
A fastener or fastening is a hardware device that mechanically joins or affixes two or more objects together. In general, fasteners are used to create non-permanent joints; that is, joints that can be removed or dismantled without damaging the joining components. Welding is an example of creating permanent joints. Steel fasteners are usually made of stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloy steel.

Bolted joints are one of the most common elements in construction and machine design. They consist of fasteners that capture and join other parts, and are secured with the mating of screw threads.

Safety wire or locking-wire is a type of positive locking device that prevents fasteners from falling out due to vibration and other forces. The presence of safety wiring may also serve to indicate that the fasteners have been properly tightened.

A lug nut or wheel nut is a fastener, specifically a nut, used to secure a wheel on a vehicle. Typically, lug nuts are found on automobiles, trucks (lorries), and other large vehicles using rubber tires.

A sex bolt,, is a type of fastener (nut) that has a barrel-shaped flange and protruding boss that is internally threaded. The boss sits within the components being fastened, the flange provides the bearing surface. The sex bolt and accompanying machine screw sit flush on either side of the surfaces being fastened. It is normally chosen because of its low profile compared to other nuts. The sex bolt often has a built-in feature, such as a slot, to aid in tightening the fastener. Some sex bolts, more commonly known as "architectural bolts", have knurled barrels to allow one-sided assembly. "Binding posts" are similar to architectural bolts in that they are designed to be assembled from one side, but they have teeth on the flanged surface to keep them fixed.
A threaded insert, also known as a threaded bushing, is a fastener element that is inserted into an object to add a threaded hole. They may be used to repair a stripped threaded hole, provide a durable threaded hole in a soft material, place a thread on a material too thin to accept it, mold or cast threads into a work piece thereby eliminating a machining operation, or simplify changeover from unified to metric threads or vice versa.

A jam nut is a low profile type of nut, typically half as tall as a standard nut. It is commonly used as a type of locknut, where it is "jammed" up against a standard nut to lock the two in place. It is also used in situations where a standard nut would not fit.

A knurled nut is a nut with a knurled outside surface. This facilitates tightening by hand or secures the nut into a handle or cover.

A T-nut, T nut, or tee nut is a type of nut used to fasten a wood, particle or composite materials workpiece, leaving a flush surface.
A distorted thread locknut, is a type of locknut that uses a deformed section of thread to keep the nut from loosening from vibrations or rotation of the clamped item. They are broken down into four types: elliptical offset nuts, centerlock nuts, toplock nuts and partially depitched (Philidas) nuts.
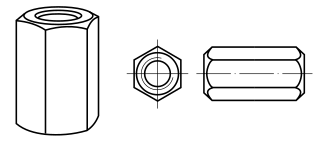
A coupling nut, also known as extension nut, is a threaded fastener for joining two male threads, most commonly a threaded rod, but also pipes. The outside of the fastener is usually a hex so a wrench can hold it. Variations include reducing coupling nuts, for joining two different size threads; sight hole coupling nuts, which have a sight hole for observing the amount of engagement; and coupling nuts with left-handed threads. These are used to make up long rod assemblies from shorter lengths of rods. The rods are threaded into the coupling nut for a certain distance. Coupling nut dimensions are described by the Industrial Fasteners Institute in standard IFI-128. It is given a plain finish. It is either cold drawn or hot rolled depending on the bar stock used. Coupling nuts threaded with two different thread sizes and profiles are called reducing coupling nuts.

A rivet nut, also known as a blind rivet nut, or rivnut, is a one-piece internally threaded and counterbored tubular rivet that can be anchored entirely from one side. It is a kind of threaded insert. There are two types: one is designed to form a bulge on the back side of the panel as a screw is tightened in its threads. The other is similarly drawn in using a screw, but is drawn into the sleeve instead of creating a bulge.

A wingnut, wing nut or butterfly nut is a type of nut with two large metal "wings", one on each side, so it can be easily tightened and loosened by hand without tools.

A weld nut is a special type of nut specifically designed to be welded to another object. There are various types for different applications.
A plate nut, also known as a nut plate, anchor nut or anchor plate, is a stamped sheet metal nut that is usually riveted to a workpiece. They have a long tube that is internally threaded and a plate with two clearance holes for rivets. The most popular versions have two lugs and they exist as fixed anchor nuts and as floating anchor nuts. The latter allows the nut to move slightly and so enlarges the positioning tolerances of the mounted parts. They were originally developed for the aerospace industry, but are now also common in automotive racing. These nuts are made up of variety of soft and hard materials. The choice of material depends on environment to which nut is subjected. Soft materials like copper or brass are used when nut is used in electrical application. Hard materials are used when nut is subjected to high stress environment. Sometimes stainless steel or nickel-plated nuts are used in order to increase corrosion resistance.
A clip-on nut, also known as a sheet metal nut or a speed nut, is a type of nut designed to be clipped to sheet metal. It is a type of captive nut commonly made as a cage nut.

A screw and a bolt are similar types of fastener typically made of metal, and characterized by a helical ridge, known as a male thread. Screws and bolts are used to fasten materials by the engagement of the screw thread with a similar female thread in the matching part.

A nut is a type of fastener with a threaded hole. Nuts are almost always used in conjunction with a mating bolt to fasten multiple parts together. The two partners are kept together by a combination of their threads' friction, a slight stretching of the bolt, and compression of the parts to be held together.

A bolt is a form of threaded fastener with an external male thread requiring a matching pre-formed female thread such as a nut. Bolts are very closely related to screws.

A square nut is a four-sided nut. Compared to standard hex nuts, square nuts have a greater surface in contact with the part being fastened, and therefore provide greater resistance to loosening. They are also much less likely to become rounded-off after repeated loosening/tightening cycles. Square nuts are typically mated with square-headed bolts. Square nuts are used along with flat washers in order to avoid damage from its sharp edges and increase the strength of the fastener. Square nuts can have standard, fine or coarse threading with platings of zinc yellow, plain, zinc clear, tin and cadmium, among others. Most can meet either the ASTM A194, ASTM A563, or ASTM F594 standard.















