Related Research Articles

Peter Williston Shor is an American professor of applied mathematics at MIT. He is known for his work on quantum computation, in particular for devising Shor's algorithm, a quantum algorithm for factoring exponentially faster than the best currently-known algorithm running on a classical computer.
PlanetMath is a free, collaborative, mathematics online encyclopedia. The emphasis is on rigour, openness, pedagogy, real-time content, interlinked content, and also community of about 24,000 people with various maths interests. Intended to be comprehensive, the project is currently hosted by the University of Waterloo. The site is owned by a US-based nonprofit corporation, "PlanetMath.org, Ltd".
Eric Wolfgang Weisstein is an American mathematician and encyclopedist who created and maintains the encyclopedias MathWorld and ScienceWorld. In addition, he is the author of the CRC Concise Encyclopedia of Mathematics. He works for Wolfram Research.

Rudolf Haag was a German theoretical physicist, who mainly dealt with fundamental questions of quantum field theory. He was one of the founders of the modern formulation of quantum field theory and he identified the formal structure in terms of the principle of locality and local observables. He also made important advances in the foundations of quantum statistical mechanics.

Yuri Ivanovich Manin was a Russian mathematician, known for work in algebraic geometry and diophantine geometry, and many expository works ranging from mathematical logic to theoretical physics.

Bruno Buchberger is Professor of Computer Mathematics at Johannes Kepler University in Linz, Austria. In his 1965 Ph.D. thesis, he created the theory of Gröbner bases, and has developed this theory throughout his career. He named these objects after his advisor Wolfgang Gröbner. Since 1995, he has been active in the Theorema project at the University of Linz.
Robert Duncan Luce was an American mathematician and social scientist, and one of the most preeminent figures in the field of mathematical psychology. At the end of his life, he held the position of Distinguished Research Professor of Cognitive Science at the University of California, Irvine.

Francis Paul Heylighen is a Belgian cyberneticist investigating the emergence and evolution of intelligent organization. He presently works as a research professor at the Vrije Universiteit Brussel, where he directs the transdisciplinary research group on "Evolution, Complexity and Cognition" and the Global Brain Institute. He is best known for his work on the Principia Cybernetica Project, his model of the Internet as a global brain, and his contributions to the theories of memetics and self-organization. He is also known, albeit to a lesser extent, for his work on gifted people and their problems.

Roy Patrick Kerr is a New Zealand mathematician who discovered the Kerr geometry, an exact solution to the Einstein field equation of general relativity. His solution models the gravitational field outside an uncharged rotating massive object, including a rotating black hole. His solution to Einstein's equations predicted spinning black holes before they were discovered.
The Mathematics Subject Classification (MSC) is an alphanumerical classification scheme collaboratively produced by staff of, and based on the coverage of, the two major mathematical reviewing databases, Mathematical Reviews and Zentralblatt MATH. The MSC is used by many mathematics journals, which ask authors of research papers and expository articles to list subject codes from the Mathematics Subject Classification in their papers. The current version is MSC2020.

The Institut d'optique Graduate School, nicknamed SupOptique or IOGS, is one of the most prestigious French Grandes Ecoles and the leading French grande école in the field of Optics and its industrial and scientific applications, and a graduate school of the prestigious Paris-Saclay University and ParisTech.

The Mathematical Institute is the mathematics department at the University of Oxford in England. It is one of the nine departments of the university's Mathematical, Physical and Life Sciences Division. The institute includes both pure and applied mathematics and is one of the largest mathematics departments in the United Kingdom with about 200 academic staff. It was ranked as the top mathematics department in the UK in the 2021 Research Excellence Framework. Research at the Mathematical Institute covers all branches of mathematical sciences ranging from, for example, algebra, number theory, and geometry to the application of mathematics to a wide range of fields including industry, finance, networks, and the brain. It has more than 850 undergraduates and 550 doctoral or masters students. The institute inhabits a purpose-built building between Somerville College and Green Templeton College on Woodstock Road, next to the Faculty of Philosophy.

Erwin Madelung was a German physicist. He was born in 1881 in Bonn. His father was the surgeon Otto Wilhelm Madelung. He earned a doctorate in 1905 from the University of Göttingen, specializing in crystal structure, and eventually became a professor. It was during this time he developed the Madelung constant, which characterizes the net electrostatic effects of all ions in a crystal lattice, and is used to determine the energy of one ion.
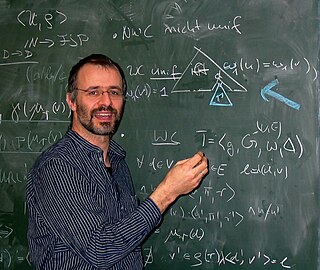
Michael Kohlhase is a German computer scientist and professor at University of Erlangen–Nuremberg, where he is head of the KWARC research group.
Peter D. Jarvis is an Australian physicist notable for his work on applications of group theory to physical problems, particularly supersymmetry in the genetic code. He has also applied classical invariant theory to problems of quantum physics, and also to phylogenetic reconstruction.

Shahn Majid is an English pure mathematician and theoretical physicist, trained at Cambridge University and Harvard University and, since 2001, a Professor of Mathematics at the School of Mathematical Sciences, Queen Mary, University of London.
PlanetPhysics was a virtual community with several Internet sites supported by a non-profit organization registered in the USA in an open science, open data, peer-to-peer review mode that aimed to help make physics, and related mathematics, knowledge much more accessible, as well as to further develop physical, logical, computational and mathematical physics concepts.
Philip Candelas, is a British physicist and mathematician. After 20 years at the University of Texas at Austin, he served as Rouse Ball Professor of Mathematics at the University of Oxford until 2020 and is a Fellow of Wadham College, Oxford.
The Department of Information Studies is a department of the UCL Faculty of Arts and Humanities.
The Global Digital Mathematics Library (GDML) is a project organized under the auspices of the International Mathematical Union (IMU) to establish a digital library focused on mathematics.
References
- ↑ Short biography (page 57) as a part of his article on the SKOS version of MSC 2010
- ↑ "The Global Digital Mathematical Library Working Group". Archived from the original on 2017-09-21. Retrieved 2015-05-09.