
Multiple endocrine neoplasia is a condition which encompasses several distinct syndromes featuring tumors of endocrine glands, each with its own characteristic pattern. In some cases, the tumors are malignant, in others, benign. Benign or malignant tumors of nonendocrine tissues occur as components of some of these tumor syndromes.

A benign tumor is a mass of cells (tumor) that does not invade neighboring tissue or metastasize. Compared to malignant (cancerous) tumors, benign tumors generally have a slower growth rate. Benign tumors have relatively well differentiated cells. They are often surrounded by an outer surface or stay contained within the epithelium. Common examples of benign tumors include moles and uterine fibroids.
An oncolytic virus is a virus that preferentially infects and kills cancer cells. As the infected cancer cells are destroyed by oncolysis, they release new infectious virus particles or virions to help destroy the remaining tumour. Oncolytic viruses are thought not only to cause direct destruction of the tumour cells, but also to stimulate host anti-tumour immune system responses. Oncolytic viruses also have the ability to affect the tumor micro-environment in multiple ways.
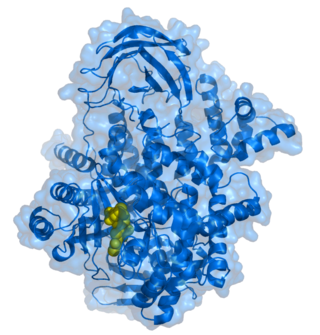
The phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase, catalytic subunit alpha, also called p110α protein, is a class I PI 3-kinase catalytic subunit. The human p110α protein is encoded by the PIK3CA gene.
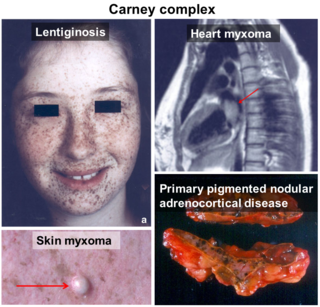
Carney complex and its subsets LAMB syndrome and NAME syndrome are autosomal dominant conditions comprising myxomas of the heart and skin, hyperpigmentation of the skin (lentiginosis), and endocrine overactivity. It is distinct from Carney's triad. Approximately 7% of all cardiac myxomas are associated with Carney complex.

The sodium/iodide cotransporter, also known as the sodium/iodide symporter (NIS), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC5A5 gene. It is a transmembrane glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 87 kDa and 13 transmembrane domains, which transports two sodium cations (Na+) for each iodide anion (I−) into the cell. NIS mediated uptake of iodide into follicular cells of the thyroid gland is the first step in the synthesis of thyroid hormone.

Menin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MEN1 gene. Menin is a putative tumor suppressor associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 and has autosomal dominant inheritance. Variations in the MEN1 gene can cause pituitary adenomas, hyperparathyroidism, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, gastrinoma, and adrenocortical cancers.

Cyclin D1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCND1 gene.
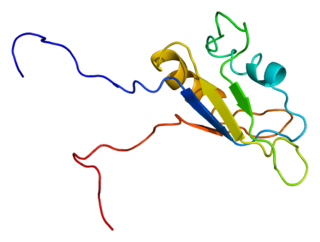
RNA-binding protein EWS is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EWSR1 gene on human chromosome 22, specifically 22q12.2. It is one of 3 proteins in the FET protein family.

NK2 homeobox 1 (NKX2-1), also known as thyroid transcription factor 1 (TTF-1), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the NKX2-1 gene.

Securin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PTTG1 gene.

Discoidin domain receptor family, member 1, also known as DDR1 or CD167a, is a human gene.

ERG is an oncogene. ERG is a member of the ETS family of transcription factors. The ERG gene encodes for a protein, also called ERG, that functions as a transcriptional regulator. Genes in the ETS family regulate embryonic development, cell proliferation, differentiation, angiogenesis, inflammation, and apoptosis.

Ras association domain-containing protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RASSF5 or F5 gene.

Immunoglobulin superfamily, member 1 is a plasma membrane glycoprotein encoded by the IGSF1 gene, which maps to the X chromosome in humans and other mammalian species.

Suppressor of tumorigenicity protein 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ST7 gene. ST7 orthologs have been identified in all mammals for which complete genome data are available.

Large tumor suppressor kinase 1 (LATS1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the LATS1 gene.

Follicular thyroid cancer accounts for 15% of thyroid cancer and occurs more commonly in women over 50 years of age. Thyroglobulin (Tg) can be used as a tumor marker for well-differentiated follicular thyroid cancer. Thyroid follicular cells are the thyroid cells responsible for the production and secretion of thyroid hormones.

Deleted in esophageal cancer 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DEC1 gene.
Measles virus encoding the human thyroidal sodium iodide symporter or MV-NIS is an attenuated oncolytic Edmonston (Ed) strain of measles virus.





















