
Chlorophyta or Prasinophyta is a taxon of green algae informally called chlorophytes. The name is used in two very different senses, so care is needed to determine the use by a particular author. In older classification systems, it refers to a highly paraphyletic group of all the green algae within the green plants (Viridiplantae) and thus includes about 7,000 species of mostly aquatic photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. In newer classifications, it refers to the sister of the streptophytes/charophytes. The clade Streptophyta consists of the Charophyta in which the Embryophyta emerged. In this sense the Chlorophyta includes only about 4,300 species. About 90% of all known species live in freshwater. Like the land plants, green algae contain chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b and store food as starch in their plastids.

The Ulvophyceae or ulvophytes are a class of green algae, distinguished mainly on the basis of ultrastructural morphology, life cycle and molecular phylogenetic data. The sea lettuce, Ulva, belongs here. Other well-known members include Caulerpa, Codium, Acetabularia, Cladophora, Trentepohlia and Monostroma.

The Embryophyta or land plants are the most familiar group of green plants that form vegetation on earth. Embryophyta is a clade within the Phragmoplastophyta, a larger clade that also includes several green algae groups, and within this large clade the embryophytes are sister to the Zygnematophyceae/Mesotaeniaceae and consist of the bryophytes plus the polysporangiophytes. Living embryophytes therefore include hornworts, liverworts, mosses, ferns, lycophytes, gymnosperms and flowering plants.

The green algae are a large, informal grouping of algae consisting of the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/Streptophyta, which are now placed in separate divisions, together with the more basal Mesostigmatophyceae, Chlorokybophyceae and Spirotaenia.

Streptophyta, informally the streptophytes, is a clade of plants. The composition of the clade varies considerably between authors, but the definition employed here includes land plants and all green algae except the Chlorophyta and possibly the more basal Mesostigmatophyceae, Chlorokybophyceae, and Spirotaenia.

The Charophyta or charophytes is a group of freshwater green algae, sometimes treated as a division, but also as a superdivision, or an unranked clade. The terrestrial plants, the Embryophyta most likely emerged within Charophyta, possibly from terrestrial unicellular charophytes, with the class Zygnematophyceae as a sister group.
Sphaeropleales is an order of green algae that used to be called Chlorococcales. The order includes some of the most common freshwater planktonic algae such as Scenedesmus and Pediastrum. The Spaeropleales includes vegetatively non-motile unicellular or colonial taxa that have biflagellate zoospores with flagella that are directly opposed in direction : Sphaeroplea, Atractomorpha, Neochloris, Hydrodictyon, and Pediastrum. All of these taxa have basal body core connections.

Viridiplantae are a clade of eukaryotic organisms that comprise approximately 450,000–500,000 species and play important roles in both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. They are made up of the green algae, which are primarily aquatic, and the land plants (embryophytes), which emerged from within them. Green algae traditionally excludes the land plants, rendering them a paraphyletic group. Since the realization that the embryophytes emerged from within the green algae, some authors are starting to include them. They have cells with cellulose in their cell walls, and primary chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria that contain chlorophylls a and b and lack phycobilins.

Charophyceae is a class of charophyte green algae, and consists of the single order Charales, commonly known as "stoneworts" and "brittleworts". It is a basal Phragmoplastophyta clade as sister of another unnamed clade which contains the Embryophytes. Charophyceae are a class within the Streptophyta. Current consensus treats Charophyceae as a class under division Charophyta, with Chlorophyta remaining a distinct division. In 2018, the first nuclear genome sequence from a species belonging to the most basal branch within the Phragmoplastophyta, the Charophyceae, has been published: that of Chara braunii

The Archaeplastida are a major group of eukaryotes, comprising the red algae (Rhodophyta), the green algae, and the land plants, and some smaller groups such as the glaucophytes. All of the lineages of Archaeplastida have become photoautotrophic, except for the lineage Rhodelphidia, sister to the Rhodophyta, which is still a non-photosynthetic predatorial (eukaryotrophic) flagellate. The Archaeplastida have chloroplasts that are surrounded by two membranes, suggesting that they were acquired directly through a single endosymbiosis event by feeding on a cyanobacterium. All other groups which have chloroplasts, besides the amoeboid Paulinella chromatophora, have chloroplasts surrounded by three or four membranes, suggesting they were acquired secondarily from red or green algae. Unlike red and green algae, glaucophytes have never been involved in secondary endosymbiosis events.

The Prasinophytes or chlorophyta are a class of unicellular green algae. Prasinophytes mainly include marine planktonic species, as well as some freshwater representatives. The prasinophytes are morphologically diverse, including flagellates with one to eight flagella and non-motile (coccoid) unicells. The cells of many species are covered with organic body scales; others are naked. Well studied genera include Ostreococcus, considered to be the smallest free-living eukaryote, and Micromonas, both of which are found in marine waters worldwide. Prasinophytes have simple cellular structures, containing a single chloroplast and a single mitochondrion. The genomes are relatively small compared to other eukaryotes.

Bryopsis is a genus of marine green algae in the family Bryopsidaceae. It is frequently a pest in aquariums, where it is commonly referred to as hair algae.
The Mesostigmatophyceae are a class of basal green algae found in freshwater originally containing two species in a single genus, Mesostigma. Now, a clade containing Chlorokybus and Spirotaenia has been added.. The Mesostigmatophyceae are either placed as sister to all other green algae, or more conventionally as sister to all Streptophyta.
eEF-1 are two eukaryotic elongation factors. It forms two complexes, the EF-Tu homolog EF-1A and the EF-Ts homolog EF-1B, the former's guanide exchange factor. Both are also found in archaea.
Chlorokybus is a multicellular (sarcinoid) genus of basal green algae or Streptophyte containing the sole species Chlorokybus atmophyticus, a soil alga found in alpine areas. It sometimes has been classified as the sole member of the class ChlorokybophyceaeSluiman & Guihal, 1999.
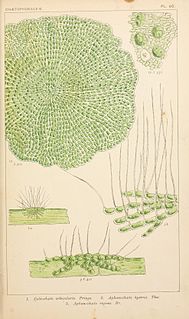
The Coleochaetales are an order of parenchymous charophyte algae, that includes some of the closest multicellular relatives of land plants. They questionably include the fossil genus Parka.
Chaetosphaeridiales is an order of green algae.
The Palmophyllophyceae are a proposed basal Chlorophyte clade consisting of the Palmophyllales and Prasinococcales.

The Phragmoplastophyta or Streptophytina are a proposed sister clade of the Klebsormidiaceae, with which they form the Streptophyte/Charophyte clade. The Phragmoplastophyta consist of the Charophycaea and another unnamed clade which contains the Coleochaetophyceae, Zygnematophyceae, Mesotaeniaceae, and Embryophytes. It is an important step in the emergence of land plants within the green algae. It is equivalent to the ZCC clade/grade, cladistically granting the Embryophyta.

The Chlorophytina are a proposed basal Tetraphytina clade. It is currently seen as sister of the Pedinomonadaceae.











