
Branchiopoda is a class of crustaceans. It comprises fairy shrimp, clam shrimp, Diplostraca, Notostraca and the Devonian Lepidocaris. They are mostly small, freshwater animals that feed on plankton and detritus.
The halophiles, named after the Greek word for "salt-loving", are extremophiles that thrive in high salt concentrations. While most halophiles are classified into the domain Archaea, there are also bacterial halophiles and some eukaryotic species, such as the alga Dunaliella salina and fungus Wallemia ichthyophaga. Some well-known species give off a red color from carotenoid compounds, notably bacteriorhodopsin. Halophiles can be found in water bodies with salt concentration more than five times greater than that of the ocean, such as the Great Salt Lake in Utah, Owens Lake in California, the Urmia Lake in Iran, the Dead Sea, and in evaporation ponds. They are theorized to be a possible analogues for modeling extremophiles that might live in the salty subsurface water ocean of Jupiter's Europa and similar moons.

The Kalahari Desert is a large semi-arid sandy savanna in Southern Africa extending for 900,000 square kilometres (350,000 sq mi), covering much of Botswana, and parts of Namibia and South Africa.
Halotolerance is the adaptation of living organisms to conditions of high salinity. Halotolerant species tend to live in areas such as hypersaline lakes, coastal dunes, saline deserts, salt marshes, and inland salt seas and springs. Halophiles are organisms that live in highly saline environments, and require the salinity to survive, while halotolerant organisms can grow under saline conditions, but do not require elevated concentrations of salt for growth. Halophytes are salt-tolerant higher plants. Halotolerant microorganisms are of considerable biotechnological interest.
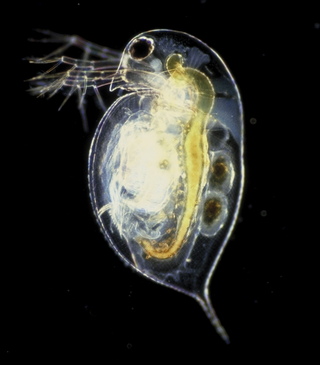
Daphnia is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, 0.2–6.0 mm (0.01–0.24 in) in length. Daphnia are members of the order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. Daphnia spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to freshwater lakes and ponds.

Lake Makgadikgadi was a paleolake that existed in what is now the Kalahari Desert in Botswana from 2,000,000 years BP to 10,000 years BP. It may have once covered an area of from 80,000 to 275,000 km2 and was 30 m deep. The Okavango, Upper Zambezi, and Cuando rivers once all emptied into the lake. Its remains are seen in the Makgadikgadi salt pans, one of the largest salt pans in the world.

Gloeocapsa is a genus of cyanobacteria. The cells secrete individual gelatinous sheaths which can often be seen as sheaths around recently divided cells within outer sheaths. Recently divided cell pairs often appear to be only one cell since the new cells cohere temporarily. They are also known as glow caps, a term derived from the yellowish hue given off by the cap.

Nodularia is a genus of filamentous nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria, or blue-green algae. They occur mainly in brackish or salinic waters, such as the hypersaline Makgadikgadi Pans, the Peel-Harvey Estuary in Western Australia or the Baltic Sea. Nodularia cells occasionally form heavy algal blooms. Some strains produce a cyanotoxin called nodularin R, which is harmful to humans.

The Makgadikgadi Pan, a salt pan situated in the middle of the dry savanna of north-eastern Botswana, is one of the largest salt flats in the world. The pan is all that remains of the formerly enormous Lake Makgadikgadi, which once covered an area larger than Switzerland, but dried up tens of thousands of years ago. Recent studies of human mitochondrial DNA suggest that modern Homo sapiens first began to evolve in this region some 200,000 years ago, when it was a vast, exceptionally fertile area of lakes, rivers, marshes, woodlands and grasslands especially favorable for habitation by evolving hominins and other mammals.

The Kalahari Basin, also known as the Kalahari Depression, Okavango Basin or the Makgadikgadi basin, is an endorheic basin and large lowland area covering approximately 725,293 km2 covering most of Botswana and Namibia, as well as parts of Angola, South Africa, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. The outstanding physical feature in the basin, and occupying the centre, is the large Kalahari Desert.
Paradiaptomus excellens is a species of copepod in the family Diaptomidae. It is endemic to South Africa.
Paradiaptomus simplex is a species of copepod in the family Diaptomidae. It is endemic to South Africa.
Paradiaptomus is a genus of crustacean in the family Diaptomidae. It includes the following species:

Diaptomidae is a family of freshwater pelagic copepods. It includes around 50 genera:

Nitzschia is a common pennate marine diatom. In the scientific literature, this genus, named after Christian Ludwig Nitzsch, is sometimes termed Nitzchia, and it has many species described, which all have a similar morphology.

Daphnia barbata is a species of water flea within the family Daphniidae. It occurs in several places within Africa including Lake Chad in northwest Africa and in the Makgadikgadi Pan in Botswana.

A hypersaline lake is a landlocked body of water that contains significant concentrations of sodium chloride, brines, and other salts, with saline levels surpassing that of ocean water.

Sigara is a genus of water boatmen in the family Corixidae. Some species within this genus are halophiles; for example, occurrences of the genus have been noted in the hypersaline Makgadikgadi Pans in Botswana.

Prof Sven Ludvig Lovén, was a Swedish marine zoologist and malacologist. The Sven Lovén Centre for Marine Sciences within the University of Gothenburg was named in his honour.

A soda lake or alkaline lake is a lake on the strongly alkaline side of neutrality, typically with a pH value between 9 and 12. They are characterized by high concentrations of carbonate salts, typically sodium carbonate, giving rise to their alkalinity. In addition, many soda lakes also contain high concentrations of sodium chloride and other dissolved salts, making them saline or hypersaline lakes as well. High pH and salinity often coincide, because of how soda lakes develop. The resulting hypersaline and highly alkalic soda lakes are considered some of the most extreme aquatic environments on Earth.














