breakers, or instruments. The device numbers are enumerated in ANSI/IEEE Standard C37.2 Standard for Electrical Power System Device Function Numbers, Acronyms, and Contact Designations.
In an electric power system, a fault or fault current is any abnormal electric current. For example, a short circuit is a fault in which a live wire touches a neutral or ground wire. An open-circuit fault occurs if a circuit is interrupted by a failure of a current-carrying wire or a blown fuse or circuit breaker. In three-phase systems, a fault may involve one or more phases and ground, or may occur only between phases. In a "ground fault" or "earth fault", current flows into the earth. The prospective short-circuit current of a predictable fault can be calculated for most situations. In power systems, protective devices can detect fault conditions and operate circuit breakers and other devices to limit the loss of service due to a failure.
Islanding is the intentional or unintentional division of an interconnected power grid into individual disconnected regions with their own power generation.

An electric power system is a network of electrical components deployed to supply, transfer, and use electric power. An example of a power system is the electrical grid that provides power to homes and industries within an extended area. The electrical grid can be broadly divided into the generators that supply the power, the transmission system that carries the power from the generating centers to the load centers, and the distribution system that feeds the power to nearby homes and industries.

In electrical engineering, a protective relay is a relay device designed to trip a circuit breaker when a fault is detected. The first protective relays were electromagnetic devices, relying on coils operating on moving parts to provide detection of abnormal operating conditions such as over-current, overvoltage, reverse power flow, over-frequency, and under-frequency.
A voltage sag or voltage dip is a short-duration reduction in the voltage of an electric power distribution system. It can be caused by high current demand such as inrush current or fault current elsewhere on the system.
In an electrical grid, the short circuit ratio is the ratio of: the short circuit apparent power (SCMVA) in the case of a line-line-line-ground (3LG) fault at the location in the grid where some generator is connected, to: the power rating of the generator itself (GMW).
References
- ↑ Keller, Kimberley J. (2010). Overcurrent Protection. Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-1-85617-654-5 . Retrieved July 5, 2021.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - ↑ Li, Nie & Wang 2022, p. 536.