The plagiopylids are a small order of ciliates, including a few forms common in anaerobic habitats.

The Litostomatea are a class of ciliates. The group consists of three subclasses: Haptoria, Trichostomatia and Rhynchostomatia. Haptoria includes mostly carnivorous forms such as Didinium, a species of which preys primarily on the ciliate Paramecium. Trichostomatia (trichostomes) are mostly endosymbionts in the digestive tracts of vertebrates. These include the species Balantidium coli, which is the only ciliate parasitic in humans. The group Rhynchostomatia includes two free-living orders previously included among the Haptoria, but now known to be genetically distinct from them, the Dileptida and the Tracheliida.

Paramecium is a genus of eukaryotic, unicellular ciliates, commonly studied as a model organism of the ciliate group. Paramecium are widespread in freshwater, brackish, and marine environments and are often abundant in stagnant basins and ponds. Because some species are readily cultivated and easily induced to conjugate and divide, they have been widely used in classrooms and laboratories to study biological processes. The usefulness of Paramecium as a model organism has caused one ciliate researcher to characterize it as the "white rat" of the phylum Ciliophora.

A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and eukaryotic organisms. Most prokaryotes are unicellular and are classified into bacteria and archaea. Many eukaryotes are multicellular, but some are unicellular such as protozoa, unicellular algae, and unicellular fungi. Unicellular organisms are thought to be the oldest form of life, with early protocells possibly emerging 3.8–4.8 billion years ago.

The Colpodea are a class of ciliates, of about 200 species common in freshwater and soil habitats. The body cilia are typically uniform, and are supported by dikinetids of characteristic structure, with cilia on both kinetosomes. The mouth may be apical or ventral, with more or less prominent associated polykinetids. Many are asymmetrical, the cells twisting sideways and then untwisting again prior to division, which often takes place within cysts. Colpoda, a kidney-shaped ciliate common in organic rich conditions, is representative.

Balantidium is a genus of ciliates. It contains the parasitic species Balantidium coli, the only known cause of balantidiasis.
Tracy Morton Sonneborn was an American biologist. His life's study was ciliated protozoa of the group Paramecium.

The oligotrichs are a group of ciliates, included among the spirotrichs. They have prominent oral cilia, which are arranged as a collar and lapel, in contrast to the choreotrichs where they form a complete circle. The body cilia are reduced to a girdle and ventral cilia. In Halteria and its relatives, they form bristles or cirri; however these forms may be closer relatives of the stichotrichs than of other oligotrichs. These organisms are very common in plankton communities, especially in marine systems. Usually found in concentrations of about 1 per ml, they are the most important herbivores in the sea, the first link in the food chain.
Myzocytosis is a method of feeding found in some heterotrophic organisms. It is also called "cellular vampirism" as the predatory cell pierces the cell wall and/or cell membrane of the prey cell with a feeding tube, the conoid, sucks out the cellular content and digests it.
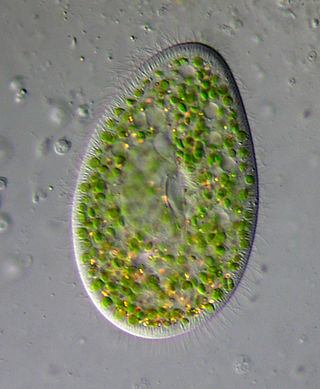
Paramecium bursaria is a species of ciliate found in marine and brackish waters. It has a mutualistic endosymbiotic relationship with green algae called Zoochlorella. About 700 Chlorella cells live inside the protist's cytoplasm and provide it with food, while the Paramecium provides the algae with movement and protection. P. bursaria is 80-150 μm long, with a wide oral groove, two contractile vacuoles, and a single micronucleus as well as a single macronucleus. P. bursaria is the only species of Paramecium that forms symbiotic relationships with algae, and it is often used in biology classrooms both as an example of a protozoan and also as an example of symbiosis.

Paramecium caudatum is a species of unicellular protist in the phylum Ciliophora. They can reach 0.33 mm in length and are covered with minute hair-like organelles called cilia. The cilia are used in locomotion and feeding. The species is very common, and widespread in marine, brackish and freshwater environments.

Protozoa are a polyphyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic debris. Historically, protozoans were regarded as "one-celled animals".
In biology, Kappa organism or Kappa particle refers to inheritable cytoplasmic symbionts, occurring in some strains of the ciliate Paramecium. Paramecium strains possessing the particles are known as "killer paramecia". They liberate a substance also known as paramecin into the culture medium that is lethal to Paramecium that do not contain kappa particles. Kappa particles are found in genotypes of Paramecium aurelia syngen 2 that carry the dominant gene K.

The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation.

Paramecium aurelia are unicellular organisms belonging to the genus Paramecium of the phylum Ciliophora. They are covered in cilia which help in movement and feeding.Paramecium can reproduce sexually, asexually, or by the process of endomixis. Paramecium aurelia demonstrate a strong "sex reaction" whereby groups of individuals will cluster together, and emerge in conjugant pairs. This pairing can last up to 12 hours, during which the micronucleus of each organism will be exchanged. In Paramecium aurelia, a cryptic species complex was discovered by observation. Since then, some have tried to decode this complex using genetic data.
Autogamy or self-fertilization refers to the fusion of two gametes that come from one individual. Autogamy is predominantly observed in the form of self-pollination, a reproductive mechanism employed by many flowering plants. However, species of protists have also been observed using autogamy as a means of reproduction. Flowering plants engage in autogamy regularly, while the protists that engage in autogamy only do so in stressful environments.

Condylostoma is a genus of unicellular ciliate protists, belonging to the class Heterotrichea.
Paramecium woodruffi is a species of unicellular organisms belonging to the genus Paramecium of the phylum Ciliophora. It was first isolated in 1928 by D. H. Wenrich. It is a member of the Paramecium aurelia species complex.
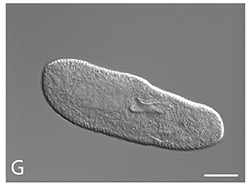
Paramecium biaurelia is a species of unicellular ciliates under the genus Paramecium, and one of the cryptic species of Paramecium aurelia. It is a free-living protist in water bodies and harbours several different bacteria as endosymbionts. Although the bacteria are parasites by definition, they also exhibit mutual relationship with the protist by providing survival benefits. It is used as an organism model in the study of the effects of gravitational forces in different environments.

Protists are the eukaryotes that cannot be classified as plants, fungi or animals. They are mostly unicellular and microscopic. Many unicellular protists, particularly protozoans, are motile and can generate movement using flagella, cilia or pseudopods. Cells which use flagella for movement are usually referred to as flagellates, cells which use cilia are usually referred to as ciliates, and cells which use pseudopods are usually referred to as amoeba or amoeboids. Other protists are not motile, and consequently have no built-in movement mechanism.
2. Przyboś, E., Tarcz, S., Rautian, M., & Sawka, N. (2015). Delimiting species boundaries within a PARAPHYLETIC SPECIES Complex: Insights from MORPHOLOGICAL, genetic, and molecular data on PARAMECIUM SONNEBORNI (Paramecium Aurelia species complex, Ciliophora, Protozoa). Protist, 166(4), 438-456. doi:10.1016/j.protis.2015.07.001
3. Sonneborn, T. (1970). Chapter 12 methods In PARAMECIUM RESEARCH. Methods in Cell Biology, 241-339. doi:10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61758-6











