Related Research Articles
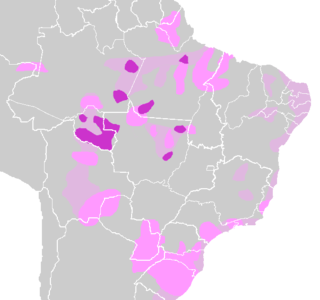
The Tupi or Tupian language family comprises some 70 languages spoken in South America, of which the best known are Tupi proper and Guarani.

The Cariban languages are a family of languages indigenous to north-eastern South America. They are widespread across northernmost South America, from the mouth of the Amazon River to the Colombian Andes, and they are also spoken in small pockets of central Brazil. The languages of the Cariban family are relatively closely related. There are about three dozen, but most are spoken only by a few hundred people. Macushi is the only language among them with numerous speakers, estimated at 30,000. The Cariban family is well known among linguists partly because one language in the family—Hixkaryana—has a default word order of object–verb–subject. Prior to their discovery of this, linguists believed that this order did not exist in any spoken natural language.
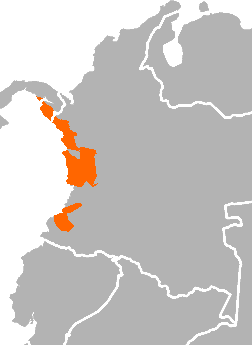
The Choco languages are a small family of Native American languages spread across Colombia and Panama.
The Peba–Yaguan language family is located in the northwestern Amazon, but today Yagua is the only remaining spoken language of the family.

Macro-Jê is a medium-sized language family in South America, mostly in Brazil but also in the Chiquitanía region in Santa Cruz, Bolivia, as well as (formerly) in small parts of Argentina and Paraguay. It is centered on the Jê language family, with most other branches currently being single languages due to recent extinctions.

The Borôroan languages of Brazil are Borôro and the extinct Umotína and Otuke. They are sometimes considered to form part of the proposed Macro-Jê language family, though this has been disputed.
Tiriyó is the Cariban language used in everyday life by the Tiriyó people, the majority of whom are monolingual. Although Tiriyó is the preferred spelling, the Tiriyó refer to themselves as tarëno; other variations, including tarano, tirió, and trio, exist. The Tiriyó are located on both sides of the Brazil-Suriname border in Lowland South America. Because Tiriyó is spoken by the entire Tiriyó population, its level of endangerment is low. However, it may be threatened by the presence of a newly installed radar station staffed by a considerable number of non-Indigenous people close to the main village.
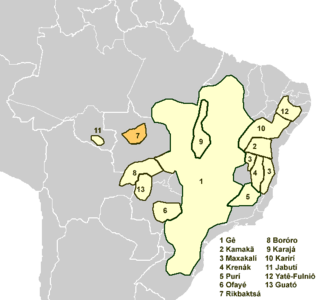
The Rikbaktsa language, also spelled Aripaktsa, Erikbatsa or Erikpatsa and known ambiguously as Canoeiro, is a language spoken by the Rikbaktsa people of Mato Grosso, Brazil, that forms its own branch of the Macro-Gê languages.
Taruma (Taruamá) is a divergent language of northeastern South America. It has been reported to be extinct several times since as far back as 1770, but Eithne Carlin discovered the last three speakers living in Maruranau among the Wapishana, and is documenting the language. The people and language are known as Saluma in Suriname.
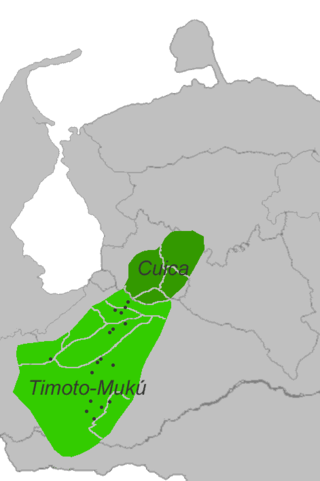
The Timotean languages were spoken in the Venezuelan Andes around what is now Mérida. It is assumed that they are extinct. However, Timote may survive in the so-far unattested Mutú (Loco) language, as this occupies a mountain village (Mutús) within the old Timote state.
Jaikó is an extinct language of southeastern Piauí, Brazil.
Bakairí (Bacairí) is a Cariban language, spoken by the Bakairi people in the state of Mato Grosso in Brazil.
Tamanaku (Tamañkú) is an extinct Cariban language of Venezuela.
Sérgio Meira de Santa Cruz Oliveira is a Brazilian linguist who specializes in the Cariban and Tupian language families of lowland South America and in the Tiriyó language in particular. He has worked on the classification of the Cariban language family, and has collected primary linguistic data from speakers of 14 Cariban languages and 5 non-Cariban languages.
Proto-Tupian (PT) is the reconstructed common ancestor of all the Tupian languages. It consists, therefore, of a hypothetical language, reconstructed by the comparative method from data of the descendant languages.
The Maweti–Guarani languages of Brazil form a branch of the Tupian language family according to Meira and Drude (2015). The branch was originally proposed by Rodrigues (1984), and is also accepted by Jolkesky (2016).
The Pidjanan languages are a subgroup of Arawakan languages of northern South America.
The Taranoan languages are a subgroup of the Cariban language family. The languages are spoken in Brazil, Suriname, and Colombia.
The Chaco linguistic area is a linguistic area that includes various South American language families and isolates of the Chaco region of South America, in southern Brazil, southeastern Bolivia, Paraguay, Uruguay, and Argentina.
The Pekodian languages are a subgroup of the Cariban language family. The languages are spoken in Mato Grosso and Pará states of Brazil and make up the southernmost branch of Cariban.
References
- ↑ Meira, Sérgio. 2006. A família lingüística Caribe (Karíb). Revista de Estudos e Pesquisas v.3, n.1/2, p.157-174. Brasília: FUNAI. (PDF)
- ↑ Gildea, Spike. 2012. "Linguistic studies in the Cariban family", in Campbell & Grondona, eds, The Indigenous Languages of South America: A Comprehensive Guide. Berlin/Boston: De Gruyter Mouton.
- ↑ Jolkesky, Marcelo Pinho De Valhery. 2016. Estudo arqueo-ecolinguístico das terras tropicais sul-americanas . Ph.D. dissertation, University of Brasília.
- ↑ Meira S, Birchall J, Chousou-Polydouri S. 2015. A character-based internal classification of the Cariban family . Talk presented at the 48th Annual Meeting of the Societas Linguisticae Europaea, Leiden, Netherlands, Sept. 4.