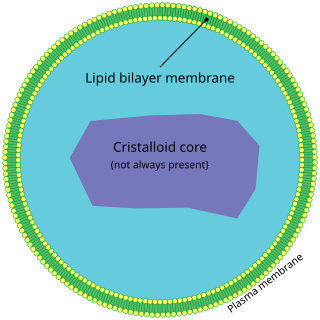
A peroxisome (IPA: [pɛɜˈɹɒksɪˌsoʊm]) is a membrane-bound organelle, a type of microbody, found in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. Peroxisomes are oxidative organelles. Frequently, molecular oxygen serves as a co-substrate, from which hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is then formed. Peroxisomes owe their name to hydrogen peroxide generating and scavenging activities. They perform key roles in lipid metabolism and the conversion of reactive oxygen species. Peroxisomes are involved in the catabolism of very long chain fatty acids, branched chain fatty acids, bile acid intermediates (in the liver), D-amino acids, and polyamines, the reduction of reactive oxygen species – specifically hydrogen peroxide – and the biosynthesis of plasmalogens, i.e., ether phospholipids critical for the normal function of mammalian brains and lungs. They also contain approximately 10% of the total activity of two enzymes (Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase) in the pentose phosphate pathway, which is important for energy metabolism. It is vigorously debated whether peroxisomes are involved in isoprenoid and cholesterol synthesis in animals. Other known peroxisomal functions include the glyoxylate cycle in germinating seeds ("glyoxysomes"), photorespiration in leaves, glycolysis in trypanosomes ("glycosomes"), and methanol and/or amine oxidation and assimilation in some yeasts.

Peroxisomal disorders represent a class of medical conditions caused by defects in peroxisome functions. This may be due to defects in single enzymes important for peroxisome function or in peroxins, proteins encoded by PEX genes that are critical for normal peroxisome assembly and biogenesis.
Infantile Refsum disease (IRD) is a rare autosomal recessive congenital peroxisomal biogenesis disorder within the Zellweger spectrum. These are disorders of the peroxisomes that are clinically similar to Zellweger syndrome and associated with mutations in the PEX family of genes. IRD is associated with deficient phytanic acid catabolism, as is adult Refsum disease, but they are different disorders that should not be confused.

Peroxisomal targeting signal 1 receptor (PTS1R) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PEX5 gene.

Peroxisome biogenesis factor 1, also known as PEX1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PEX1 gene.
Peroxisomal biogenesis factor 19 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PEX19 gene.
Peroxisomal membrane protein PEX14 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PEX14 gene.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family D member 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCD3 gene.

Peroxisomal biogenesis factor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PEX2 gene.

Peroxisomal membrane protein PEX13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PEX13 gene. It located on chromosome 2 next to KIAA1841

Peroxisomal biogenesis factor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PEX3 gene.

Peroxisome assembly factor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PEX6 gene. PEX6 is an AAA ATPase that localizes to the peroxisome. PEX6 forms a hexamer with PEX1 and is recruited to the membrane by PEX26.

Peroxisome biogenesis factor 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PEX10 gene. Alternative splicing results in two transcript variants encoding different isoforms.

Peroxisomal membrane protein PMP34 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC25A17 gene.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family D member 2 is a membrane pump/transporter protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCD2 gene.

Peroxisomal membrane protein PEX16 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PEX16 gene.

Peroxisome assembly protein 26 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PEX26 gene.

Peroxisomal membrane protein 11B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PEX11B gene. It is involved in the regulation of peroxisome abundance.

Peroxisomal membrane protein 11A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PEX11A gene.

Peroxisomal membrane protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PXMP4 gene.