
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the "ascus", a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of Ascomycota are asexual and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewers' and bakers' yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens such as Cladonia belong to the Ascomycota.

Penicillium is a genus of ascomycetous fungi that is part of the mycobiome of many species and is of major importance in the natural environment, in food spoilage, and in food and drug production.
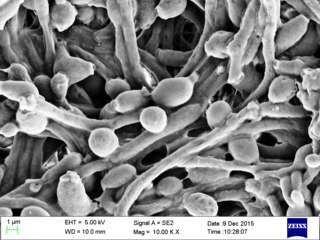
Candida albicans is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usually a commensal organism, but it can become pathogenic in immunocompromised individuals under a variety of conditions. It is one of the few species of the genus Candida that cause the human infection candidiasis, which results from an overgrowth of the fungus. Candidiasis is, for example, often observed in HIV-infected patients. C. albicans is the most common fungal species isolated from biofilms either formed on (permanent) implanted medical devices or on human tissue. C. albicans, C. tropicalis, C. parapsilosis, and C. glabrata are together responsible for 50–90% of all cases of candidiasis in humans. A mortality rate of 40% has been reported for patients with systemic candidiasis due to C. albicans. By one estimate, invasive candidiasis contracted in a hospital causes 2,800 to 11,200 deaths yearly in the US. Nevertheless, these numbers may not truly reflect the true extent of damage this organism causes, given new studies indicating that C. albicans can cross the blood–brain barrier in mice.

Candida is a genus of yeasts. It is the most common cause of fungal infections worldwide and the largest genus of medically important yeast.

The Eurotiales are an order of sac fungi, also known as the green and blue molds. It was circumscribed in 1980.

The Trichocomaceae are a family of fungi in the order Eurotiales. Taxa are saprobes with aggressive colonization strategies, adaptable to extreme environmental conditions. Family members are cosmopolitan in distribution, ubiquitous in soil, and common associates of decaying plant and food material.

Penicillium roqueforti is a common saprotrophic fungus in the genus Penicillium. Widespread in nature, it can be isolated from soil, decaying organic matter, and plants.

The white-footed saki, buffy saki or white saki is a species of saki monkey, a type of New World monkey, endemic to western Brazil south of the Amazon.

A chlamydospore is the thick-walled large resting spore of several kinds of fungi, including Ascomycota such as Candida, Basidiomycota such as Panus, and various Mortierellales species. It is the life-stage which survives in unfavourable conditions, such as dry or hot seasons. Fusarium oxysporum which causes the plant disease Fusarium wilt is one which forms chlamydospores in response to stresses like nutrient depletion. Mycelia of the pathogen can survive in this manner and germinate in favorable conditions.

Potato dextrose agar and potato dextrose broth are common microbiological growth media made from potato infusion and dextrose. Potato dextrose agar is the most widely used medium for growing fungi and bacteria.

Iris albicans, also known as the cemetery iris, white cemetery iris, or the white flag iris, is a species of iris which was planted on graves in Muslim regions and grows in many countries throughout the Middle East and northern Africa. It was later introduced to Spain, and then other European countries. It is a natural hybrid.
The parasexual cycle, a process restricted to fungi and single-celled organisms, is a nonsexual mechanism of parasexuality for transferring genetic material without meiosis or the development of sexual structures. It was first described by Italian geneticist Guido Pontecorvo in 1956 during studies on Aspergillus nidulans. A parasexual cycle is initiated by the fusion of hyphae (anastomosis) during which nuclei and other cytoplasmic components occupy the same cell. Fusion of the unlike nuclei in the cell of the heterokaryon results in formation of a diploid nucleus (karyogamy), which is believed to be unstable and can produce segregants by recombination involving mitotic crossing-over and haploidization. Mitotic crossing-over can lead to the exchange of genes on chromosomes; while haploidization probably involves mitotic nondisjunctions which randomly reassort the chromosomes and result in the production of aneuploid and haploid cells. Like a sexual cycle, parasexuality gives the species the opportunity to recombine the genome and produce new genotypes in their offspring. Unlike a sexual cycle, the process lacks coordination and is exclusively mitotic.

Dimorphic fungi are fungi that can exist in the form of both mold and yeast. This is usually brought about by change in temperature and the fungi are also described as thermally dimorphic fungi. An example is Talaromyces marneffei, a human pathogen that grows as a mold at room temperature, and as a yeast at human body temperature.

Oxalis albicans, commonly known as radishroot woodsorrel, is North American species of perennial herbs in the woodsorrel family. It is widespread in Mexico and the southwestern United States.
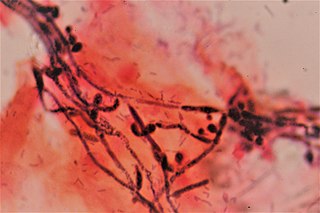
Vaginal yeast infection, also known as candidal vulvovaginitis and vaginal thrush, is excessive growth of yeast in the vagina that results in irritation. The most common symptom is vaginal itching, which may be severe. Other symptoms include burning with urination, a thick, white vaginal discharge that typically does not smell bad, pain during sex, and redness around the vagina. Symptoms often worsen just before a woman's period.

Penicillium chrysogenum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. It is common in temperate and subtropical regions and can be found on salted food products, but it is mostly found in indoor environments, especially in damp or water-damaged buildings. It has been recognised as a species complex that includes P. notatum, P. meleagrinum, and P. cyaneofulvum. Molecular phylogeny has established that Alexander Fleming's first discovered penicillin producing strain is of a distinct species, P. rubens, and not of P. notatum. It has rarely been reported as a cause of human disease. It is the source of several β-lactam antibiotics, most significantly penicillin. Other secondary metabolites of P. chrysogenum include roquefortine C, meleagrin, chrysogine, 6-MSA YWA1/melanin, andrastatin A, fungisporin, secalonic acids, sorbicillin, and PR-toxin.

Penicillium brevicompactum is a mould species in the genus Penicillium.
Penicillium citrinum is an anamorph, mesophilic fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces tanzawaic acid A-D, ACC, Mevastatin, Quinocitrinine A, Quinocitrinine B, and nephrotoxic citrinin. Penicillium citrinum is often found on moldy citrus fruits and occasionally it occurs in tropical spices and cereals. This Penicillium species also causes mortality for the mosquito Culex quinquefasciatus. Because of its mesophilic character, Penicillium citrinum occurs worldwide. The first statin (Mevastatin) was 1970 isolated from this species.
Penicillium striatisporum is an anamorph species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from the rhizosphere of chilli peppers. Penicillium striatisporum has a selective antifungal activity against Candida albicans This species produces striatisporin A, striatisporolide A, versiol, calbistrin C, deformylcalbistrin A, citromycetin, citromycin, fulvic acid, (-)-2,3-dihydrocitromycetin and (+)-hexylitaconic acid















