
The province of Pavia is a province in the Lombardy region of Italy. Its capital is Pavia. As of 2015, the province has a population of 548,722 inhabitants and an area of 2,968.64 square kilometres (1,146.20 sq mi); the town of Pavia has a population of 72,205.

Bastida de' Dossi is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Pavia in the Italian region Lombardy, located about 60 kilometres (37 mi) southwest of Milan and about 25 kilometres (16 mi) southwest of Pavia. It is situated in the Oltrepò Pavese plain and the municipal territory also include a part of Lomellina.

Bereguardo is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Pavia in the Italian region Lombardy, located about 25 kilometres (16 mi) southwest of Milan and about 12 kilometres (7 mi) northwest of Pavia.

Borgo San Siro is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Pavia in the Italian region Lombardy, located about 25 kilometres (16 mi) southwest of Milan and about 12 kilometres (7 mi) northwest of Pavia, in the western Lomellina.
Candia Lomellina is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Pavia in the Italian region Lombardy, located about 50 kilometres (31 mi) southwest of Milan and about 45 kilometres (28 mi) west of Pavia. As of 31 December 2004, it had a population of 1,639 and an area of 27.8 square kilometres (10.7 sq mi).

Casorate Primo is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Pavia in the Italian region Lombardy, located about 20 kilometres (12 mi) southwest of Milan and about 20 kilometres (12 mi) northwest of Pavia.
Cava Manara is a comune (municipality) in the province of Pavia in the Italian region Lombardy, located about 35 km south of Milan and about 7 km southwest of Pavia, not far from the confluence of the Ticino and the Po rivers.

Sannazzaro de' Burgondi is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Pavia in the Italian region Lombardy, located about 45 km southwest of Milan and about 20 km southwest of Pavia, in Lomellina, on the Agogna River.

Santa Giuletta is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Pavia in the Italian region Lombardy, located about 50 km south of Milan and about 15 km south of Pavia. As of 31 December 2004, it had a population of 1,605 and an area of 11.7 km².
Velezzo Lomellina is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Pavia in the Italian region Lombardy, located about 50 km southwest of Milan and about 35 km west of Pavia. As of 31 December 2004, it had a population of 113 and an area of 8.6 km².

The Naviglio Pavese is one of the canals making up the Navigli system in Lombardy, Italy. Once navigable, it is 33 km (21 mi) long and connected the city of Milan to Pavia, and through a flight of six locks to the River Ticino.
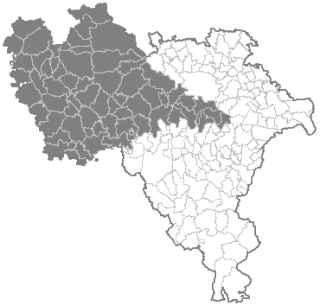
The Lomellina is a geographical and historical area in the Po Valley of northern Italy, located in south-western Lombardy between the Sesia, Po and Ticino rivers. It is one of three areal divisions of the Province of Pavia.
Oltrepò may refer to one of three geographical regions in Northern Italy, to a wine, and to a football team:

The Oltrepò Pavese is a historical region making up the southern portion of the province of Pavia, in the northwest Italian region of Lombardy. The area is named after its location south of the River Po as considered from the provincial capital Pavia and in general from the rest of Lombardy.

Lombardy wine is the Italian wine produced in the Lombardy region of north central Italy. The region is known particularly for its sparkling wines made in the Franciacorta and Oltrepò Pavese areas. Lombardy also produces still red, white and rosé wines made from a variety of local and international grapes, including Nebbiolo wines in the Valtellina region and Trebbiano di Lugana white wines produced with the Chiaretto style rosé along the shores of Lake Garda. The wine region currently has 22 denominazione di origine controllata (DOC), 5 denominazione di origine controllata e garantita (DOCG) and at least 13 indicazione geografica tipica (IGT) designations. The main cities of the region are Milan, Bergamo and Brescia. The region annually produces around 1.3 million hectolitres of wine, more than the regions of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, Marche, Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol and Umbria.
San Damiano is the Italian for Saint Damian. It may also refer to:

Lombard cuisine is the style of cooking in the Northern Italian region of Lombardy. The historical events of its provinces and of the diversity of its territories resulted in a varied culinary tradition. First courses in Lombard cuisine range from risottos to soups and stuffed pasta, and a large choice of second course meat or fish dishes, due to the many lakes and rivers of Lombardy.

Lombardy is an administrative region of Italy that is split into four geographic regions — mountains, alpine forest, and the upper and lower plains south of the Po river. These are crossed and dotted by dozens of rivers and lakes, the latter of which include some of the largest in Italy. The territory is the fourth largest in Italy by surface area with 24,000 square kilometres (9,300 sq mi).

Principality of Pavia was an historic division of the Duchy of Milan, which was ranked as a principality as an honor to the reigning House of Milan.

The hydrography of Milan and the area of the neighboring municipalities is particularly complex, both for natural causes, given the conspicuous presence of rivers, streams and fountains that form a real water tangle, and for issues related to the work of canalization and diversion of waterways made by man, having their beginning during the Roman era, which led to the creation of numerous irrigation ditches, canals and lakes.



















