Penicillium griseofulvum is a species of the genus of Penicillium which produces patulin, penifulvin A, cyclopiazonic acid, roquefortine C, shikimic acid, griseofulvin, and 6-Methylsalicylic acid. Penicillium griseofulvum occurs on cereals and nuts.
Karl Hult(born 1944) is a Swedish biochemist and researcher. He is a professor emeritus at the Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, and has contributed to research within the fields of metabolism and biocatalysis.

Antarctica is one of the most physically and chemically extreme terrestrial environments to be inhabited by lifeforms. The largest plants are mosses, and the largest animals that do not leave the continent are a few species of insects.

Penicillium chrysogenum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. It is common in temperate and subtropical regions and can be found on salted food products, but it is mostly found in indoor environments, especially in damp or water-damaged buildings. It has been recognised as a species complex that includes P. notatum, P. meleagrinum, and P. cyaneofulvum. Molecular phylogeny has established that Alexander Fleming's first discovered penicillin producing strain is of a distinct species, P. rubens, and not of P. notatum. It has rarely been reported as a cause of human disease. It is the source of several β-lactam antibiotics, most significantly penicillin. Other secondary metabolites of P. chrysogenum include roquefortine C, meleagrin, chrysogine, 6-MSA YWA1/melanin, andrastatin A, fungisporin, secalonic acids, sorbicillin, and PR-toxin.
Penicillium aethiopicum is a fungus species of the genus of Penicillium. Penicillium aethiopicum produces viridicatumtoxin and griseofulvin, two structurally interesting polyketides.
Penicillium brefeldianum is an anamorph fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces Brefeldin A a fungal metabolite.
Penicillium brocae is a fungal species of the genus Penicillium, which was isolated in Chiapas in Mexico. It is a symbiont of the mangrove tree Avicennia marina.
Penicillium chermesinum is an anamorph fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which was isolated from soil from Nova Scotia in Canada.Penicillium chermesinum produces plastatin, luteosporin, xanthomegnin, azaphilones, p-terphenyls and costaclavine.
Penicillium coralligerum is a species of the genus of Penicillium. It is a marine species sometimes referred to as a deep-sea fungus and in some languages named the equivalent of "deep-sea mold".
Penicillium decaturense is a species of the genus of Penicillium which was isolated from a fungus in North America. Penicillium decaturense produces citrinin, 15-Deoxyoxalicine B, decaturins A and decaturins A
Penicillium duclauxii is an anamorph species of the genus of Penicillium which produces xenoclauxin and duclauxin.
Penicillium herquei is an anamorph, filamentous species of the genus of Penicillium which produces citreorosein, emodin, hualyzin, herquline B, janthinone, citrinin and duclauxin,.
Penicillium janczewskii is an anamorph and filamentous species of the genus of Penicillium which was isolated from the rhizosphere of Vernonia herbacea. Penicillium janczewskii produces griseofulvin
Penicillium multicolor is an anamorph species of the genus Penicillium which produces alpha-L-fucosidase, tilactase, sclerotiorin, 8-O-Methylsclerotiorinamine, multicolosic acid and isochromophilones.
Penicillium paxilli is an anamorph, saprophytic species of the genus Penicillium which produces paxilline, paxisterol, penicillone, pyrenocine A, paspaline B and verruculogene. Penicillium paxilli is used as a model to study the biochemistry of the indol-diterepene biosynthesis
Penicillium raistrickii is an anamorph species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which produces griseofulvin, patulin and verruculogen.

Penicillium solitum is an anamorphic, mesophilic, salinity-tolerant, and psychrotolerant species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. It is known to produce various compounds including polygalacturonase, compactin, cyclopenin, cyclopenol, cyclopeptin, dehydrocompactin, dihydrocyclopeptin, palitantin, solistatin, solistatinol, viridicatin, viridicatol.

The phomoxanthones are a loosely defined class of natural products. The two founding members of this class are phomoxanthone A and phomoxanthone B. Other compounds were later also classified as phomoxanthones, although a unifying nomenclature has not yet been established. The structure of all phomoxanthones is derived from a dimer of two covalently linked tetrahydroxanthones, and they differ mainly in the position of this link as well as in the acetylation status of their hydroxy groups. The phomoxanthones are structurally closely related to other tetrahydroxanthone dimers such as the secalonic acids and the eumitrins. While most phomoxanthones were discovered in fungi of the genus Phomopsis, most notably in the species Phomopsis longicolla, some have also been found in Penicillium sp.
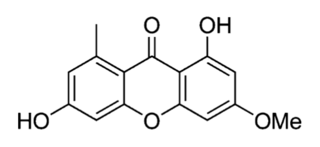
Griseoxanthone C is an organic compound in the structural class of chemicals known as xanthones. Its chemical formula is 1,6-dihydroxy-3-methoxy-8-methylxanthen-9-one, and its molecular formula is C15H12O5. It is found in a plant and some fungi, including a lichen.




