
The Eurotiales are an order of sac fungi, also known as the green and blue molds. It was circumscribed in 1980.

Paecilomyces is a genus of fungi. A number of species in this genus are plant pathogens.

Radiotrophic fungi are fungi that can perform the hypothetical biological process called radiosynthesis, which means using ionizing radiation as an energy source to drive metabolism. It has been claimed that radiotrophic fungi have been found in extreme environments such as in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant.
Paecilomyces fulvus is a plant pathogen that causes Byssochlamys rot on strawberries.
Byssochlamys is a former genus of fungi in the Trichocomaceae family, containing teleomorph forms of Paecilomyces. Several species of the genus Byssochlamys were well known to be associated with food spoilage, especially acidic heat-processed foods. A health concern was the production the mycotoxin patulin in fruit juices, as well as byssochlamic acid and mycophenolic acid.

Purpureocillium is a fungal genus in the Ophiocordycipitaceae family. The genus now contains at least 5 species with the type species Purpureocillium lilacinum, a common saprobic, filamentous fungus. It has been isolated from a wide range of habitats, including cultivated and uncultivated soils, forests, grassland, deserts, estuarine sediments and sewage sludge, and insects. It has also been found in nematode eggs, and occasionally from females of root-knot and cyst nematodes. In addition, it has frequently been detected in the rhizosphere of many crops. The species can grow at a wide range of temperatures – from 8 to 38 °C for a few isolates, with optimal growth in the range 26 to 30 °C. It also has a wide pH tolerance and can grow on a variety of substrates. P. lilacinum has shown promising results for use as a biocontrol agent to control the growth of destructive root-knot nematodes.

Purpureocillium lilacinum is a species of filamentous fungus in the family Ophiocordycipitaceae. It has been isolated from a wide range of habitats, including cultivated and uncultivated soils, forests, grassland, deserts, estuarine sediments and sewage sludge, and insects. It has also been found in nematode eggs, and occasionally from females of root-knot and cyst nematodes. In addition, it has frequently been detected in the rhizosphere of many crops. The species can grow at a wide range of temperatures – from 8 to 38 °C for a few isolates, with optimal growth in the range 26 to 30 °C. It also has a wide pH tolerance and can grow on a variety of substrates. P. lilacinum has shown promising results for use as a biocontrol agent to control the growth of destructive root-knot nematodes.
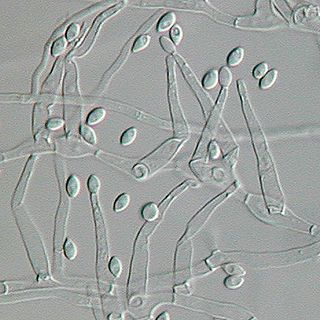
Paecilomyces variotii, also known by the name Byssochlamys spectabilis for the sexual state, is a common environmental mold from the Phylum Ascomycota. It is widespread in the environment and can be found in composts, soils and wood, as well es a common environmental contaminant in indoor air and carpet dust. Ascospores of the sexual state of P. variotii are strongly heat-resistant. As such the fungus is a common contaminant of heat-treated foods and juices. Paecilomyces variotii has been associated with a number of infective diseases of humans and animals.
Rasamsonia is a genus of fungi in the family Trichocomaceae, circumscribed in 2011 by mycologists Jos Houbraken and Jens Frisvad. It is characterized from other genera of the Trichocomaceae by the following combination of features: species are thermotolerant or thermophilic; their conidiophores have distinctly rough-walled stipes; conidia are olive brown; and ascomata, if present, have minimal covering. Rasamsonia phenotypically resembles Paecilomyces, in that both have thermotolerant species, produce olive-brown conidia, and form ascomata with no or scarce ascomatal covering; Rasamsonia, however, differs from Paecilomyces in having more regularly branched conidiophores with distinct rough-walled structures. The type species is Rasamsonia emersonii, a fungus formerly classified in the genus Talaromyces.
Isaria fumosorosea is an entomopathogenic fungus, formerly known as Paecilomyces fumosoroseus. It shows promise as a biological pesticide with an extensive host range.
Paecilomyces marquandii is a soil-borne filamentous fungus distributed throughout temperate to tropical latitudes worldwide including forest, grassland, sewage sludge and strongly metal polluted area characterized by high tolerance in heavy metals. Simultaneous toxic action of zinc and alachlor result an increase in uptake of metal in this fungus but disrupts the cell membrane. Paecilomyces marquandii is known to parasitize the mushroom, Cuphophyllus virgineus, in the family, Hygrophoraceae. Paecilomyces marquandii is categorised as a biosafety risk group 1 in Canada and is not thought to be a significant pathogen of humans or animals.
Fictibacillus is a genus of bacteria from the family of Bacillaceae.

Mariannaea elegans an anamorphic fungus. It is mainly found on rotting wood and soil. M. elegans is not pathogenic to humans, animals, or plants.
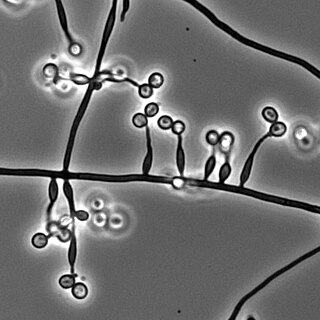
Metarhizium granulomatis is a fungus in the family Clavicipitaceae associated with systemic mycosis in veiled chameleons. The genus Metarhizium is known to infect arthropods, and collectively are referred to green-spored asexual pathogenic fungi. This species grows near the roots of plants and has been reported as an agent of disease in captive veiled chameleons. The etymology of the species epithet, "granulomatis" refers to the ability of the fungus to cause granulomatous disease in susceptible reptiles.
Paecilomyces niveus is a species of fungus in the genus Paecilomyces in the order of Eurotiales.
Paecilomyces lagunculariae is a species of fungus in the genus Paecilomyces in the order of Eurotiales.
Thermoascus aegyptiacus is a species of fungus in the genus Thermoascus in the order of Eurotiales.
Paecilomyces formosus is a species of fungus in the genus Paecilomyces in the order of Eurotiales.
Evansstolkia leycettana is a species of fungus in the monotypic genus Evansstolkia in the order of Eurotiales.
Paecilomyces dactylethromorphus is a species of fungus in the genus Paecilomyces in the order of Eurotiales.






